-
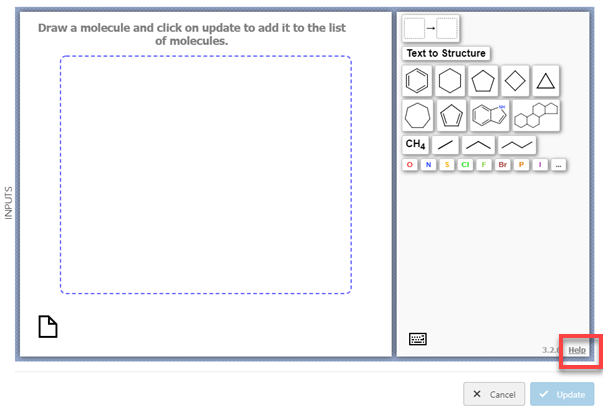
While editing an experiment, cick .
Pipette Sketcher opens.
-
Use Pipette Sketcher to create the molecule you want to use as input for the
experiment.
Pipette Sketcher is a tool for drawing and editing chemistry in a browser. For more
information about using Pipette Sketcher, click Help in the
lower-right corner.
-
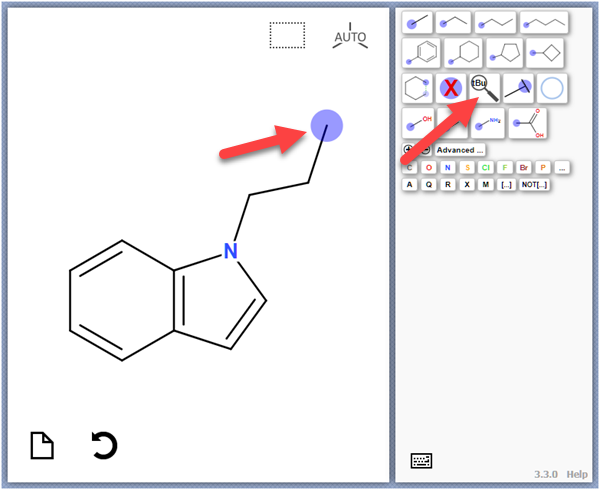
Select a terminal atom, and then click the Search Chemistry
icon:
-
Click Homology Group and choose a group:
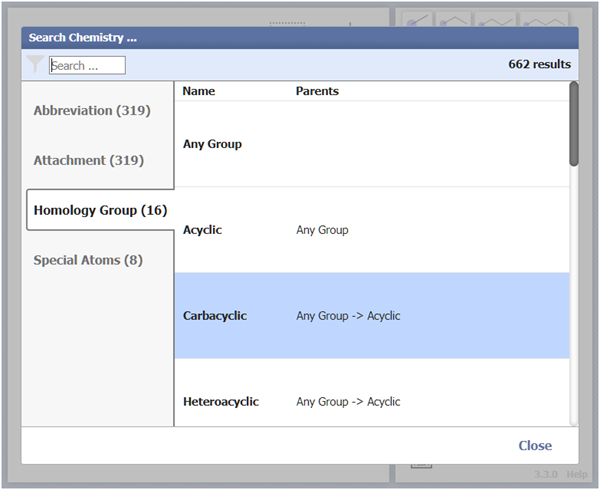
Table 1. Homology Groups
| Name |
Description |
| Acyclic |
Acyclic (chain) |
| Carbacyclic |
Acyclic all-carbon |
| Heteroacyclic |
Acyclic with at least one heteroatom |
| Alkoxy |
Acyclic with carbon and oxygen |
| Alkyl |
Acyclic all-carbon with all single bonds |
| Alkenyl |
Acyclic all-carbon with double bond |
| Alkynyl |
Acyclic all-carbon with triple bond |
| Cyclic |
Cyclic (ring assembly) |
| Heterocyclic |
Cyclic with at least one heteroatom |
| Carbocyclic |
Cyclic all-carbon |
| Cyclic, no Carbon |
Cyclic with no carbon |
| Heteroaryl |
Heteroaromatic |
| Aryl |
Aromatic all-carbon |
| Cycloalkyl |
Cyclic nonaromatic all-carbon |
| Cycloalkenyl |
Cyclic nonaromatic all-carbon with double bond |
-
Click Update to save and return to GTD.
The location is labeled with the name of the homology group:
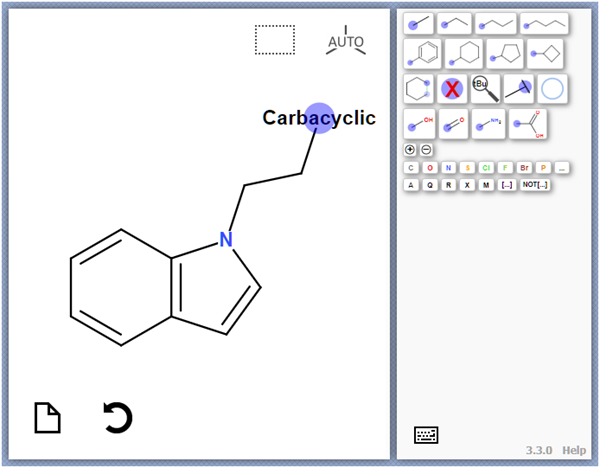
When you run the experiment, everything other than the homology
group is preserved in the generated molecules. The structure from the homology group is
highlighted in light blue when you view the molecule.