-
Select 1D geometry as the Support.
The local specifications are now available.
- Choose the Element order.
- Select
 to mesh the support using 1D elements without an
intermediate node. to mesh the support using 1D elements without an
intermediate node. - Select
 to mesh the support using 1D elements with
an intermediate node. to mesh the support using 1D elements with
an intermediate node.
- Specify the global Mesh size.
- Specify the mesh size and mesh sag attributes.
To initialize the Mesh size and Absolute sag values based on the overall support size, click Initialize from geometry. - In the Mesh size box, enter a value for the element
size.
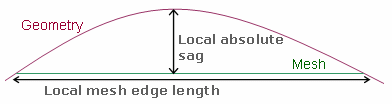
- To specify a maximum gap between the mesh and the geometry, select Absolute sag, and enter a value.
- To
create a 1D mesh compatible with an existing mesh, select Automatic mesh capture.
- Enter a tolerance value in the Tolerance box.
- Select the mesh you want to capture.
- To project external points on the geometry:
- Click Imposed Points
 . .The Imposed Points dialog box appears. - Select the points you want to project.
- In the Tolerance box, enter a tolerance value.
- If you want to project the selected points on the geometry, select Projection on geometry.
- Click OK.
- To distribute nodes on an edge:
- Click Edge Distribution
 . .The Edge Distribution dialog box appears. - Select the edges on which you want to impose nodes. You can select several edges only if they form a continuous curve.
- In the Type list, select one of the
following distribution methods:
- Uniform to distribute nodes on the selected edge with the same distance between nodes.
- Arithmetic to distribute nodes on the selected edge with a distance between nodes defined by a common difference computed with parameters.
- Geometric to distribute nodes on the selected edge with a distance between nodes defined by a common ratio computed with parameters.
- User law to distribute nodes on the selected edge with a distance between nodes defined by a knowledge law previously defined in the Knowledge Advisor app.
- Define the distribution parameters.
The list and number of parameters to define vary depending on the distribution method. For
Uniform, Arithmetic,
and Geometric distributions, select the
parameters you want to use to define the distribution in the
Defined by list. - If you selected Arithmetic or Geometric, you can distribute nodes symmetrically by selecting Symmetric.
- If you selected User law, you can reverse the direction of the distribution by selecting Reverse direction.
- Click OK.
- You can manually move, freeze, and unfreeze nodes or split and condense
edges of 1D beam elements.
- Click one of the following:
If you click
OK or
Mesh, the mesh specification is created and appears in
the
tree.
|