Creating a Grid | |||
| |||
-
From the Material section of the action bar,
click Quick Grid
 .
.
-
In the 3D view, select the reference surface for the grid creation.
A grid is automatically created, with a single cell that fits the entire surface. The boundaries and the intersections of the grid are stored in a grid panel, compatible with Composites Design.
A default laminate is assigned to this cell.
The creation of the grid can fail if the selected surface contains multiple contours . In this case, you can:
- Exit the command, and modify the surface.
- Add additional geometries to the grid, so that the initial cells no longer have multiple contours.
Note: To select multiple cells, press Ctrl and click the cells. You can also remove a cell from the selection by pressing Ctrl, and selecting a cell. -
Optional: Click Draping Direction
 to invert
the draping direction.
to invert
the draping direction.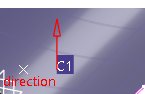
Note: The default draping direction is computed from the orientation of the selected surface. You can see it in the 3DView. - In the Rosette list, select a rosette for your grid.
-
Split the default cells using one of the following
commands:
- Create Spline
 : Click
the surface to create points to create a spline goes that through these points. The
points appear in the Spline Creation panel.
: Click
the surface to create points to create a spline goes that through these points. The
points appear in the Spline Creation panel. - Create Multi-Plane
 : On the
surface, select a curve, and then select a starting and an ending point on that curve.
In the Plane Creation panel, define the Number
Planes you want to create along the selected segment of curve.
: On the
surface, select a curve, and then select a starting and an ending point on that curve.
In the Plane Creation panel, define the Number
Planes you want to create along the selected segment of curve. - Add Existing Geometry
 : Select existing curves or planes, that lies on or intersects the surface, and use
them to split cells.Note: This command remains active after the first selection. To deactivate it, click the command again or click another command.
: Select existing curves or planes, that lies on or intersects the surface, and use
them to split cells.Note: This command remains active after the first selection. To deactivate it, click the command again or click another command. - Create Isoparametric Curve
 : Hover the pointer over the surface, and click to create a curve. Repeat the
operation to create other curves.
: Hover the pointer over the surface, and click to create a curve. Repeat the
operation to create other curves. - Create Normal Plane
 : Select an existing curve, hover the pointer over the surface, and click to create a
plane normal to the selected curve. Repeat the operation to create other
curves.
: Select an existing curve, hover the pointer over the surface, and click to create a
plane normal to the selected curve. Repeat the operation to create other
curves. - Merge Cells
 : On the surface, select to cells and click Merge Cells.Note: If the merged cells have different laminates, the thickest laminate is automatically kept. If after a merge, a geometry is not used by any cell, it is deleted, except if it is pointed by another feature in the part.
: On the surface, select to cells and click Merge Cells.Note: If the merged cells have different laminates, the thickest laminate is automatically kept. If after a merge, a geometry is not used by any cell, it is deleted, except if it is pointed by another feature in the part.
Notes:- All these actions are performed only on the selected cells. Cells can be selected by clicking them in the 3DView, or in the list of the Quick Grid dialog box. Selected cells are highlighted in both.
- If no cell is selected, the actions are performed on all the cells.
- Split actions can be undone by pressing Ctrl + z. This operaton brings you back after the previous split action and any laminate changes that occur in-between is undone as well.
- Create Spline
-
Optional: To hide labels displayed in the 3D view, on top of each cell,
clear the Display label option.
Note: By default, only the names of the cells appear , but you can display other information by clicking Options… and selecting other information in the 3D Display Option dialog box.
-
To assign a laminate to a cell, right-click it, select Row
Edition
 , and select
a laminate in the Laminate list.
Note: You can also click Edit cells
, and select
a laminate in the Laminate list.
Note: You can also click Edit cells The cells are colored with the color of their laminate.
The cells are colored with the color of their laminate. -
To manage the displayed labels, click Open display options
 ,
and select the labels to be displayed or clear those to be hidden.
,
and select the labels to be displayed or clear those to be hidden.
-
Click OK to validate the creation of the grid.
In the tree, QuickGrid Panel and QuickGrid features are added under the Grid Definition root node.
A geometrical set is created to store the geometry created with the Quick Grid command. its name is “name_of_grid” Geometry. The geometrical set is created under the Quick Grid Refs root node .
Once the grid is created, the input surface can no longer be modified. Modifying it will make the update of the grid impossible.
- To edit an existing grid, double-click it.