About the Moving Frame | ||||
|
| |||
The moving frame determines a local coordinate system that moves along the dominant guiding curve thus defining the profile's position on the curve.
The coordinate axes appear as:
-
N (x-axis) = Binormal vector of the moving frame
It is the vector being normal to N and T.
-
B (y-axis) = Normal of an automatic plane
A plane is computed reflecting the position of the guiding curve as good as possible, that is with a minimum distance from the guiding curve. The y-axis of the local coordinate system then aligns normal to this automatic plane.
-
T (z-axis) = Tangent of the dominant guiding curve
Depending on the selected guide and profile curves, the following moving frame types are available:
| Selected curves | Available moving frame types |
| 2 profiles | No moving frame options |
|
1 guide and 1 profile OR 1 guide and 2 or more profiles |
3 moving frame options:
|
|
2 guides OR 2 or more guides and 2 or more profiles |
5 moving frame options. Additionally:
|
- Using one guiding curve and parallel planes
-

- Parallel to Plane
The local coordinate system moves parallel to the Robot’s xz-plane. It is always defined independent from the guiding curve’s tangent.

- Parallel to Plane
- Using one guiding curve and radial planes
-
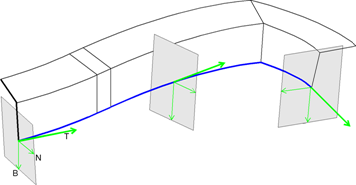
- Perpendicular to the dominant guiding curve
The tangent of the guiding curve determines the z-axis (T). The y-axis (B) points in the normal direction of the automatic plane.
The xy-plane is always perpendicular to the tangent of the guiding curve.

- Pseudo-Perpendicular to the dominant guiding
curve
The normal of the automatic plane determines the y-axis (B). The z-axis (T) points in the tangent direction of the guiding curve.
The xy-plane is not implicitly perpendicular to the guiding curve. It only appears perpendicular when looking in the direction of the normal.

- Perpendicular to the dominant guiding curve
- Using two guiding curves
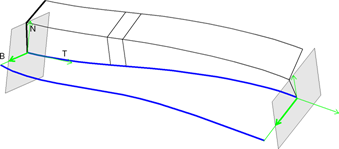
The connection to the second guiding curve determines the x-axis (N).- Two guiding curves and perpendicular to the dominant guiding
curve
The tangent of the guiding curve (z-axis, T) aligns the coordinate system.

- Two guiding curves and pseudo-perpendicular to the dominant guiding
curve
The normal of the automatic plane (y-axis, B) aligns the coordinate system.

- Two guiding curves and perpendicular to the dominant guiding
curve