Healing Geometry | |||
| |||
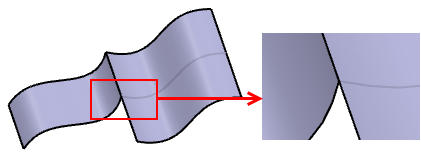
-
From the section of
the action bar, click
Healing
 .
.
- Select the surfaces to be healed.
The selected elements are added to the Elements To Heal list.
Note: Right-clicking an element in the list activates a context menu. The contextual commands are carried out for the right-clicked element and selected (highlighted) elements in the list. - In the Merging distance box, specify the maximum distance up to which gaps shall be repaired.
You can change the default value in Me
 > Preferences > Standards:
> Preferences > Standards:- In the Standard Definition dialog box, select Category: 3DModelingDefaultValues and 3DModelingDefaultValues > Transform- > Healing > Merging distance in the Standard area.
- Specify the value in the Merging distance text box.
- Optional: In the Distance objective box, specify the minimum distance from which gaps shall not be repaired.
- In the Continuity list box, select Tangent.
Tangency angle and Tangency objective boxes are enabled. You can specify the maximum angle up to which tangency deviation shall be corrected and the minimum angle from which tangency deviation is allowed, respectively.
- Click the Freeze Plane elements and Freeze Canonic elements check boxes to exclude planar and canonic elements from the healing operation.
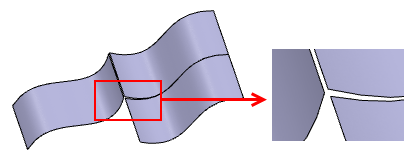
-
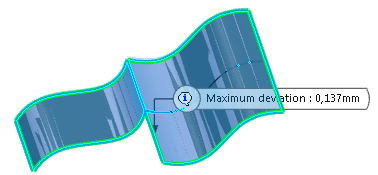
Click Preview to visualize the result and the maximum
deviation between the input surfaces.
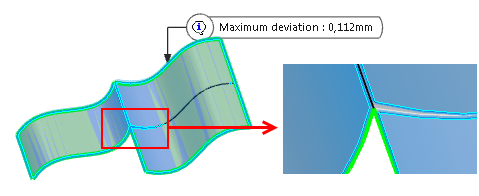
Important: The value is displayed only at the edge or the face concerned but not at the exact maximum deviation location. -
Click the Freeze
tab.
- Select Freeze elements to exclude elements from the healing operation.
- Select Unfreeze elements to include elements in the healing operation.
Note: Topological healing is used to create healed surfaces. If a gap still exists, geometrical healing takes place. The list of frozen elements can only include elements treated with geometrical healing which can deform surfaces. Topological healing bases on surface intersections without any deformation (extrapolation is not considered as deformation). - In the elements to freeze or unfreeze list, click "No selection" and then select the elements to be frozen or unfrozen.
-
Click the Sharpness
tab.
The options of this tab are only available, if Continuity type Tangent on the Parameters tab is selected.
-
Select one or more sharp edges to be retained.
The selected edges are added to the Edges to keep sharp list.
-
In the Sharpness angle box, define the maximum
value up to which an angle is considered as sharp.
This can be useful when offsetting the resulting healed geometry, for example.
Tips: - Depending on the geometry configuration and the parameters set, the Multi-Result Management dialog box is displayed.
- If the healing fails, an update error dialog is issued. Click OK to improve the geometry. The erroneous elements are emphasized on the geometry.
-
Select one or more sharp edges to be retained.
-
Click the Visualization
tab.
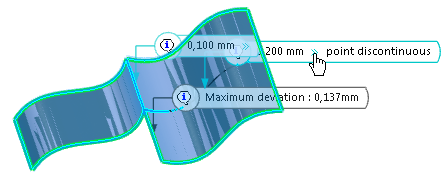
The Visualization tab enables you to better understand the discontinuities in the model and the results of the healing action.
You can select:
- All
- Displays corrected and not corrected discontinuity.
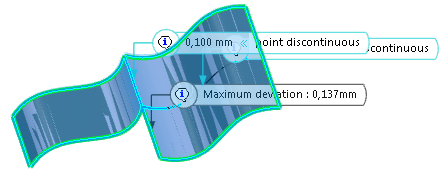
- Not corrected
- Displays only not corrected discontinuity.
- None
- Hides the callouts.
- Display information interactively
- Expands the callout when moving the pointer to it.
- Display information sequentially
- Displays only one callout. Use Previous and Next options to toggle the callouts.
-
Click OK.