-
From the section of the action bar, click Connect Checker Analysis
 . .
-
Click
OK. The analysis
is added to the
tree
and will be updated automatically whenever you modify any of the input
elements.
- Select one or several elements.
- Select Quick display mode.
The quick analysis mode's options are displayed. If a connection
deviation is greater than a threshold value, text is displayed next to the
connection point indicating the value and units of the connection
deviation. The color of the text depends upon the type of
deviation.
In this example, the text on the geometry disappears because the distance
between the two curves is smaller than the G0
threshold value. 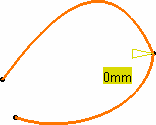
-
Select the continuity analysis type to display.
- Overlap Defect : overlapping elements (selecting
this disables the other analysis types)
- G0 continuity: continuity in
point
- G1 continuity: continuity in
tangency
- G2 continuity: continuity in
curvature
- G3 continuity: continuity in
curvature tangency
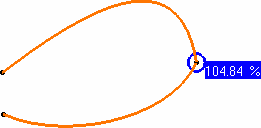
In this example, G1
continuity is selected and a text is displayed on a green
background (as defined by default for the Tangency criterion) to indicate that
the G1 continuity (tangency) criterion is not respected,
because the first text displayed is the one for which the set tolerance is not
complied with. You can then increase the Tangency value, or modify the geometry
to comply with your needs. 
- Modify the tolerance values, or the geometry to comply
with the tolerances.
For example, if you modify the Tangency value to set it to 16
degrees, the geometry instantly reflects the compliance with the new value.
-
Click
OK. The analysis
is added to the
tree
and will be updated automatically whenever you modify any of the input
elements.
- Optional:
Double-click the Curve Connection Analysis from the specification tree to edit it.
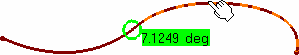
- You can analyze internal edges of a element, such as a Join for example,
by selecting only one of the initial elements:
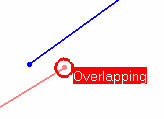
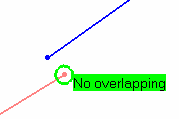
- Use the Overlapping mode to highlight where, on
the common boundary, the two curves overlap. When Overlap
Defect is selected, other analysis types are
deactivated. In Full mode, a text is displayed indicating whether the
curves overlap.
|