-
Set up the appropriate hardware configuration.
-
Set up the graphic adaptor configuration for stereoscopic display.
This step depends on hardware and operating system
configuration. Some systems require administrator privileges to change the
graphic adaptor display mode. You are required to determine the height, width
and frequency characteristics of the graphic interface.
-
In your session, access the Immersive
Configuration preferences, and then click Enables
stereoscopic display.
-
Exit the session to save your options, then restart.
-
Load an object.
-
From the AR-VR section of the action bar, click the stereoscopic mode of your
choice.
| Mode | Description |
|---|
|
Activates active or passive stereoscopic effects in the current
view. |

|
Activates anaglyph stereoscopic effects in the current view using
partial color reproduction. |

|
Activates anaglyph stereoscopic effects in the current view using
shades of gray. |

|
Activates anaglyph stereoscopic effects in the current view using
fewer colors than iV Color Anaglyph mode, in
order to decrease retinal rivalry. |

|
Activates anaglyph stereoscopic effects in the current view using no
shades of red, in order to decrease retinal rivalry as much as possible.
|
In this scenario, iV Active or Passive Stereoscopy
 is selected. is selected.
Stereoscopic viewing is enabled and has the following impacts:
- The view is switched to a perspective view.
- The 2D mouse pointer is replaced by a 3D immersive pointer to avoid
perception conflicts and keep the stereoscopic effect.
- The Robot and the Compass are hidden.
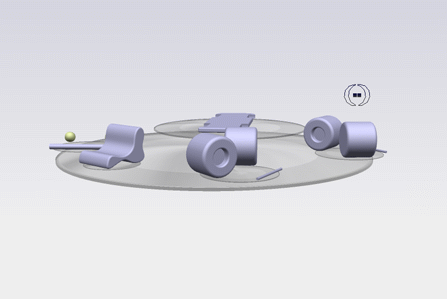
This immersive pointer  is made of two concentric circles: a small one
filled in black and a larger one with no fill color. The circles are
displayed on each eye (which is why you can see two pair of concentric
circles in the picture above) and their depth is based on the depth of the
object the pointer is snapped to. The distance between the two pairs of
concentric circles is based on the inter-eye distance and the depth of the
underlying object. is made of two concentric circles: a small one
filled in black and a larger one with no fill color. The circles are
displayed on each eye (which is why you can see two pair of concentric
circles in the picture above) and their depth is based on the depth of the
object the pointer is snapped to. The distance between the two pairs of
concentric circles is based on the inter-eye distance and the depth of the
underlying object.
- Optional:
For an optimized visualization, you can:
- Press
F3 to remove the
tree.
- Select
then deactivate the
Preselect in geometry view option.
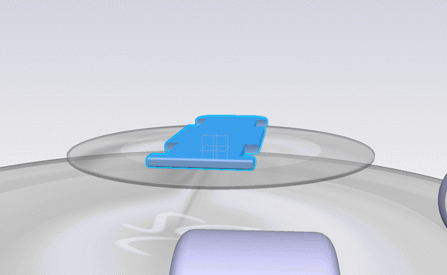
-
Set the object of your choice in the screen plane by
right-clicking it in the
3D area
then selecting
Reframe On.
In the picture below, the object highlighted in blue has been set
in the screen plane and is centered in the
tab:
-
Zoom out to view the whole scene.
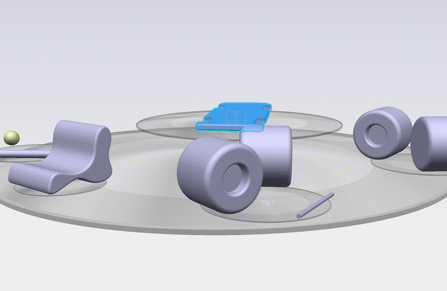
- Any object located in front of the screen plane has a smaller
depth and thus, has a 3D pop-out effect.
- Any object located behind the screen plane has a larger depth.
-
Move the immersive pointer over the objects.
The immersive pointer is rendered using a furtive technique: when the
pointer is moved, only the two circles are rendered and not the whole scene to
enhance the rendering time. This is why the color of the pointer matches the one
of the underlying object. As the distance between the two pairs of circle
depends on the inter-eye distance, the look of the pointer varies according
to the object you point at. In the pictures below, you can see that as we
get closer to the center of the screen, the concentric circles get closer to
each other:
-
To exit, click
No iV Stereoscopy
 . .
|