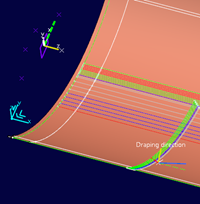
You can use the Location Points Creation Wizard as an
alternative.
-
Open the Location Points Creation Wizard
 .
.
-
Verify the number of plies and cut-pieces. Their sum determines the number of
location points to create.
-
Select or create the reference point from the context menu.
All other points are computed from this reference.
-
Optional: Click the proposed axis to invert the orientation.
-
Key in the Number of Flattens per Row.
-
Key in the Minimum Clearance Value.
The distance between points is computed as
(Current ply size+Next ply
size)/2+Minimum clearance value
-
Select an option to create a pattern.
- Create Rectangular Pattern.
- Equidistant Pattern: Creates a grid of equidistant
points, equivalent to a rectangular grid, from the reference point and the
Number of Flattens per Row.
- Space Optimized Pattern: Optimizes the creation of
points, useful where there are large differences in the plies sizes.
- Gather Cut-pieces of same ply in a row: Points associated
with cut-pieces of the same plies are in the same row. This way, you have a clear
view of the flatten bodies of plies and their cut-pieces.
- If plies have no cut-pieces, only flattenings of plies are shown.
- If Only consider cut-pieces is selected, plies
corresponding to cut-pieces are not taken into account to compute points.
- If Only consider cut-pieces is cleared, cut-pieces and
their parent ply are in one row.
-
Click OK in the wizard.
The number of location points is displayed in the main dialog
box.