SORT | |||||
|
| ||||
ResultSet Order VS SORT Operator
If defined, the ResultSet order has always precedence over SORT operators. That is why you should always prefer setting an order in the ResultSet over adding a SORT operator when possible.
Configuration
Whenever you set an order in the ResultSet or use the SORT operator, the configuration is the same: elements are ordered according to a list of sorters. A sorter can be either a value sorter or an explicit sorter.
The value sorter works as in SQL and asks for 3 elements:
- A sort expression to get the comparable value.
- The sort order: ASC/DESC.
- How to handle NULL elements: LAST/FIRST.
For example, to sort a list of tickets by rising id:
expression=ticket.id, orderAsc=true, nullsLast=true
The explicit sorter takes an expression that extracts a value, and another one to specify this value order.
For example, to sort tickets by status ("new" < "qa" < "closed"):
expression=ticket.status, order=["new","qa","closed"],
orderAsc=true, nullsLast=true
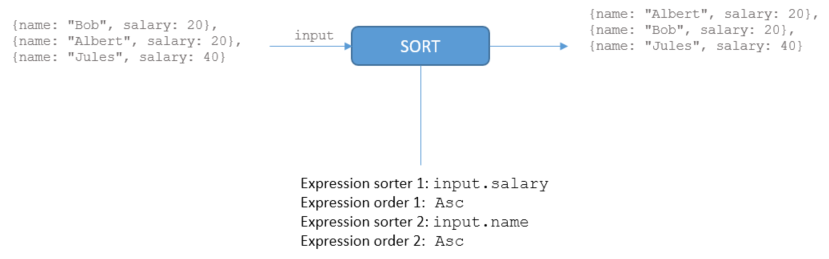
If you want to sort by multiple attributes, you specify a list of sorters. It is possible to sort by an attribute in ascending order and then by another attribute in descending order.
For example, to sort tickets by status and then by descending ticket id:
- Add an explicit sorter:
expression=ticket.status, order=["new","qa","closed"], orderAsc=true, nullsLast=true - Then add a value sorter:
expression=ticket.id, orderAsc=false, nullsLast=true
Input
There is one Input. There are no constraints on the element type or on the number of elements in the stream.
Output
There is one Output. The output stream counts as many elements as the input stream. The elements are not modified. Only the order in the stream might change.
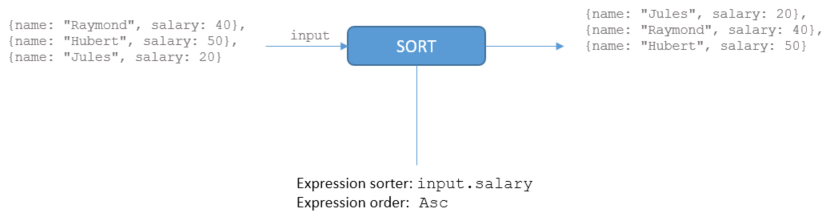
Example
In this example, we sort the employee by salary.
The output stream is ordered.
| Important: With a SORT operator, the result order can change when the DataQuery is run again if several persons have the same salary. The ResultSet offers a stable result order by choosing an arbitrary order that does not change when the DataQuery is run again. Choose this option if pagination is used on a ResultSet, to avoid having elements ordered in a different way when the user goes back and forth on the same page. |