Interpolation Dialog Box | ||
| ||
Statistical Method
- Multinormal
- This is the default mode of calculation. This mode allows you to modify one variable
while taking into consideration: All the correlation between variables and limit values
for each variable.
This defines these limitations according to the percentage of accommodation selected by you. Selecting this mode the manikins created realistically exist in the target population. After selecting the required percentage of accommodation, the boundary value automatically updates.
This mode also allows you to generate boundary manikins to accurately achieve the accommodation of the target population.
- None
- As its name suggests, this mode removes all the limitations on the variable values. If there is no database available for your specific needs, this mode generates manikins that are not in the current population. For example, if there is no database available on pregnant women, you can generate these women by removing the limitations of the current database. Be careful when using this mode; as you can you generate manikins excluded in the target population, and you can generate manikins that are totally unrealistic. Be aware that impossible manikins may not necessarily look unrealistic.
Accommodation
This is about the statistic and more precisely the body measurement values of a population. The population normally distributed and this illustrates it by the curve called the Gaussian Distribution or Frequency Curve or Normal Distribution:
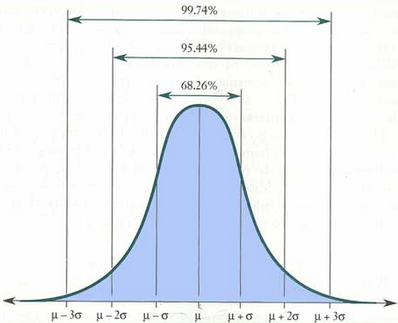
You can see when normally distributed, 95.44 % of the values are between m - 2 s (the Mean minus two times Standard Deviation) and m + 2s. Here the number 2 is the boundary. So, 99.99 percent of the values (of a measurement like the stature, for example) are between m - 4.00829s and m + 4.00829s.
- Percentage
- This shows the percentage used.
- Boundary
- This shows the boundary limits.