Instruction Support
The DELMIA Motoman Translator provides support for upload and download of all instructions in the DELMIA Robotics language that are available in the Motoman INFORM language. All features of the supported instructions which apply to Motoman are supported.
Motoman File Support The following table summarizes the level of support for each Motoman file by the DELMIA Motoman translator and DELMIA simulation. | Motoman File | Level of Support | DELMIA Equivalent | Comments | | JBI-file | Supported | Task | INFORM allows multiple JOBs defined in a single JBI file. This is supported during upload but download is always into separate files. | | TOOL.CND | Supported. Controllers:
| Tool Profile | If file TOOL.CND is not present in the JBI file selected to upload, a file whose name starts with <Robot Name> and with the extension name ".tol" will be looked for and uploaded if found. | | UFRAME.CND | Supported. Controllers:
| Object Frame Profile | If file UFRAME.CND is not present in the JBI file selected to upload, a file whose name starts with <Robot Name> and with the extension name ".uf" will be looked for and uploaded if found. | | SPRESS.CND (DX100), SGPRS.CND (DX200) | Supported | Applicative Profile | Spot servo pressure schedules. If file SPRESS.CND is not present, a file whose name starts with <Robot Name> and with the extension name ".spr" will be looked for and uploaded if found. | | CLEARNCE.DAT (DX100), SGCLARNC.DAT (DX200) | Supported | Applicative Profile | Clearance schedules. | | WDELAY.SCD | Supported | Applicative Profile | Weld time schedules. This is NOT a Motoman controller file, but user created. | | MACRO.DAT | Supported. Controllers:
| | The system Macro definition file. For each Macro number, it defines Macro name, argument types, argument comments, etc. | | Macro Job JBI-file | Supported | Task | Each Macro job JBI file defines a subroutine. There is an identifier "MC" in "///ATTR" pseudo instruction. | | ALL.PRM | Supported
Controllers: - XRC
- NX100
- DX100
- DX200
- YRC1000
| N/A | The Motoman Batch Parameter file. It contains robot system information. It is
used to calculate axis Pulse parameters and upload Soft Limits. For upload, if this file
exists in the same folder as the program files, it will be read for Pulse parameter
calculation. For download to use this file, set the Template folder to where the file is
located. Limitation: This is invalid for Shelf-mount robots, except YRC1000. | | SGUN.DAT | Supported
Controllers:
| N/A | The Motoman Spot Gun Condition Data file. It defines encoder Pulse counts and open stroke mapping table for weld guns. It is most useful for Rocker guns with non-linear Pulse-Stroke relation. Put this file in the same folder as program files to upload, and set the Template folder to its location to use on download. | | TOOLINTF.DAT (DX100) | Supported | Tool Volume | This is the Motoman Tool Interference data file. There are up to 64 tools (tool volumes), and each tool volume can be a combination of up to 5 shapes (models). Motoman tool volume shape is capsule, consists of 2 points with a radius. | | RNGROBO2.CND (DX100) | Supported | TCP Safety Zone | This is the Motoman Robot Range Limit file. There are up to 8 Range definitions, and each Range definition can have up to 8 safety areas. Each safety area is defined as a polygonal prism of up to 16 contiguous lines. Inside the range is safe. | | VAR.DAT | Supported. Controllers:
| N/A | This file stores Motoman variable values. It is used to support variables used in Servo Spot weld. | | Other | Not Supported | | |
The following table summarizes the level of support for each Motoman instruction by the DELMIA Motoman translator and DELMIA simulation. Any instruction which does not appear in this list is uploaded as a V6 Comment instruction and is not used in simulation. | Motoman INFORM Instructions | Level of Support | DELMIA Instruction | Comments | | Motion Instructions | | MOVJ | Supported | Robot Motion | See below for details on support for each motion options. | | MOVL | Supported | Robot Motion | | MOVC | Supported | Robot Motion | | MOVS | Partial Support | Robot Motion | Uploaded as linear move | | EIMOVL | Supported | Robot Motion | See below for details on support for each motion options. | | EIMOVC | Supported | Robot Motion | | SMOVL | Partial Support | Robot Motion | Uploaded as a normal motion. No support for download. | | SMOVC | Partial Support | Robot Motion | | IMOV | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | SPEED | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | UNTIL | Partial Support | Motoman Motion Profile | Not simulated | | ENWAIT | Partial Support | Motoman Motion Profile | Not simulated | | Spot Instructions | | SVSPOT | Supported | Spot Operation | No Clearance Profile | | SVSPOTMOV | Supported | Spot Operation | Has Clearance Profile | | SPOT | Supported | Spot Operation | No Pressure Profile | | GUNCL | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Air not supported | | STROKE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Air not supported | | GUNCHG | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | STRWAIT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | SVGUNCL | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | Arc Instructions | | ARCON | Supported | Arc Operation | | | ARCOF | Supported | Arc Operation | | | VWELD | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | AWELD | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ARCSET | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | WVON | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | WVOF | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ARCCTS | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ARCCTE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | Search and Shift Instructions | | REFP | Partial Support | Seam Search | REFP instructions are treated as seam search operations. See below for details. | | SFTON | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | SFTOF | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | MSHIFT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | Handling Instructions | | HAND | Supported | Grab/Release | | | HSEN | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | TOOLON | Supported | Grab | | | TOOLOF | Supported | Release | |
| Paint Instructions |
| SPYON |
Supported |
Trigger |
Action: Nozzle Activation; State: ON |
| SPYOF |
Supported |
Trigger |
Action: Nozzle Activation; State: OFF |
| Conveyor Synchronized
Instructions |
| SYSTART |
Supported |
Wait |
The wait condition must be Referential > a constant value or a
declared constant. If a declared constant has a dot ('.') in its name, it must be used in
double quotes and prefixed with the dollar symbol ('$') to use in the condition. |
| SYEND |
Supported |
|
Subsequent motions will be regular motions, non-conveyor
tracking. |
| SYMOVJ |
Supported |
Robot Motion |
Conveyor tracking, joint move |
| SYMOVL |
Supported |
Robot Motion |
Conveyor tracking, linear move |
| SYMOVC |
Supported |
Robot Motion |
Conveyor tracking, circular move |
| Logic Instructions | | JUMP | Partial Support | Goto | The INFORM JUMP statement includes options which are not supported by DELMIA. See below for details. | | * (label) | Supported | Label on another instruction | The label is set on the DELMIA instruction which follows it. | | IF | Partial Support | Condition | INFORM IF statements are appended to other instructions (JUMP, CALL, RET, PAUSE) to make them conditional. Upload is not if used with PAUSE. Variable array indexes are not supported. Not all DELMIA IF instructions are supported for download. |
| IFTHEN |
Supported |
Condition |
The uploaded Activity OLP content stores the keyword IfThenExp, and this Condition
activity will be downloaded as IFTHEN instruction. |
| FOR |
Partial Support |
For |
STEP size 1 is supported. |
| WHILE |
Supported |
While Do |
|
| SWITCH |
Supported |
Test |
|
| RET | Supported | Return | | | CALL | Partial Support | Run (procedure) | The INFORM CALL instruction has options which are not supported by DELMIA. Some CALL instructions are uploaded as grab or release instructions. See below for details. | | MACRO# | Supported | Run (procedure) | Supported. The procedure can have arguments. | | PAUSE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | IO and Arithmetic Instructions | | SET | Partial Support | Assign | Upload/Download may not result in the same INFORM syntax when SET, ADD or SUB are uploaded. Variable array indexes are not supported. | | ADD | Partial Support | Assign | | SUB | Partial Support | Assign | | MUL | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | INC | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | DEC | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | DIV | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | AND | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | OR | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | NOT | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | XOR | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | SQRT | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | SIN | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | COS | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | ATAN | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | DIN | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | DOUT | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | AOUT | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | GETARG | Partial Support | Assign | Variable array indexes and position type variables are not supported. | | WAIT | Partial Support | Wait | Variable array indexes are not supported. Wait time may be a constant or an integer
variable. | | TIMER | Partial Support | Wait | Wait time may be a constant or an integer variable. | | PULSE | Partial Support | Pulse | Variable array indexes are not supported. | | PAUSE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | CLEAR | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | CNVRT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | MFRAME | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | SETE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | GETE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | GETS | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | MULMAT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | INVMAT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | GETPOS | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | VAL | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | VAL2STR | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ASC | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | CHR$ | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | MID$ | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | LEN$ | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | CAT$ | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | STRSTR | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | SETREG | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | GETREG | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | Other Instructions | | ' (Comment) | Supported | V6 Comment | These instructions have no impact on the program execution. | | NOP | Supported | V6 Comment | | ARATION | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ARATIOF | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ANTOUT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | CWAIT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ADVINT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | ADVSTOP | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | GETFILE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | SETFILE | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | INPUT | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | MSG | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | TCPON | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated | | TCPOF | Partial Support | V6 Comment | Not simulated |
The following table summarizes the level of support for each DELMIA instruction by the DELMIA Motoman translator.
|
DELMIA Instruction
|
Level of Support
|
Motoman INFORM
Instructions
|
Comments
|
|
Task
|
Supported
|
JBI-file
|
INFORM allows multiple JOBs defined in a single
JBI file. This is supported during upload but download is always into
separate files.
|
|
Goto
|
Partial Support
|
JUMP
* (label)
|
The INFORM JUMP statement includes options
which are not supported by DELMIA. See below for
details.
|
| Condition |
Partial Support |
IF
|
INFORM IF statements are appended to other
instructions (JUMP, CALL, RET, PAUSE) to make them conditional.
Upload is fully supported except if used with PAUSE. Not all DELMIA
IF instructions are supported for download.
|
| IFTHEN |
If the string in the Activity’s OLP Content starts with keyword “IfThenExp”, the
Condition activity is downloaded as IFTHEN instruction. The OLP Content is automatically
set for tasks created by uploading Motoman programs. |
|
For
|
Partial Support |
FOR |
INFORM FOR does not support negative STEP size. |
| Do While |
Not Supported
|
NA
|
INFORM has no Do While loop |
| While Do |
Supported |
WHILE |
|
| Test |
Supported |
SWITCH |
|
|
Return
|
Supported
|
RET
|
|
|
Break
|
Not Supported
|
NA
|
INFORM has no break
|
|
Run (service)
|
Not Supported
|
NA
|
Service calls run procedures from other
resources, this is not possible with INFORM.
|
|
Run (procedure)
|
Partial Support
|
CALL
|
INFORM does not support arguments. The INFORM
CALL instruction also has options which are not supported by
DELMIA. See details below.
|
| Run (procedure) | Supported | MACRO# | When Template is selected to a folder containing system file MACRO.DAT, and a procedure name is defined in the file MACRO.DAT, the procedure is downloaded as Motoman Macro call. It supports arguments. |
|
Grab/Release
|
Supported
|
CALL
HAND
|
|
|
Assign
|
Partial Support
|
SET, ADD, MUL, INC, DEC, SUB, DIV, AND, OR,
NOT, XOR, SQRT, SIN, COS, ATAN, DIN, DOUT, AOUT
|
INFORM has limited expression support in the
SET instruction and also has other instruction which can do math
functions. Not all DELMIA expressions are supported for
download.
Upload/Download may not result in the same
INFORM syntax when SET, ADD or SUB are uploaded.
|
|
Wait
|
Partial Support
|
WAIT, TIMER, SYSTART |
INFORM has limited wait expression. Not all
DELMIA expressions are supported for download.
|
|
Pulse
|
Partial Support
|
Pulse
|
|
|
Robot Motion
|
Supported
|
MOVJ, MOVL, MOVC, EIMOVL, EIMOVC, SYMOVL, SYMOVJ, SYMOVC |
|
|
Spot Operation
|
Supported
|
SVSPOT, SVSPOTMOVE
|
|
|
Arc Operation
|
Supported
|
ARCON, ARCOF
|
|
|
Seam Search
|
Partial Support
|
REFP
|
REFP instructions are treated as seam search
operations. |
|
V6 Comment
|
Supported
|
' (Comment), NOP
|
These instructions have no impact on the
program execution.
|
|
V6 Comment
|
Not supported
|
PULSE, ARATION, ARATIOF, ANTOUT, PAUSE, CWAIT,
ADVINT, ADVSTOP, CLEAR, CNVRT, MFRAME, SETE, GETE, GETS, MULMAT,
INVMAT, GETFILE, SETFILE, MOVS, IMOV, SPEED, SFTON, SFTOF, MSHIFT,
UNTIL, ENWAIT, VWELD, AWELD, ARCSET, WVON, WVOF1
, ARCCTS, ARCCTE,
HSEN, SPOT, GUNCL, STROKE, STRWAIT, GUNCHG, SVGUNCL, TOOLON,
TOOLOF, INPUT, MSG, GETPOS, VAL, VAL2STR, ASC, CHR$, MID$, LEN$,
CAT$, STRSTR, SETREG, GETREG, TCPON, TCPOF2
|
These are converted to V6 Comment instructions
and their effect on simulation is ignored.
|
[1] WVON and WVOF are not simulated, but can be scripted during download using the ARCStart and ARCEnd profiles. For more details
see the arc welding section below.
[2] Any instruction not mentioned, is also converted to a
V6 Comment instruction. These could be instructions from an add-on
option or from newer controller versions.
Instruction Details
Task MOTOMAN tasks are called jobs. Jobs are stored
in a .JBI file. A single JBI-file can contain multiple jobs;
however the controller always saves each job into a separate file.
Multiple jobs in a JBI file are supported for upload. During download, all jobs are stored in separate files. JBR-files are not
supported.
The job name can be 8 characters long (32 for DX100 controller)
and can contain uppercase letters, numbers, or the
punctuation -!%&'()_. During download, invalid characters are
removed, names that are too long are truncated, and a unique
number is appended to the end of the task name if it is not
unique.
Unsupported Instructions Any DELMIA instruction (for, while, break, run service) that is not supported during download is skipped. A message is displayed indicating that this DELMIA instruction is not supported by the INFORM language. This ensures that the generated file is a valid INFORM task. If an unsupported logic instruction contains other instructions, such as the instructions inside a DO WHILE loop, they are skipped. In order to download those instructions, you must remove them from the DO WHILE loop. GotoA DELMIA Goto instruction is translated into an INFORM JUMP instruction. In DELMIA, the label is added to another instruction. In INFORM, the label, denoted by a *, is its own instruction. During upload, the label is set on the first instruction after the label. If there are no more instructions or more than one consecutive label instruction, a V6 Comment activity is created with the name “*MyLabel”. During download, the INFORM label instruction is created before the instruction that the label is defined on. If the label is defined on a V6 Comment instruction which starts with “*”, the V6 Comment instruction is ignored. This ensures that an uploaded program is downloaded exactly the same. For example, if the last line of a Motoman program is "* ENDLBL". A V6 Comment instruction with the text "* ENDLBL" is created and the label is set to "ENDLBL". When this instruction is downloaded, only one line is added to the program instead of one for the label and one for the V6 Comment instruction. A message is displayed if the label does not match the V6 Comment instruction text. INFORM Labels can be a maximum 8 characters long, can contain upper or lower case letters, numbers, or punctuation “-!%&’()_”. During download, invalid characters are removed, names which are too long are truncated, and a unique number is appended to the end of the label if it is not unique. During download, there are no restrictions translating a DELMIA Goto into an INFORM JUMP. During upload, there are many restrictions because the INFORM JUMP instruction has more options than can be supported in DELMIA. If the “*” format is used, a normal DELMIA Goto instruction is created. If the “JOB:” format is used, a DELMIA run instruction is created. All other formats (LABEL, B, LB, IG, QUE, I, LI, D, LD, and JET) are not supported and are uploaded as V6 Comment instructions. The UF option for the “JOB:” format is not supported and, if specified, a V6 Comment instruction is created. The LBLST and LBLDF options are also not supported and a V6 Comment instruction is created if encountered. See the Condition section for details on how the IF option is handled. If the label referenced by a JUMP does not exist in the program, a warning is displayed and the Goto instruction will not point to any label. Condition A DELMIA Condition instruction is translated
into an IF. IF statements in INFORM are options added onto other
instructions. For example, an IF condition can be added to a JUMP,
CALL, RET or PAUSE instruction.
Since PAUSE is not supported for upload, the IF
on a PAUSE instruction is uploaded as part of the PAUSE V6 Comment
instruction.
During download, any instructions in the DELMIA
else clause are ignored. If it is not empty, a warning is displayed. The DELMIA Then clause must contain only one instruction
and that instruction must be either a run procedure (CALL), a Goto (JUMP),
or a return (RET). If the first instruction is not one of
these instructions, the Condition instruction is skipped and a
warning is displayed. If any other instruction exists in the clause,
they are ignored and a warning is displayed.
During download, the expression for the DELMIA IF
must conform to the INFORM IF rules. An INFORM IF instruction can
contain one Boolean comparison operator. The operands can be an input
(IN#), an input group (IG#), a byte (B, LB), an integer (I, LI), a
double (D, LD) or a register (R, LR). Allowed operators are =,>,
<, =>, <=, <>. The input and input group variables
have further restrictions on how they can be used.
During upload, a condition instruction with one
instruction in the then sequence is created. The expression
is an exact translation of the INFORM expression.
ReturnA DELMIA return instruction is translated into an INFORM RET instruction. See the Condition section for details on how the INFORM IF option is handled.
Run (procedure)A DELMIA run instruction, where the run is calling a procedure, is translated into a INFORM CALL instruction. DELMIA run instructions can have arguments, but INFORM CALL instructions do not. During download, any run instruction with arguments is skipped and a warning is displayed. During upload, there are many restrictions because the INFORM CALL instruction has more options than can be supported in DELMIA. If the “JOB:” format is used, a DELMIA run instruction is created. All other formats (B, LB, IG, QUE, I, LI, D, LD, and JET) are not supported and are uploaded as V6 Comment instructions. The UF option for the “JOB:” format is also not supported and if specified, a V6 Comment instruction is created. See the Condition section for details on how the IF option is handled. Grab/Release INFORM has a HAND instruction which corresponds
to Grab/Release. A CALL job is also often used for this
purpose (for example, HANDON and HANDOF).
During upload, HAND … ON is translated to a grab
instruction and HAND … OFF is translated to a release instruction.
Additionally, CALLs for some special JOB names are uploaded as
grab or release instructions. For example, CALL JOB:HANDON are
uploaded as a grab and CALL JOB:HANDOF are uploaded as a
release, unless a task already exists with the special JOB name or
if a JBI-file with those names was explicitly selected for upload. The part to grab or release is specified in the
parameter PartGrabbed of the "Motoman Controlledddr
Profile".
| Grab JOB Names | Release JOB Names | | HANDON | HANDOF | | TOOLON | TOOLOF | | GRAB | RELEASE | | PICK | DROP |
During download, the instruction name is based on the grab or release instruction name. If the instruction name is valid INFORM syntax (either a HAND or CALL instruction), it is downloaded as-is. If the instruction name is not valid syntax, it is treated as a job name. For example "Grab.1" is downloaded as "CALL JOB:GRAB1" ("." is removed because JOB names cannot contain periods). Assign A DELMIA assign instruction is translated into
one of several INFORM arithmetic instructions. The supported INFORM
variable manipulation functions are SET, ADD, MUL, CLEAR, INC, DEC,
SUB, DIV, AND, OR, NOT, XOR, SQRT, SIN, COS, ATAN, DIN, DOUT, and
AOUT. When a task’s Motoman Task Profile attribute "Header_Attr" contains identifier "MC", and the task name is found in MACRO.DAT, DELMIA assign instructions in the form LB000:=B1 are downloaded as GETARG instructions. The GETARG instruction is only valid in Macro job files. The data types can be Byte, Integer, Double precision Integer, or Real. (Instead of calling a Macro with variable input argument, constant input arguments are uploaded as LI000:=KI2, for example.)
During download, the instruction used is dependent on
the source expression of the assignment.
| INFORM Instructions | INFORM syntax | Equivalent DELMIA assign | | ADD, MUL, SUB, DIV, AND, OR, NOT, XOR | INSTR A B | A:=A op B | | SET [1] | INSTR A exp | A:=exp | | DIN, DOUT, AOUT [2] | INSTR A B | A:=B | | SQRT, SIN, COS, ATAN | INSTR A B | A:=func(B) | | INC | INC A | A:=A+1 | | DEC | DEC A | A:=A-1 | | GETARG | GETARG LB000 IARG#(1) | LB000:=B1 |
[1] SET allows
expressions for the source of the assignment. Expressions only
support +, -, * and / operators and a maximum of 7 operators are
allowed. Parentheses are supported. If the expression happens to be
equivalent to a dedicated INFORM instruction, the same instruction
will not be downloaded. For example. if the instruction is "SET B000
B000+1", this is uploaded as "B000:=B000+1" and then
downloaded again as "INC B000". This same limitation applies to ADD
and SUB.
[2] DOUT and
AOUT are used during download if the target of the DELMIA assign
instruction is an output variable. DOUT is used for Boolean and
integer outputs, AOUT is used for double outputs. DIN is used if
the source variable is an external IO. The INVERT option for DOUT
is translated as A:=NOT A or A:=not A depending on if the output is
a Boolean or an Integer. Any DELMIA assign expression not listed in the table above cannot be downloaded. When encountered, a warning is displayed and the instruction skipped.
Wait A DELMIA Wait instruction is translated as an INFORM WAIT, TIMER, or SYSTART instruction.
During download, the expression for the DELMIA Wait
must conform to the INFORM WAIT expression syntax. WAIT
instructions only allow + or <> operators, and there are
limitations on the variables allows for each operand. The INFORM "TIMER" instruction corresponds to a
DELMIA Wait instruction with the expression set to the constant
"false." This is a pure delay.
The T= option of the INFORM WAIT instruction corresponds to the timeout option of the DELMIA
wait instruction if the WAIT instruction is not a pure delay. The WAIT time may be a constant
or an integer variable (I, LI) variable. When an integer variable is used, the wait time is
1/100 of the value of the integer variable. For example, if I002 is 5, the stop time is 0.05
sec.
When the Wait Condition is "Referential > constant", a conveyor synchronization start
instruction SYSTART is generated. The constant in the wait condition can be a constant value or
a declared constant. If a declared constant has a dot ('.') in its name, it must be used in
double quotes and prefixed with the dollar symbol ('$') to use in the condition.
During upload, WAIT instructions are uploaded as V6
Comment activities if the parameter "CommentWaitSignal" of the
profile "Motoman Controller Profile" is set to true (the
default value). This occurs because the robot program pauses during
simulation at the WAIT instruction unless all the robot's IO have
been set up and you are simulating the full station
behavior.
Pulse A DELMIA Pulse instruction is translated as an
INFORM Pulse instruction.
Output number and output value for OG# and OGH# cannot be specified as a variable. It must be
specified as a number. Pulse duration (Time) may be a constant or an integer variable in which
case the stop time is 1/100 of the value of the integer variable.
For Boolean IO, Pulse instruction with value
'false' or 'Invert' is assumed to be the value 'true'.
When pulse duration is set to Infinite, it will
download to the maximum of 60 seconds.
Non-zero Delay value is not supported in
Motoman and warning about it being ignored is issued.
Trigger
A DELMIA Trigger instruction is translated as an INFORM paint instruction SPYON or SPYOF.
When the Trigger Action is "Nozzle Activation" and its State is "ON", it is downloaded as
SPYON (spray start). If the State is "OFF", it is downloaded as SPYOF (spray stop).
The Condition may be Time or Distance, and it is downloaded as Anticipation time or
distance.
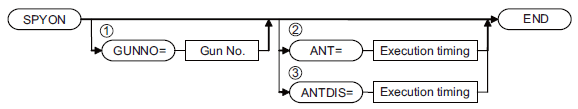
Gun number is the Parameter set number in the Paint
Profile dialog box.
Robot MotionThe table below gives basic information on the level of support of different motion options. Any unsupported options are stored in an applicative profile attached to the motion instruction so they can be downloaded again.
|
Motoman Motion Option
|
Support Level
|
DELMIA Equivalent
|
Description
|
Translation Notes
|
|
MOVJ, MOVL, MOVC, MOVS
|
MOVS (spline) not supported.
|
Joint, Linear, Circular
|
motion type
|
INFORM requires 3 MOVC instructions in a row. [3]
MOVS is uploaded as
a linear move.
|
|
Pxxx, LPxxx, BPxxx, LBPxxx, EXxxx,
LEXxxx
|
Global positions supported, not
local
|
Position Type / Position Number
|
Position storage location
|
By default positions are stored internally in
the JOB in "C" variables. For example: C000, BC000, EC000. It is
not possible to control the numbering of the C variables. If P
variables are used the property "Position Number" is set to "P000"
or if aux axes are used a comma separated list "P000, BP000". The
local variables LP, LBP, LEX are not supported since they are used
for temporary storage and position computation is not supported in
DELMIA. Array indexing with non-constant arrays for P variables is
also not supported.
|
|
T
|
Not supported
|
|
Point variable
|
|
|
VJ, V, VR, VE
|
Support
|
Motion Profile
|
Speed
|
If the speed is omitted in INFORM, the speed is
taken from the last SPEED instruction or from the last ARCON
instruction. The arc welding case is supported by DELMIA, the more
general case is not supported. See the Arc Welding section below for more details on that case. In
the general case, the motion profile MotomanDefault or
MotomanDefaultJnt is used.
MOVJ can only use the VJ speed
option.
MOVL, MOVC, MOVS only use the V, VR or VE
options. VE is only valid with jobs that have a robot and a station
axis. There is a parameter "UseVE" set on a motion profile that is
associated with the VE speed option. Please refer to Motion Profile
Parameter section.
VJ & VE are motion basis %, and V & VR
are motion basis absolute. VR is an angular speed.
Upon upload, when there are predefined motion
profiles (e.g. VJ=25 or V=150) matching the moves' speed settings,
they are used. Otherwise new motion profiles are
created.
Speeds specified as a variable are not
supported. The speed is uploaded as MotomanDefault or
MotomanDefaultJnt.
|
|
PL, CR
|
Parial Support
|
Accuracy Profile
|
Accuracy
|
For an omitted accuracy setting, the Motoman
manual states "If the position level is not set, the precision
depends on the operating speed." That functionality is not
supported by DELMIA so we create an accuracy profile called
MotomanDefaultJnt (for MOVJ) or MotomanDefault (for MOVL and MOVC)
with FlyBy=On and accuracy type speed. The problem is that we don't
know what value to specify so we use 63%. This value can be changed
with the parameter MotomanDefaultJnt and MotomanDefault (see
below)
Specified Position levels (e.g. PL=0~8) are
distance accuracy settings. The NX100 (and XRC when parameter
XRCPositionLevel is set to 8) default values for the position
levels 1 through 8 are 25mm, 50mm, 100mm, 150mm, 200mm, 300mm,
400mm, 500mm. Accuracy profiles named PL=1~8 are set to the values
specified here during upload. Accuracy profile "PL=0" is treated
differently. If its Flyby Mode is On, or Accuracy Type is Speed, or
Accuracy Value is not zero, a new accuracy profile is created during upload with the default settings. Either way the profile indices
are set to the PL value.
During download, if an accuracy profile index is
set, then PL=<index> is downloaded. If the profile name and
setting mismatch, a warning is issued.
If CR is specified, the distance is set to the
CR value.
During download if the profile is not named
MotomanDefault, MotomanDefaultJnt, PL=x, CR=x, or SPDL=x, PL is used and the position level closest to the values specified
above is used.
FlyBy off corresponds to PL=0.
Accuracy values specified as a variable is not
supported. A profile with the same name as the accuracy expression
is created or used if it already exists.
See also Accuracy Parameter section.
|
|
SPDL
|
Not supported
|
|
Servo Float
|
|
|
MT,MTE
|
Not Supported
|
|
Amount of T axis or station axis
rotation.
|
|
|
NWAIT, WAIT
|
Not Supported
|
|
Continue execution before target
reached
|
|
|
UNTIL
|
Not Supported
|
|
Move until condition satisfied
|
|
|
NSRCH, SRCH, ASRCH,
HPSRCH
|
Not supported
|
|
Search
|
|
|
ACC/DEC
|
Partial Support
|
Motion Profile
|
Acceleration
|
Combined with V, VJ, VR, VE to create motion
profile.
Acceleration values specified as a variable is
not supported.
DELMIA only supports one value for
acceleration/deceleration. If ACC and DEC are different (or one is
missing) then a warning is issued and the average value is used in
the motion profile.
|
|
Comment
|
Supported
|
Position Comment
|
|
|
|
+MOVJ, +MOVL, +MOVC,
+MOVS
|
Partial Support
|
|
Multiple Groups
|
Only supported for station (positioner/end of
arm tooling) and base (rail/track) devices. Multiple robots is not
supported. You must set the StationGroup and/or BaseGroup
parameters in the controller profile.
|
|
EIMOVL, EIMOVC
|
Supported
|
Robot motion
|
Fixed TCP
|
The Motoman user frame (UF#) is equivalent to a
fixed tcp tool profile and the tool is equivalent to the object
frame used with the fixed TCP move.
|
| SYMOVJ, SYMOVL, SYMOVC |
Supported |
Robot Motion |
Conveyor synchronized move |
These are conveyor synchronized motions, or line tracking. |
|
Relative Job
|
Supported
|
|
Cartesian coordinates for positions
|
Normally all positions are stored in Pulse
counts in Motoman programs. The Relative Job option allows
positions to be stored in Cartesian coordinates.
To download a relative job, set
DownloadTarget="RECTAN" in the Motoman Controller Profile. You can
control the coordinates of Base axes (rails) using the parameter
DownloadTargetBC.
The coordinates used depend on the object frame
profile. If the object frame profile is named "BASE" then
coordinates are relative to the base axis origin. If it is named
"ROBOT" then coordinates are relative to the robot origin. In the
"BASE" and "ROBOT" case, the object frame profile should be
0.
Positions for all other object frame profiles
are downloaded in USER coordinates.
|
|
TOOL.CND
|
Supported
|
Tool profile
|
Tool TCP offset condition file
|
Tool profiles are created or updated from this
file if it exists. The file is also generated during download. This
file contains only mobile TCP tool profiles or fixed TCP object
frames.
|
|
UFRAME.CND
|
Supported
|
Object Profile
|
User frame condition file
|
Object frames are created or updated from this
file if it exists. This file is also generated during download. This
file contains fixed TCP tool profiles and mobile TCP object
frames.
|
[3] INFORM requires 3 circular motions to form
an arc. The 1st position is moved to with linear interpolation and
the next 2 points, with circular interpolation. There can also be
more than 3 points, in which case the circle is recomputed after
each move. This mode is not supported for translation. If more than
3 circular moves are encountered, all but the last 2 moves are
uploaded with linear interpolation.
Notes on Continuous Circular Moves NX100 Controller: It is necessary to program a Joint or Linear move (P4) between the two arcs, and the three targets (P3, P4, and P5) are identical. 3DEXPERIENCE & OLP supports this kind of continuous circular move. When continuous circular movement is required, the two arcs must be separated from each other by a joint or linear interpolation step. This step must be inserted between two steps at an identical point. The step at the end point of the preceding circular move must coincide with the beginning point of the following circular move.
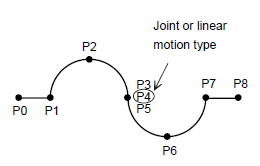
Table 1. Interpolation type for continuous circular arc| Point | Interpolation type | Instruction |
|---|
| P0 | Joint or Linear | MOVJ, MOVL | | P1, P2, P3 | Circular | MOVC | | P4 | Joint or Linear | MOVJ, MOVL | | P5, P6, P7 | Circular | MOVC | | P8 | Joint or Linear | MOVJ, MOVL | DX100/DX200/FS100/YRC100 Controllers: In
addition to the 3-identical point method used in NX100, these newer
controllers support an FPT Tag in MOVC instruction that specifies
the End-point of an arc (arc curvature is to be
changed).
OLP support is
as follows:
Download:
After a Circular move is encountered, a Circular-Via breaks the
current arc, therefore its preceding Circular move will have an FPT
tag. In the following motion sequence, since P4 is a Circular-Via
after Circular move, therefore Circular move P3 will have an FPT
tag.
|
P0
|
P1
|
P2
|
P3
|
P4
|
P5
|
P6
|
|
Joint
|
Linear
|
Circular-Via
|
Circular
|
Circular-Via
|
Circular
|
Joint
|
|
Joint
|
Circular
|
Circular
|
Circular
|
Circular-Via
|
Circular
|
Joint |
Upload: When a
MOVC instruction with an FPT tag is encountered, the following MOVC
will be uploaded as Circular-Via move.
Alternatively, to continue movements without adding an extra joint or linear interpolation step in between, add "FPT" tag to the step whose curvature is needed to be changed.

| Point | Interpolation type | Instruction |
|---|
| P0 | Joint or Linear | MOVJ, MOVL | | P1, P2 | Circular | MOVC | | P3 | Circular | MOVC, FPT | | P4, P5 | Circular | MOVC | | P6 | Joint or Linear | MOVJ, MOVL |
Notes on Conveyor Synchronized Motions
To upload a program with conveyor synchronized motions, you must create a Referential profile
on the conveyor and a Tracking profile beforehand.
Motoman synchronization start instruction SYSTART:
SYSTART CV#(1) STP=50.000 OL=10.0
Synchronization Start Position STP is equivalent to Part detect offset
in the Tracking profile.
Over Limit (OL) is equivalent to Outbound offset in the Tracking
profile.
Upon upload, a Wait instruction is created in the following format:
wait Referential > $”<tracking profile>_INBOUND”
A constant is created:
<tracking profile>_INBOUND
Motoman synchronized motion instructions:
SYMOVJ VJ=50.00 CV#(1) CTP=100.000
SYMOVL V=200.00 CV#(1) CTP=100.000
SYMOVC V=200.00 CV#(1) CTP=100.000
CV#(1) is the conveyor number, and User Identifier in the Tracking
profile.
CTP is the Conveyor Taught Position. It is set on each robot motion.
For link tracking upload, it is necessary to click the button Click To Attach
Part in the Object Frames tab of the Import
Industrial Robot Program dialog box and select a conveyor to which the path is to
be attached. Alternatively, you can set the default Reference to
Object in the Object Frame Profile dialog box and
select a conveyor beforhand to skip this step.
I/O Output Timing Control Function
A motion instruction with +DOUT is uploaded as a robot motion followed by a Trigger
instruction with Distance or Time Condition. Motion instructions with +PULSE is not
supported.
MOVx … +DOUT OT#(1) ON ADJD=-50.0 ` distance mm
MOVx … +DOUT OT#(1) ON ADJT=-1.00 ` time sec
Position Registers Position
registers are global positions that are reused among many robot
programs. A position register can be joint values or a Cartesian
location. Motoman position registers are called P-vars and are
named Pxxxx for the robot target and aux targets are named either
BP-vars for rail targets or EX-vars for other aux axes. Motoman
regular move targets are called C-vars and are named Cxxxx for
robot targets. Auxiliary device targets are named BC-vars for rail
targets or EC-vars for other aux axes.
Tags
have a lock property which prevents users from modifying their
positions in one or more dimensions. If x, y, z, yaw, pitch and
roll are all locked, the user cannot modify the tag's position in
teach, in the trajectory editor or with the robot compass without
first unlocking the tag.
Home
positions can only be modified through the "manage home positions"
command. They are not modified when you use the modify command for
a robot motion in teach.
On
upload, robot Home positions will be created for P-vars with Pulse
values. Auxiliary device home positions will also be created for
BP-vars and/or EX-vars. For Cartesian values, locked tags in a
dedicated tag group "<robot>_GlobalTags.1" will be created.
The Home position and locked tag names will be the same as the
P-vars, and in the cases of auxiliary axes BP-vars and/or
EX-vars.
On
download, Home positions will be output as P-vars based on the Home
name. All moves which reference tags in the tag group with
"GlobalTags" in the name are downloaded as
P-vars.
If a
motion OLP Activity Property "Position Type" is set to "C" or "P",
it will be downloaded as a C-var or P-var. This takes precedence
over target type (Home or tags in "GlobalTags"). OLP Activity
Property "Position Number" can also be set in the form of
"P<number>, BP<number>, EX<number>" to download
P-vars etc. and "Position Number" takes precedence over "Position
Type".
Spot WeldingOnly servo guns are supported for spot welding. Gun changes are not supported. Spot instruction translation depends upon the weld gun stationary tip clearance settings of the spot profile associated with the spot operation. If the Pressure Start Move and Pressure End Move stationary tip clearances are zero (0), the Spot instruction is downloaded as SVSPOT with a MOV* instruction created prior to it, otherwise the spot instruction is downloaded as an SVSPOTMOV. If the parameter NameOverride is set to “true”, the profile name is output as a spot instruction. This can be used for dry spot SVGUNCL or SVSPOTMOV with settings WP (weld pressure) and/or BWS (gun stroke for welding start). In the following spot weld instructions: SVSPOT GUN#(1) PRESS#(1) WTM=1 WST=1 SVSPOTMOV C0000 EC0000 V=1000.0 PLIN=1 CLF#(1) GUN#(1) PRESS#(1) WTM=2 WST=1 WGO=1 the gun number(GUN#) is used for gun selection in DELMIA Spot Profile; applicative profiles created for the pressure schedule(PRESS#), weld time schedule(WTM), and clearance schedule(CLF#) are linked to the Spot Profile. WST(weld start timing) and WGO(weld group output) are not used in simulation. They are set in the controller parameters of the Spot Profile, if present. During upload, spot profiles with the instruction text are created if they do not exist. - Applicative Profiles
Pressure schedules specify the weld pressure, touch speed, and press times. They are created automatically from the pressure schedule file “SPRESS.CND” (DX100) or "SGPRS.CND" (DX200) if present in the same folder with the program file selected for upload. The profiles are named in the format PRESS#(<index>) to match the way the schedules are referenced on the spot instruction. They can also be created manually from the “Applicative Profile” command. Table 2. Example PRESS applicative profile | Parameter | Example Value | Default Value | Measure | | Index | 1 | 1 | Integer | | Comment | Standard | <blank> | String | | Touch Speed | 10% | 10% | Percent | | Touch Press | 100.0kgf | 0 | Force | | 1st Press | 200.0kgf | 0 | Force | | 1st Press Time | 0.20s | 0 | Time | | 2nd Press | 300.0kgf | 0 | Force | | 2nd Press Time | 0.20s | 0 | Time | | 3rd Press | 200.0kgf | 0 | Force | | 3rd Press Time | 0.20s | 0 | Time | | 4th Press | 300.0kgf | 0 | Force | SPRESS.CND is a file which can be exported from Motoman XRC, NX100, and DX100 controllers. It has the same format for all controllers except for DX100 which has an additional comment field. Below is the DX100 file format. | DX100 SPRESS.CND file | DX200 SGPRS.CND file |
|---|
//SPRESS 1
///COMMENT Standard
10
100.0
200.0,0.20
300.0,0.20
200.0,0.20
300.0,0.00 | //SGPRS 1
///COMMENT
30
100.0, 655.35
0.0, 655.35
0.0, 655.35
1.0, 2.00 |
The index is used for download, and the touch speed is used in simulation. The other values are not used. Clearance schedules specify the weld gun tip clearances and part thicknesses. They are created automatically from the clearance file “CLEARNCE.DAT” (DX100) or "SGCLARNC.DAT (DX200) when present in the same folder with the program file selected for upload. The profile is named CLF#(<index>) to match the way the schedules are referenced on the spot instruction. They can also be created manually from the command “Applicative Profile”. Table 3. Example CLF applicative profile | Parameter | Example Value | Default Value | Measure | | Index | 1 | 1 | Integer | | Moving | 1 | 1 | Integer | | Upper Tip | 20.00mm | 100mm | Length | | Lower Tip | 15.00mm | 100mm | Length | | Thickness | 2.0mm | 0mm | Length | CLEARNCE.DAT is a file that can be exported from Motoman NX100 and DX100 controllers. It has the same format for both controllers. DX200 uses file SGCLARNC.DAT. | DX100 or NX100 CLEARNCE.DAT | DX200 SGCLARNC.DAT
|
|---|
//CLEARNCE 1
1
20.000, 15.000
2.000 | //SGCLARNC 1
1
10.000, 15.000
1.000,4.000
2.500 |
The index is used for download, and the upper tip, lower tip, and thickness parameters are used in simulation. The other values are not used. Weld Delay schedules specify weld times. They are created automatically from the file “WDELAY.SCD” when present in the same folder with the program file selected for upload. The profile is named WTM=<index> to match the way the schedules are referenced on the spot instruction. They can also be created manually from the command “Applicative Profile”. | Parameter | Example Value | Default Value | Measure | | Index | 1 | 1 | Integer | | Weld Delay | 0.44s | 0s | Time |
The file “WDELAY.SCD” is not a file that can be exported from Motoman controllers. You must create this file based on the weld controller’s schedule files because those files are not robot controller-specific, and depend on the welder controller. This is a text file using the same encoding as the JBI files, and is a comma delimited list. The format has one schedule per line. Any number of lines can be in the file. The time is in seconds. Index, Time(sec) The following is a sample file with 3 schedules: 1,0.5
2,0.25
3,0.0 - SVSPOT and SVSPOTMOV Instructions
The upload and download behavior of SVSPOT
and SVSPOTMOV is linked to the applicative profiles created from
uploading the SPRESS.CND (SGPRS.CND), CLEARNCE.DAT (SGCLARNC.DAT) and WDELAY.SCD files with
the spot profile, so that the uploaded values are used in
simulation. Other spot profile parameters are also configured
with the appropriate values.
If any of the SPRESS.CND (SGPRS.CND), CLEARNCE.DAT (SGCLARNC.DAT) or
WDELAY.SCD files are not present during upload, the spot profile
is created with default values for these profiles.
For most cases, the SVSPOT and
SVSPOTMOV instructions are automatically generated during download
based on the parameters in the spot profile. In these cases,
the spot profile will also be configured during upload so that
simulation with and without RRS is as accurate as possible. In
less common cases, you can override the auto
generation feature and specify the exact SVSPOT or SVSPOTMOV syntax
in the spot profile name.
The following table lists all of the known arguments to
SVSPOT and SVSPOTMOV instructions used in the XRC, NX100 and DX100
controllers. The parameters that are used in simulation are GUN#,
PRESS#, WTM, CLF#, PLIN and PLOUT. WST and WGO do not impact
simulation but are commonly used. This table describes any
limitations regarding auto generation of the instruction
during download and simulation support. Table 4. Motoman spot instruction options | Measure | Used in SVSPOT or SVSPOTMOV | Specify for each gun? | Optional? | Can be set to Variable? | Meaning | Supported for Auto Generation / Simulation | | GUN# | Integer | Both | Yes | No | Yes | | Only if value is 1 or 2 | | PRESS# | Integer | Both | Yes | Yes | Yes | Pressure schedule (SPRESS) | Only as Integer and cannot be omitted. | | WTM | Integer | Both | Yes | No | Yes | Weld condition schedule (WDELAY) | Only as Integer. | | WST | Integer | Both | Yes | Yes | Yes | Start timing | Full support / not used in simulation | | WP | Double (kgf?) | Both | Yes | Yes | No | Can specify pressure directly instead of PRESS# schedule. May only be available for NX100. | No | | WGO | Integer | Both | Yes | Yes | Yes | Weld group output | Full Support / not used in simulation | | BWS | Double (mm?) | SVSPOT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Gun stroke value for welding start | No | | CLF# | Integer | SVSPOTMOV | NA - Only available for 1 gun. | No | No | Clearance schedule (CLEARANCE) - | Full Support | | PLIN | Integer | SVSPOTMOV | No | Yes | Yes | PL for move to clearance position | Full Support / not supported for simulation if value is a variable | | PLOUT | Integer | SVSPOTMOV | No | Yes | Yes | PL for move from weld position | Full Support / not supported for simulation if value is a variable |
- Auto Generation of Instruction
By default, the SVSPOT or SVSPOTMOV
instructions are automatically generated. In cases where an
instruction cannot be automatically generated, the parameter "use
profile name for instruction" can be set to "true" on the
"Controller Parameters" tab page of the spot profile. When this
value is true, the spot profile name is copied as-is to the job during download. If the spot profile name is not valid Motoman syntax, a
warning is displayed. The spot profile name is always set to
the instruction text during upload.
This value is set to false during upload
unless the uploaded instruction is not supported for automatic
generation.
The value is set to true for all
existing spot profiles.
- SVSPOT vs SVSPOTMOV
SVSPOT is a servo welding instruction and
does not move the robot. SVSPOTMOV is a compound instruction which
includes moving the robot to a clearance position, to the weld
position, performing the welding, and finally back to the clearance
position.
During upload, an SVSPOT instruction is
combined with the previous move to form the spot
operation.
Both instructions are configured with the
"pressure start" and "pressure end" moves enabled. An SVSPOT is
configured with the stationary tip clearance for these moves as 0
(the tip is touching the metal). The moving tip clearance is set to
be abs(GunPosition-GunClosePos)-partthickness. The gun position
comes from the move which precedes the SVSPOT.
For SVSPOTMOV, the instruction is configured with
the stationary tip clearance having the value from the clearance
file. See below for more details.
During download, the instruction is
downloaded as an SVSPOT if the stationary tip clearance is 0;
otherwise it is downloaded as an SVSPOTMOV.
Full support for Auto generation.
- Gun#
- If Gun# is an integer (not a variable) and is either 1 or 2, it is supported for auto generation and simulation. Gun# corresponds to the "Gun 1" and "Gun 2" check boxes in the spot profile. If both are checked this means that an SVSPOT instruction has two GUN# parameters, each followed by the options for that gun.
- PRESS#
PRESS# identifies the pressure schedule from
the SPRESS file. A PRESS# parameter is used for each
gun.
The applicative profile instance created from
the SPRESS file for this schedule number is linked to the spot
weld profile. The speed factor for "pressure weld and move" is linked to the "Touch Speed" parameter of the linked pressure
profile.
If the SPRESS file does not exist and an
existing PRESS applicative profile instance for this schedule
number exists, it is used. If none exist, a new profile
instance is created with default values and linked to the
profile.
If the PRESS# is specified as a
variable or if no PRESS#, no PRESS applicative profile is linked and the default speed factor of 100% is used. The
property "use profile name for instruction" is set to false to
disable auto generation during download.
- WTM
WTM identifies the weld condition schedule
from the WDELAY.SCD file.
The applicative profile instance created from
the WDELAY file for this schedule number is linked to the spot
weld profile. The weld delay factor for "pressure weld and move"
is linked to the "Weld Delay" parameter of the linked WDELAY
profile.
If the WDELAY.SCD file does not exist and an
existing WDELAY applicative profile instance for this schedule
number exists, it is used. If none exist, a new profile
instance is created with default values and linked to the
profile.
If WTM is specified as a variable, no WDELAY
applicative profile is linked and the default delay of 0s is used. The property "use profile name for instruction" is set to false to disable auto generation during download.
- WST and WGO
WST (weld start timing) and WGO (weld group
output) are not used in simulation. These two parameters are configurable on the controller parameters tab of the spot profile.
Different values can be set for each gun. If the value is blank, the parameter is not used for that gun. The value can be
specified as an integer or as a variable name.
Full support for auto generation.
- WP and BWS
- WP (weld pressure) and BWS (gun stroke for welding start) are not supported for simulation or automatic instruction generation. If these parameters are used, the property "use profile name for instruction" is set to true during upload.
- CLF#
The CLF# (Clearance file schedule) is only
used with SVSPOTMOV instructions. It identifies the clearance
schedule from the CLEARNCE.DAT (or SGCLARNC.DAT) file. A CLF# parameter is used for
each gun.
The applicative profile instance created from
the CLEARANCE file for this schedule number is linked to the
spot weld profile. The moving and stationary tip clearance
parameters for the pressure start and pressure end moves are
linked to the clearance profile.
If the CLEARANCE file does not exist and an
existing clearance applicative profile instance for this schedule
number exists, it is used. If none exist, a new profile
instance is created with default values and linked to the
profile.
If the CLF# is specified as a variable, no
CLEARANCE applicative profile is linked. The property "use
profile name for instruction" is set to false to disable auto
generation during download.
- PLIN and PLOUT
PLIN and PLOUT specify the accuracy profile
for the Approach Move and Pressure End Move. The appropriate
accuracy profile is set in the Approach Move and Pressure End Move during
upload based on the PL level set for these parameters. If PLIN or
PLOUT are not specified, the "no PL" accuracy profile is used.
Full support for auto generation.
- Default values for Spot Parameters
- All other spot profile parameters are set to default values. The following table summarizes the value of each spot profile parameter.
Table 5. Spot profile default values | Parameter | Measure | Specify for each gun? | Uploaded Value | | Profile Name | String | No | SVSPOT or SVSPOTMOV instruction text | | Gun Enabled | Boolean | Yes | True if GUN# present in instruction | | Joint Number | Integer | Yes | Identified from motion group. | | Gun Closed Joint Value | Double (mm) | Yes | 0 | | Approach Enabled | Boolean | No | False for SVSPOT, True for SVSPOTMOV | | Pressure Start Enabled | Boolean | No | True | | Pressure End Enabled | Boolean | No | True | | Backup Enabled | Boolean | No | False | | Approach Direction | Enum | No | +Z-Axis | | Gun Close Direction | Enum | Yes | -ve Axis | | Part Thickness | Length | No | SVSPOT - 2mm SPSPOTMOV - Link to clearance file | | Approach Moving Tip Clearance | Length | Yes | N/A | | Pressure Start Moving Tip Clearance | Length | Yes | SVSPOT - abs(AxisValue-ClosePos)-partthickness AxisValue is the servo gun's position from the preceding move SVSPOTMOV - Link to clearance profile upper tip clearance (upper = movable) | | Pressure End Moving Tip Clearance | Length | Yes | SVSPOT - abs(AxisValue-ClosePos)-partthickness AxisValue is the servo gun's position from the preceding move SVSPOTMOV - Link to clearance profile upper tip clearance (upper = movable) | | Approach/Backup Stationary Tip Clearance | Length | No | N/A | | Pressure Start Stationary Tip Clearance | Length | No | SVSPOT - 0mm SVSPOTMOV - Link to clearance profile lower tip clearance (lower = fixed) | | Pressure End Stationary Tip Clearance | Length | No | SVSPOT - 0mm SVSPOTMOV - Link to clearance profile lower tip clearance (lower = fixed) | | Approach Move Accuracy Profile | Accuracy Profile | No | SVSPOT - N/A, SVSPOTMOV - PLIN value if PLIN not specified then no PL. | | Pressure Start Accuracy Profile | Accuracy Profile | No | PL=0 | | Pressure Move Accuracy Profile | Accuracy Profile | No | PL=0 | | Pressure End Accuracy Profile | Accuracy Profile | No | SVSPOT - PL=0, SVSPOTMOV - PLOUT value. If PLOUT not specified, then no PL. | | Backup Move Accuracy Profile | Accuracy Profile | No | NA | | Pressure Start Acceleration | Percent | No | SVSPOT - 100% SVSPOTMOV - 100% | | Pressure Move Acceleration | Percent | No | 100% | | Pressure End Acceleration | Percent | No | 100% | | Backup Move Acceleration | Percent | No | NA | | Pressure Move Push Depth | Length | Yes | 1mm | | Pressure Move Speed Factor | Percent | Yes | Link to SPRESS profile | | Weld Delay | Time | Yes | Link to WDELAY profile | | Backup Move Stroke | Length | Yes | NA | | Weld time table | Profile | No | NA |
Arc WeldingThe translation of Arc welding instructions is dependent on the Arc profile and also the Motoman-specific ARCStart and ARCEnd profiles. Generally, one arc profile is associated with all arc operations for a single weld. An ARCStart profile is associated with the arc profile start section and an ARCEnd profile with the end section. You can either configure the parameters of the ARCStart/ARCEnd profile or set the profile name. The method for setting the arc profile name is as described for the spot welding scenario described above, and is the preferred method since it offers more flexibility and is the method used during upload. The exact name of the ARCStart/ARCEnd profile is copied to the program for the INFORM instruction, therefore the name should begin with ARCON or ARCOF, or contain valid INFORM syntax such as a CALL. If the current and/or voltage parameters of the ARCStart/ARCEnd profiles are non-zero, the ARCON/ARCOF instruction is automatically generated. If VoltagePercent is specified, the AVP= option is used. If VoltagePercent is not specified, the voltage parameter is used with the V= option. The following parameters are used regardless: - Speed: if the speed parameter is linked to the arc profile, it is added to the ARCON instruction unless the ARCON instruction uses the ASF parameter.
- Timer: if the timer parameter is linked to the arc profile as a delay, it is added to the ARCON/ARCOF instruction unless the instruction uses the ASF or ASE parameter.
- WeldPreStartSubRoutine*: These parameters are used to output INFORM syntax before the ARCON instruction (between the MOV* and ARCON), and should contain valid INFORM syntax. For example, you could set WeldStartSubRoutine1 to “WVON WEV#(1)” to start weaving. It is not possible to generate REFP instructions for weaving.
- WeldStartSubRoutine*: These parameters are used to output INFORM syntax in after the ARCON instruction, and should contain valid INFORM syntax.
- WeldPreEndSubRoutine*: These three parameters are used to output INFORM syntax before the ARCOF.
- WeldEndSubRoutine*: These three parameters are used to output INFORM syntax after the ARCOF. It can be set to “WVOF” to turn off weaving.
For the Weld…SubRoutine parameters, three parameters are pre-defined. If more are needed, user parameters can be added with higher indexes (e.g. WeldStartSubRoutine4). During upload, all non-simulation instructions before ARCON or ARCOF are uploaded as WeldPre…SubRoutine parameters. If simulation activities appear between the MOVL (or MOVC) and the ARCON or ARCOF instructions, the WeldPre…SubRoutine parameters are not used and V6 Comment instructions are created for ARCON or ARCOF. All instructions up to the first comment or simulation activity after the ARCON or ARCOF are uploaded as Weld…SubRoutine Parameters. If two ARCON instructions are identical but require different profile parameters, the profile name is mangled during upload. For example, the following program has two welds that are performed with identical ARC instructions, but one is using weaving: MOVL V=200
WVON WEV#(1)
ARCON ASF#(1)
MOVL V=200
ARCOF
WVOF
MOVL V=200
ARCON ASF#(1)
MOVL V=200
ARCOF In this case, two arc profiles are created: one named “ARCON ASF#(1)” and one named “ARCON ASF#(1) '1”. The ' character indicates a comment, and any characters that follow it are removed from the instruction during download. You can modify the comment to be more descriptive, if desired. Seam Search There are many ways to perform a search in INFORM. By default, the translator supports one method that uses individual REFP instructions with search routines following them. For example: | MOVL C000 V=500 | Search operation - via Profile(s): SearchData.1 | | REFP 1 C001 CALL JOB:SEARCH | Search operation -touch point 1 of 2 Profile(s): SearchData.1 | | MOVL C002 V=500 | Search operation - via Profile(s): SearchData.1 | | REFP 1 C003 CALL JOB:SEARCH CALL JOB:CALCSHFT | Search operation -touch point 2 of 2 Profile(s): SearchData.1 | | MOVL C004 V=500 | Search operation - via Profile(s): SearchData.1 | | MOVL C005 V=500 | Robot motion | | SFTON P000 MOVL C006 V=500 ARCON ASF#(1) | Arc operation (start weld)Profile(s): ArcProfile.1 | | MOVL C007 V=200 ARCOF SFTOF | Arc operation (end weld)Profile(s): ArcProfile.1 | The DELMIA applicative profile data would be defined as follows for the above program: SearchData.1 (profile of type SearchData):
refp=1
Search1SubRoutine1=”CALL JOB:SEARCH”
Search1SubRoutine2=””
Search1SubRoutine3=””
Search2SubRoutine1=”CALL JOB:SEARCH”
Search2SubRoutine2=”CALL JOB:CALCSHFT”
Search2SubRoutine3=””
Search3SubRoutine1=””
Search3SubRoutine2=””
Search3SubRoutine3=””
ShiftOnSubRoutine1=”SFTON P000”
ShiftOnSubRoutine2=””
ShiftOnSubRoutine3=””
ArcProfile.1 (profile of type ArcProfile)
Start Section Profiles:
“ARCON ASF#(1)” (profile of type ARCStart)
SearchData.1
End Section Profiles:
“ARCOF” (profile of type ARCEnd)
A specific search path is associated with a
specific arc weld by using the same search profile on the search
operations, and in the start section of the arc profile for those
arc operations. For example, the ShiftOnSubRoutine1 (SFTON) is
output before the first arc operation because the search
profile is associated with the arc profile in the start section.
The SFTOF is output after the last arc of because there was a SHFON
output at the start of the weld. It is not possible to control the
SFTOF command syntax.
You can have more control over the program by
creating V6 Comment instructions for the search sub routines and/or
shift instructions instead of setting the parameters of the
SearchData profile.
Variable Conversion
INFORM has only a limited number of
variables, and each variable is an array. DELMIA external IO, IO
defined on the robot, is mapped to one of the MOTOMAN IO
variables. DELMIA variables are mapped to INFORM variables of
either global or local scope. On upload the IO and variables are automatically created.
During download, the corresponding INFORM IO or
variable is determined from the IO address. The IO address
also is used to determine the IO index. IO addresses for IO should
be in the format XX#(Y) where XX is the IO type (OT, IN, IG, SIN,
SOUT, IGH, OGH, AO) and Y is the port number. IO address for
variables should be in the format Vxxx, where V is the MOTOMAN
variable type (B, I, D, R) and xxx is the index. For some variables,
a number can be used by itself. If the IO address is not specified,
an IO address will automatically be assigned to an unused value and
a warning is generated.
External IO must be declared of the appropriate
type in DELMIA. Group IO must be of type integer, analog IO must be
of type double, and all other IO must be of type Boolean. If the IO
address in DELMIA specifies a type that does not match, a warning
is displayed and the type is ignored. For example, if a
Boolean input has its address specified as IG#(1), then it is
downloaded as IG#(1). This may result in a JBI-file that cannot be
loaded onto a controller.
|
MOTOMAN Variable/IO
|
Variable Type
|
Direction
|
Location
|
Address
|
|
IN#(x)
|
Boolean
|
Input
|
Robot
|
IN#(x) or x
|
|
OT#(x)
|
Boolean
|
Output
|
Robot
|
OT#(x) or x
|
|
SIN#(x)
|
Boolean
|
Input
|
Robot
|
SIN#(x)
|
|
SOUT(x)
|
Boolean
|
Output
|
Robot
|
SOUT#(x)
|
|
IG#(x)
|
Integer
|
Input
|
Robot
|
IG#(x) or x
|
|
OG#(x)
|
Integer
|
Output
|
Robot
|
OG#(x) or x
|
|
IGH#(x)
|
Integer
|
Input
|
Robot
|
IGH#(x)
|
|
OGH#(x)
|
Integer
|
Output
|
Robot
|
OGH#(x)
|
|
Not Supported
|
Double
|
Input
|
Robot
|
|
|
AO#(x)
|
Double
|
Output
|
Robot
|
AO#(x) or x
|
|
Not Supported
|
Boolean
|
Local Variable
|
Robot
|
Bxxx or x
|
|
Bxxx
|
Integer
|
Local Variable
|
Robot
|
Bxxx or x
|
|
Ixxx
|
Integer
|
Local Variable
|
Robot
|
Ixxx
|
|
Dxxx
|
Integer
|
Local Variable
|
Robot
|
Dxxx
|
|
Rxxx
|
Double
|
Local Variable
|
Robot
|
Rxxx or x
|
|
Sxxx
|
String
|
Local Variable
|
Robot
|
Sxxx or x
|
|
Pxxx
|
Not supported
|
|
|
|
|
BPxxx
|
Not supported
|
|
|
|
|
EXxxx
|
Not supported
|
|
|
|
|
LBxxx
|
Boolean
|
Local Variable
|
Procedure
|
Bxxx or x
|
|
LBxxx
|
Integer
|
Local Variable
|
Procedure
|
LBxxx or x
|
|
LIxxx
|
Integer
|
Local Variable
|
Procedure
|
LIxxx
|
|
LDxxx
|
Integer
|
Local Variable
|
Procedure
|
LDxxx
|
|
LRxxx
|
Double
|
Local Variable
|
Procedure
|
LRxxx or x
|
|
LSxxx
|
String
|
Local Variable
|
Procedure
|
LSxxx or x
|
|
LPxxx
|
Not supported
|
|
|
|
|
LBPxxx
|
Not supported
|
|
|
|
|
LEXxxx
|
Not supported
|
|
|
|
|
Not Supported
|
Unknown
|
Any
|
Any
|
|
|
Not Supported
|
Any
|
Input, Output, InOut, Unknown
|
Procedure
|
|
|
Not supported
[1]
|
Any Type
|
Constant
|
Robot or Procedure
|
|
[1] Constants are replaced by their literal value during download.
The main limitations during upload are: - Array indexing is not supported (e.g. B[B001])
- Position arithmetic is not supported
Data Conversion
INFORM uses only the least significant bit of integers for determining if a signals is true or false. For example in the instruction "DOUT #IN(1) B000" if B000 is 2 (0b00000010) then the value is OFF because the last bit is 0. When converting from an integer to a Boolean, the expression B000 AND 1 is used (instead of B000<>0).
Parameters
The Motoman Controller Profile is used to control the translation, and contains global options for configuring how the translation will occur.
| Parameter Name | Usage | Default Value | Description | | DeviceID | Download & Upload | "" | The parameter is the Station Number in the JBI program. It supersedes the value set in aux device Instance Title. | | PulseValue* | Download & Upload | 1 | The pulses per 360 degress for rotational joints. Pulses per mm for linear joints. | | ZeroValue* | Download & Upload | 0 | The pulse count when the joint value is 0 degrees or 0 mm. |
Motoman Device Parameters The pulse count and zero offset parameters are
set from a dedicated command accessed from the contextual menu of
the motion controller.
By default, the pulse counts and zero offsets
are set to the correct values for all Motoman robots. For aux
devices, the pulse count is set to 1 and zero offset to 0 by
default for all joints. The values are editable.
Motoman Task Profile An applicative profile can be associated with each task. A new applicative profile containing Motoman task properties is created, and has the values shown in the following table. You can assign a Motoman Task Profile to a task in teach from the context menu after right-clicking on the task. | Parameter Name | Default Value | Description | | DownloadTarget | Pulse | This parameter takes the values of "Pulse" and "Cartesian" and downloads pulse or Cartesian values in the program. | | DownloadTargetBC | Pulse | This parameter takes the values of "Pulse" and "Cartesian" and downloads pulse or Cartesian values in the program for BC axes. | | Header_Attr | "SC,RW" | Defines job attributes. If DownloadTarget is "Cartesian", "RJ" will be added to this value. |
The translator creates the profile on upload based on the JBI-file and uses these parameters on download when generating the JBI-file. If no profile is set on download, the default values are used. Motoman Controller Parameters Parameters that apply to the Motoman controller are available in a dialog box accessed from the contextual menu of the resource motion controller. All parameter values are editable. | Parameter Name | Usage | Default Value | Description | | BaseGroup | Download | 1 | This parameter determines if the rail axes is downloaded in the same group as the robot axes for moves and in the program header. The default places rail axes into the same group. | | BaseNumber | Download | 1 | This parameter determines the number to use for the base axes. For example BS1 or BS2. | | CommentWaitSignal | Upload | TRUE | By default, WAIT IO statements are commented out during upload. If this is not desired, set this parameter to "false". | | MotomanDefaultAccuracy | Upload | 63 | This parameter specifies the positioning accuracy of the robot for linear/circular moves which do not have a PL specified. | | MotomanDefaultJntAccuracy | Upload | 63 | This parameter specifies the positioning accuracy of the robot for joint moves which do not have a PL specified. | | OutputTools | Download | FALSE | Generate file TOOL.CND and UFRAME.CND if true. | | PartGrabbed | Upload | "" | The name of the part to be grabbed by all grab instructions on upload. | | ProgramFileEncoding | Download & Upload | UTF-8 | The parameter specifies the encoding of the robot program to be uploaded or to be created. Commonly used are ISO-8859-1 (West European), and SHIFT_JIS (Japanese) | | StationGroup | Download | 1 | This parameter determines if the positioner axes is downloaded in the same group as the robot axes for moves and in the program header. The default places positioner axes into the same group. | | StationNumber | Download | 1 | This parameter determines the number to use for the station. For example ST1 or ST2. |
| DefaultPartThickness |
Download & Upload |
0 |
For Air gun Spot weld, you can set Part Thickness. |
XRC Controllers have an additional controller parameter. | Parameter Name | Usage | Default Value | Description | | XRCPositionLevel | Download & Upload | 4 | The parameter specifies the number of position levels of XRC program(4, 8). For all other controller types this parameter is not used. - MRC has 4
- NX100 has 8
- DX100 has 8
This parameter is no longer used to determine the TOOL.CND and UFRAME.CND file format. The controller version selected in the download command is used. |
Motoman Motion Profile Parameter A parameter named "UseVE" on the motion profile is used to specify the download of speed option VE for linear motion with external axis. This parameter is automatically set to "true" when uploading a motion instruction with speed option VE. Motoman Accuracy ParameterA parameter named “Mode” on the accuracy profile is used to set the Motoman accuracy mode. Motoman supports 4 accuracy modes: PL, CR, SPDL, and no PL. PL and CR are different ways of specifying distance based accuracy. - PL is “Position Level” and on the Motoman controller each level is assigned an accuracy distance. PL=0 is always flyby off. The Index parameter is used to determine the position level. For example PL=1 is normally accuracy distance = 25mm.
MOVL C000 V=100 PL=2 - CR is “Cornering radius” and allows the accuracy distance to be specified in the Motoman motion instruction (in millimeters).
MOVL C000 V=100 CR=60 - SPDL is “speed level”, and is a special Motoman feature not supported by DELMIA default motion planning.
MOVL C000 V=100 SPDL=0 - None is used for not specifying any accuracy on the motion. When no accuracy is specified the motorman controller uses some speed-based rounding.
MOVL C000 V=100
The accuracy mode is automatically enabled for new accuracy profiles and has a default value of "PL". Valid values for the parameter are "PL", "CR", "SPDL", or "None". Existing accuracy profiles have the accuracy mode detected from the profile parameters using the logic currently used by Realistic Robot Simulation and Robot Programming. - Motoman DX100 RCONF
Motoman made a change in their RCONF values for the DX100 controller. For the XRC and NX100 controllers, the flip/no flip parameter (1st value) is based on the R-axis position (joint 4). For the DX100 controller, the parameter is based on the B-axis position (joint 5). The translator outputs the new RCONF format if the DX100 controller version is selected. - Motoman DX100 Format Changes
The Motoman JBI file format for DX100 includes higher precision numbers for angles.
| Controller Version |
Description |
| NX100 |
C00000=0.000,0.000,0.000,0.00,0.00,0.00 |
| DX100 |
C00000=0.000,0.000,0.000,0.0000,0.0000,0.0000 |
- Enhanced REFP support
Motoman REFP instructions are reference
points. The robot does not move the position defined in the REFP
instruction, it is stored for later use. REFP instructions are
commonly used for arc welding seam search instructions. All REFP instructions are uploaded as seam search instructions, and
the only way to create a REFP instruction during download is from a
seam search instruction.
REFP 1 C00005 EC00005
REFP instructions are also used for arc
welding oscillation points, and can be used for other purposes.
A REFP is a position instruction (joint
values or Cartesian), but the robot does not move to it. The closest
V6 equivalent to this is a robot motion that does not get executed.
This can be accomplished by creating an "if(false) RobotMotion"
logic structure. Any robot motion inside the "then" sequence of an "if" statement where the condition is set to "false" is downloaded as a REFP. The REFP index number comes from the applicative profile "Motoman REFP Profile". | Parameter Name | Default Value | Description | | REFPIndex | 1 | The REFP index number |
If no REFP profile has been assigned to the
motion, the REFP index will be set to 1.
During upload, most REFP instructions are uploaded as search instructions. However, if the REFP instruction
is inside an arc sequence (between the arc start move and the
arc end move), it is an oscillation point and the "if(false)"
logic is created for this position along with the REFP
profile.
The following example program
uses REFP instructions for oscillation points:
| Motoman Instruction | DELMIA equivalent | | MOVJ C00000 EC00000 VJ=100.00 | Regular move | | MOVJ C00001 EC00001 VJ=100.00 | Regular move | | MOVJ C00002 EC00002 VJ=100.00 | Regular move | | MOVJ C00003 EC00003 VJ=100.00 | Regular move | | MOVJ C00004 EC00004 VJ=100.00 | Arc Operation (arc start). Arc profile that has the a Motoman Arc Start profile in the start section and a Arc End profile in the end section. This profile is assigned to all arc operations for the arc path. | | REFP 1 C00005 EC00005 | Weave Point - to be upload as a robot motion inside an if instruction with the condition "false" so the motion is never executed. The Motoman REFP profile assigned to the motion has the index set to 1. | | REFP 2 C00006 EC00006 | Weave Point- to be upload as a robot motion inside an if instruction with the condition "false" so the motion is never executed. The Motoman REFP profile assigned to the motion has the index set to 2. | | WVON WEV#(10) | Turn on Weaving -parameter WeldPreStartSubRoutine1 of the Motoman Arc Start profile is set to this value on upload | | ARCON ASF#(17) | Turn on welding - Motoman Arc Start profile name is set to this value. | | MOVL C00007 EC00007 V=4.2 | Arc Operation (arc end) | | WVOF | Turn off weaving - parameter WeldEndSubRoutine1 of the Motoman Arc End Profile is set to this value. | | ARCOF AEF#(12) | Turn of welding - Motoman Arc End profile name is set to this value. | | MOVJ C00008 EC00008 VJ=100.00 | Regular move. |
[1] DX100, DX200, NX100, XRC, YRC1000, MRC, ERC, FD100, and INFORM are or may be
trademarks or registered trademarks of Motoman/Yaskawa or its subsidiaries in the U.S. and in
other countries.
|


