Using B.I. Essentials | ||
| ||
-
From the
Tools section of the action bar, select
B.I. Essentials
 .
The following B.I. enable you to reveal attributes specific to the Robot Surface Simulation app:
.
The following B.I. enable you to reveal attributes specific to the Robot Surface Simulation app:- Detailing Status
- Resource Monitoring and Status
- Resulting Product Usage
- Track Link Status
-
Select Detailing Status from the list.
Colors are applied to all objects in the tree and in the 3D area accordingly. - In the tree or in the work area, select an object to display detailed information.
-
To select a
B.I. Essentials value, hover over the value and click
the plus sign (+) that appears.
Targets that are assigned, and are programmed with an operation:
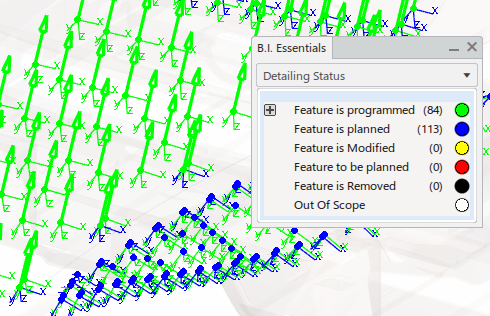
Targets that are assigned, but are not yet programmed with an operation:

-
At the right edge of the work area,
click Fastener Details
 .
.
The Fastener Details dialog box appears.
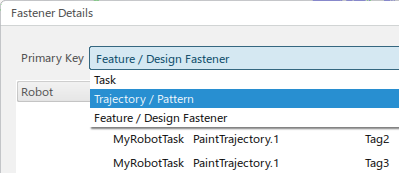
The Primary Key list allows you to select a view that is based on Task, Trajectory/Pattern, or Feature/DesignFastener.
-
Select Feature/DesignFastener.
The resulting table provides columns for:
- Robot
- Task
- Trajectory/Pattern
- Tag/Manufacturing Fastener
- Feature/DesignFastener
- Displacement, Distance Offset, Angular Offset between Design fasteners and Manufacturing welds.
-
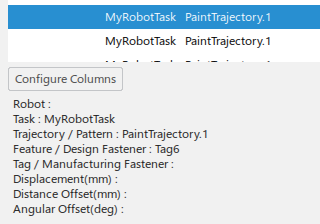
Select a row in the table to highlight it and display a summary of the row content.
-
Click Configure Columns.
The Configure Columns dialog box appears.
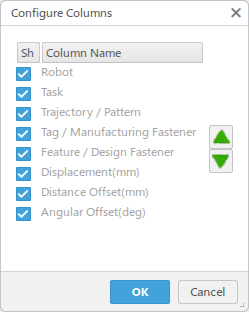
You can select which columns appear in the table, as well as select a Column Name and move it up or down in the list.
-
Click Export.
The table view is exported to an Excel document. The Excel document is stored as VPM document in the database and linked to the ASO if ASO is a manufacturing cell. If the ASO is not a manufacturing cell, it is linked to the parent manufacturing cell of the ASO.