- From the Digitized Data section of the action bar, click Mesh Smoothing
 .
. - Select a mesh with manifold edges.
- Select the type of smoothing:
- Set Coefficient to balance the effect of the new theoretical position in comparison with the original position. It varies from 0 (the vertex is not moved) to 1 (the vertex is moved to the computed position).
- Select Max Deviation check box to keep the displacement under the set value.
The deviation is the distance between a vertex and its initial position (not between its current position and that of the previous iteration). Therefore, if you want to control the maximum deviation, select the Max Deviation check box before the first Apply (it is no longer available after the first Apply).
Note:
For a better appreciation of the quality of the intermediate meshes, the meshes are displayed in Flat Shading inside Mesh Smoothing. In addition, for each step the maximum and the mean
deviations (distances between a vertex and its initial position) are displayed in the dialog box.
- Click Apply.
Mesh Smoothing is iterative: Click Apply again to smooth the proposed mesh.
A new mesh is computed.
A Smoothing.x element is created, the original mesh is sent to the No Show.
Example of the same part, with different parameters:
- Original part in Smooth Shading:
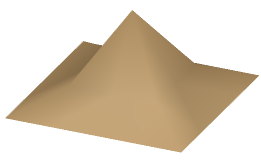
- Original part as you enterMesh Smoothing, i.e. in Flat Shading:
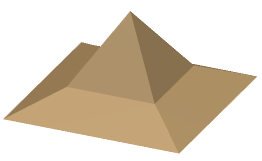
- Single effect, in Flat Shading:

- Single effect, in Smooth Shading (after exiting Mesh Smoothing):

- Dual effect, in Flat Shading:

- Dual effect, in Smooth Shading (after exiting Mesh Smoothing):






