Collections of Lists
EKL provides a unique collection object called List that can be
used to handle lists, arrays and structures. There is no type checking in
collections, they can contain any kind of object or value, including NULL.
There are lot of methods to fill and manipulate such collections.
To access an element of the list, you can use either the
GetItem(<index>) method or the [<index>]
access.
Some functions/methods use EKL expressions to provide query/filter
functionality based on complex criteria
Example 1
Let l, l2 (List)
l = List(1, 2, 3, 4)
l2 = l +l // l contains 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4
let i (integer)
i = l2[3] // equivalent to i = l2->GetItem(3)
let l3 (List)
l3.Append(List(2, 3, 5, 7))
l3.Append(List(11, 13, 17, 19))
i = l3[2][3] // i = 17 : second list, third element
// lst being a list containing different wireframe geometries including surfaces
let filtered (List)
filtered = lst.Filter(“Surface” , “area(x) > 10mm2”)
// filtered list contains only surfaces whose area is stricly superior to 10mm2
Example 2
let l, l2 (List)
l2.Init(10, 1)
l.Append(l2)
l2.Init(10, 2)
Notify("", l[1][10]) // will show 1
l[1][1] = 3
l[1][5] = 4
Notify("# #", l[1][1], l[1][5]) // will show 3 4
List Type
Example
Let lst (List)
lst.Append("car")
Message("#", lst[1])
lst[1] = "wheel"
List Functions
List functions are used to manage lists of parameters, pads
... They enable you to create lists, add items to the list, remove items from
the list, retrieve values from the list, move elements of the list to another
position, filter, and to copy the content of a list into another one. These
functions are available in the Formula, the Rule and in the Action editors.
+
Operator enabling you to add two lists and to return a third
one. Adding two lists means concatenating the elements of the two lists and
affecting the result to the returned list. The elements of the first list will
be at the beginning of the resulting list. The order of the elements is kept.
This operator works on list of
objects (persistent or not) or on list of values (persistent or not). If the
operation required is not feasible (for example, trying to fill a persistent
list with a non persistent value), evaluation errors are raised. There is no
simplification of the list (an element can be there twice after the
operation).
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
List1
|
In
|
Yes
|
List
|
|
List2
|
In
|
Yes
|
List
|
|
Example
Let L1(List)
Let L2(List)
Let L3(List)
L3=L2+L1
Copy
Function used to copy the content of a list and paste it in
another list.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
List
|
In
|
Yes
|
List
|
|
List
Function used to create a list.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Next
|
In
|
No
|
ObjectType
|
|
Example
let L1(List)
L1= List(Item1,Item2,Item3)
List Methods
Feature.ListAttributeNames()
Method used to return a list of strings corresponding to the
name of the available attributes for a given object. The generated list depends
not only on the Object Type but also on the object itself. That is to say, this
method may return attributes that have been added dynamically to the object,
through the Parameter Explorer command or through the
SetAttribute method.
When adding integer or string attributes to faces, this method
returns the attributes names and the face default values: the Color, Name,
UserInfoComment and the integers Layer, Transparency.
Signature
Feature.ListAttributeNames(TypeFilter: String, DynamicOnly:
Boolean) : List
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
TypeFilter
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
|
DynamicOnly
|
In
|
Yes
|
Boolean
|
|
Example 1
let x(List)
let s=""
let sfinal = ""
x = Product -> ListAttributeNames ("String",false)
for s in x
{
sfinal = sfinal + Product -> GetAttributeString (s)
}
Example 2
let attributes (List)
let pad(GeometricFeature)
let faces (List)
let face (CATFace)
set pad=PartBody\Pad.1
faces = pad->GetSubElements(2)
set face = faces[1]
/* Create 2 attributes on a pad face */
face->SetAttributeInteger("IntegerAttr",5) /* Creates an integer attribute of value 5 */
face->SetAttributeString("StringAttr","Value1") /* Creates an integer attribute of value Value1 */
/* Modify attribute values */
face->SetAttributeInteger("IntegerAttr",9)
face->SetAttributeString("StringAttr","NewValue")
/* Read and display attribute values */
Message("IntegerAttr " , face->GetAttributeInteger("IntegerAttr"))
Message("AttrString " , face->GetAttributeString("StringAttr"))
/* List the attributes */
attributes=face->ListAttributeNames("String",false)
attributes=face->ListAttributeNames("Integer",false)
List.AddItem()
Method used to add an item to the list. If the index is
equal to 0, the new item is added at the end of the list. If the index is equal
to 1, the new item is inserted into the list at the location indicated by the
index, meaning that the item is replaced with the new one and is therefore
removed from the list.
It is recommended to use the
InsertItem method.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Object
|
In
|
Yes
|
ObjectType
|
|
Index
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
|
Example
let list (List)
list -> AddItem(PartBody\Hole.2 ,1)
list -> AddItem(PartBodyHole.3 ,2)
Message("#",list.Size())
List.Append()
Method used to add an item at the end of the list.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Object
|
In
|
Yes
|
ObjectType
|
Object to insert into the list.
|
List.Apply()
Method used to apply a given expression to the objects of a
list that are of a given type.In this expression, the element of the list is
represented by a variable named x.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Type
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
|
Expression
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
|
Example
//Finds all rule bases and executes them
//P being Part Feature
/* Finding a value */
let L (List)
L = P -> Query("Rulebase","")
L -> Apply ("RuleBase","x -> Update()")
List.Compute()
Function used to compute the result of an operation
performed all the elements of the list. It is available for Actions, Reactions
and in
Quality Rules Reuse.
There are two usages for this method:
- On lists of values, it
simply computes an operation on the values (+, min, max)
- On list of objects, it
will compute an operation on results of expressions on the object.
Signature
List.Compute(Operation: String, Type: String,
Expression: String, Result: UndefinedType)
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Operation
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
|
Type
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
|
Expression
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
|
Result
|
Out
|
Yes
|
UndefinedType
|
|
Example 1
List.1 ->Compute("+","","",Length.1)
The example above sums all the values of the list:
Where:
- List.1 is the name of
the list on which the calculation will be performed
- + is the operator
used. (Supported operators are: +, min, and max.)
- The first string must
be empty to indicate that we work on list of values.
- The second String must
also be empty when working on list of values.
- Length.1 is the output
parameter.
Example 2
List.1 -> Compute("+","Hole","x.Diameter+x.Depth",Length.1)
The example above sums all the addition of the diameter and the
depth of all holes in the list. Where:
- List.1 is the name of
the list on which the calculation will be performed.
- + is the operator
used. (Supported operators are: +, min, and max.)
- The first string
contains the expected type of the objects of the list (in this case, it is a
list of holes).
- The second String
contains a formula that will be computed on each element of the list (holes in
this case) and that will return a value. In this expression the variable x is
used to represent the element in the list. One can then access its attributes
for instance.
Length.1 is the output parameter.
List.Extract()
Method used to extract the items of a given type.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Type
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Knowledge types considered by the
extract function meaning that the list is first filtered to take only elements
of a given type into account. The type can be a value type or an object type.
|
TypeOutput
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Type of the object produced by the
Extract method. The output list contains
the objects of this given type. The type can be a value type or an object type.
|
Expression
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Knowledge rule expression with two
arguments, x of type
Type and y of type
TypeOutput. The expression must valuates y
depending on the expression computed on x. The expression can use the
if,
else,
for,
let keywords like in a rule.
|
Example
Let L1(List)
Let L2(List)
...
L2=L1 -> Extract("Hole","LENGTH","y=x.Diameter+x.Depth")
In this example, we produce a list in output that is the
extraction of the sum of the diameter and the depth of the holes in the list.
List.Filter()
Method used to filter a list of objects by extracting the
objects that fulfill a Boolean expression.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Type
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Type of the objects that the user wants
to extract (it can be "". In this case, no filtering is done on types).
|
Condition
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Boolean expression that must fulfill
the objects of this given type. In this expression "x" is used as the variable
name of type TypeName. This string can be equal to "". In this case, no
expression is checked.
|
Example
I = (List -> Filter("Hole","x.Diameter > 3mm")).Size()
I = (List -> Filter("Hole","")).Size()
List.GetItem()
Method used to retrieve a value/item from the list. (Index
from 1).
Signature
List.GetItem(Index: Integer) : UndefinedType
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Index
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
|
List.IndexOf()
Method used to return the first index of a list item. The
item is searched for from the start index.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Element
|
In
|
Yes
|
ObjectType
|
|
StartIndex
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
|
List.IndexOf()
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Element
|
In
|
Yes
|
ObjectType
|
|
StartIndex
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
|
List.InsertItem()
Method used to insert an item into the list.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Object
|
In
|
Yes
|
ObjectType
|
Object to insert into the list.
|
Index
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
Location of the object to be inserted
into the list (Starts at 1).
|
List.Intersect()
Method used to get the intersection of two lists of objects. Optional criteria can be used to get only objects that are in both lists and that respect the condition.
Arguments
| Name | Input / Output | Required? | Type | Comment |
|---|
List1 | Out | Yes | List | List to which the intersection is applied. | List2 | In | Yes | List | - |
Type | In | No | String | Both lists are filtered to take only elements of a given type into account. The type can be a value type or an object type. |
Expression | In | No | String | Boolean expression that must fulfill the objects of this given type. In this expression “x” is used as the variable name of Type type. The expression can use the following operators:- mathematical: +, /, etc...
- comparison: ==, >, ...
- logical: AND, OR, ...
This string can be equal to "". In this case, no expression is checked. |
ExampleLet L1, L2, L3 (List)
L3 = L1.Intersect(L2, “HOle”, “x.Diameter == 15mm”)
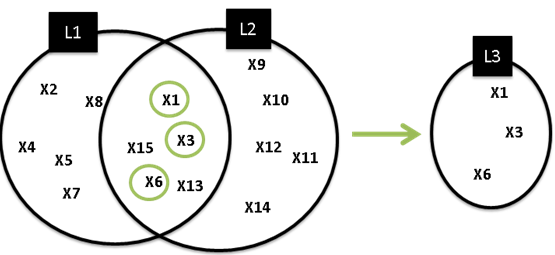 Note:
L3 = L1.Intersect(L2) generates a result list containing {X1, X3, X6, X13, X15}. If the result is not refined using a criterion, the result is a simple intersection (with common elements) of the two lists.
List.Junction()
Method used to find elements of a list that verifies a criterion between elements of this list and elements of another list.
Arguments
| Name | Input / Output | Required? | Type | Comment |
|---|
List1 | In | Yes | List | List to which the junction is applied. | List2 | In | Yes | List | Second list needed to apply junction functionality on a list. |
TypeList1 | In | Yes | String | First list is filtered to take only elements of a given type into account. The type can be a value type or an object type. |
TypeList2 | In | Yes | String | Second list is filtered to take only elements of a given type into account. The type can be a value type or an object type. |
Expression | In | Yes | String | Knowledge rule expression with two arguments: - x of
TypeList1 type for the first list - y of
TypeList2 type for the second list
The expression must be valuated depending on x and y under the form x.att == y.att. The expression can use the following operators: - mathematical: +, /, etc...
- comparison: ==, >, ...
- logical: AND, OR, ...
The expression cannot be "". | TypeList3 | Out | Yes | List | Output list. |
ExampleLet L1, L2n L3 (List)
L3 = L1.Junction(L2, “Hole”, “Hole”, “x.Diameter == y.Depth AND y.Diameter > 10mm”)
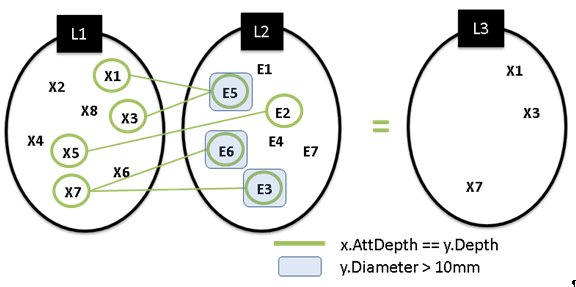
In the above example, the result returned is a list of the Holes (Xi) of L1 whose diameter is equal to the Depth of a Hole (Ei) of L2 and only if the hole diameter is greater than 10mm. List.RemoveAll()
Method used to empty the list.
Signature
List.RemoveAll()
List.RemoveDuplicates()
Method used to modify the content of the list by extracting
the duplicated elements.
When
the list references objects (features and parameters), it removes the
duplicated reference to the objects. When the list references volatile values,
it removes the equivalent values.
Note:
This method does not have the same behavior on lists of
parameters and on lists of values. On Lists of parameters, it removes the
parameter that are present twice in the list. On lists of values, it removes
the values that have the same value.
Signature
List.RemoveDuplicates()
List.RemoveItem()
Method used to remove an item from the
list.Index
is the location of the object to be removed in the list. The
index starts at 1.
Signature
List.RemoveItem(Index: Integer)
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Index
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
|
Note:
To view an example, import the
Sample_extra.3dxml file located in
win_b64\startup\Knowledgeware\PKT Samples\Sapmle1
in the installation folder.
List.ReorderItem()
Method used to move an element of the list referenced by its
position to a new position. The position starts at 1.
Signature
List.ReorderItem(Current: Integer, Target: Integer) : UndefinedType
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Current
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
|
Target
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
|
List.SetItem()
Method used to replace an item in the list.
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Object
|
In
|
Yes
|
ObjectType
|
Object to insert into the list.
|
Index
|
In
|
Yes
|
Integer
|
Location of the object to be replaced
in the list. In this case, the object to be replaced is deleted. Index starts
at 1.
|
List.Size()
Method used to return the number of items contained in the
list.
List.Sort()
Method used to sort lists. It operates the sort based on a
criteria that corresponds to an extraction (see previous method).
Arguments
| Name
|
Input / Output
|
Required?
|
Type
|
Comment
|
Operator
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Accepted values are "<", ">".
These operators are used to sort the list.
|
Type
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Type of the list objects taken into
account. It can be a type of value or a type of object. The type must be
indicated because it is used to validate the expression. All objects of the
list should be inheriting from this type.
|
TypeOutput
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Type of the object produced using the
sort method. The output list contains
objects of this given type. The type can only be a value type. It can be a Real
or a String.
|
Expression
|
In
|
Yes
|
String
|
Knowledge rule expression with two
arguments, x of type
Type and y of type
TypeOutput. The expression must valuate y
depending on the expression computed on x. The expression can the
if,
else,
for,
let keywords like in a rule.The expression
can be empty if the list is a list of values.
|
- If the operator is not
equal to ">" or "<", an evaluation error is raised.
- If Type or
TypeOutput is not a recognized type, an
evaluation error is raised.
- This method does not
operate on the list itself but produces the sorted list in output. As a
consequence, to solve the problem, we should have created a new List and
valuated it with:
NewList = FilletRadius ->
Sort(>,LENGTH,LENGTH,)
Example
NewList = HoleList -> Sort(">","LENGTH","LENGTH","y=x.Diameter") This example sorts a list of holes based on their diameter.
List.Split()
Method used to split a list in more than one list depending on criteria.
Arguments
| Name | Input / Output | Required? | Type | Comment |
|---|
List1 | In | Yes | List | List to which the split is applied. | Type | In | Yes | String | The list is filtered to take only elements of a given type into account. The type can be a value type or an object type. |
ReturnType | In | Yes | String | Type of the returned values. For example, a length will be returned in mm. |
Expression | In | Yes | String | Knowledge rule expression with two arguments: x of Type type of the list y of ReturnType type that specifies the return type of the attribute The expression must be valuated depending on x and y under the form: y = x.att. Expression should not be "". |
ExampleLet L1, L3 (List) //we declare L3 as a list, but it is good to remember that L3 will be a list of lists.
L3 = L1.Split(“Hole”, “Length”, “y = x.Diameter”)
| L1 | L3 | | |
|---|
| Reference | Diameter (attribute of length type) | 10 | 12 | 8 | 6 | | ListB | ListC | ListD | ListE | | Hole1 | 10 | X | | | | | Hole2 | 12 | | X | | | | Hole3 | 8 | | | X | | | Hole4 | 12 | | X | | | | Hole5 | 10 | X | | | | | Hole6 | 6 | | | | X |
Note:
For understanding purposes, find below the expected result showing the contents of each list. ListA, ListB, ListC, ListD and ListE do not need to be typed in the script.L1 = {Hole1, Hole2, Hole3, Hole4, Hole5, Hole6}
L3 = {ListA, ListB, ListC, ListD, ListE}
ListA = {10, 12, 8, 6}
ListB = {Hole1, Hole5}
ListC = {Hole2, Hole4}
ListD = {Hole3}
ListE = {Hole6}The first list of L3 (ListA) contains the values of the diameters. Its size is equal to the number of splits (the number of lists that contains elements with the same attribute value). ListA is sorted according to the split results (ListB, ListC, ListD and ListE). Other lists contain objects with the same diameter value.
List.Subtract()
Method used to remove objects from a list depending on another list.
Arguments
| Name | Input / Output | Required? | Type | Comment |
|---|
List1 | In | Yes | List | List to which the subtraction is applied. | List2 | In | Yes | List | - |
Type | In | No | String | Both lists are filtered to take only elements of a given type into account. The type can be a value type or an object type. |
Expression | In | No | String | Boolean expression that must fulfill the objects of this given type. In this expression "x" is used as the variable name of Type type. The expression can use the following operators: - mathematical: +, /, etc...
- comparison: ==, >, ...
- logical: AND, OR, ...
This string can be equal to "". In this case, no expression is checked. |
ExampleLet L1, L2, L3 (List)
L3 = L1.Subtract(L2, “Hole”, “x.Diameter == 15mm”)
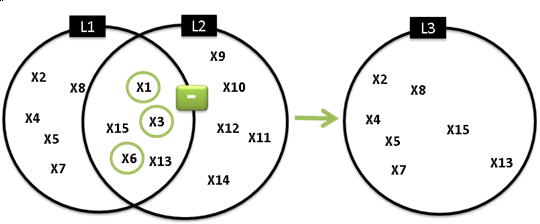 Note:
The result of L3=L1.Subtract(L2) is the same as the "-" operator.
|


