Reading and Writing XML Documents | ||
| ||
- XMLElement (<a> […] </a>): represents the structure of the XML nodes on which you can access all children nodes using the
Childrenattribute. - XMLComment (), : you can access the content of the comment using the
Textattribute - XMLText (<a> text </a>): you can access the content of the text using the
Textattribute - XMLCData (<![CDATA[...]]>): unparsed text, you can access the content using the
Textattribute
Attributes (<a attribute= "Value ">) are accessible using the GetAttributeString function for reading and the SetAttributeString for writing.
XML- EKL Objects mapping
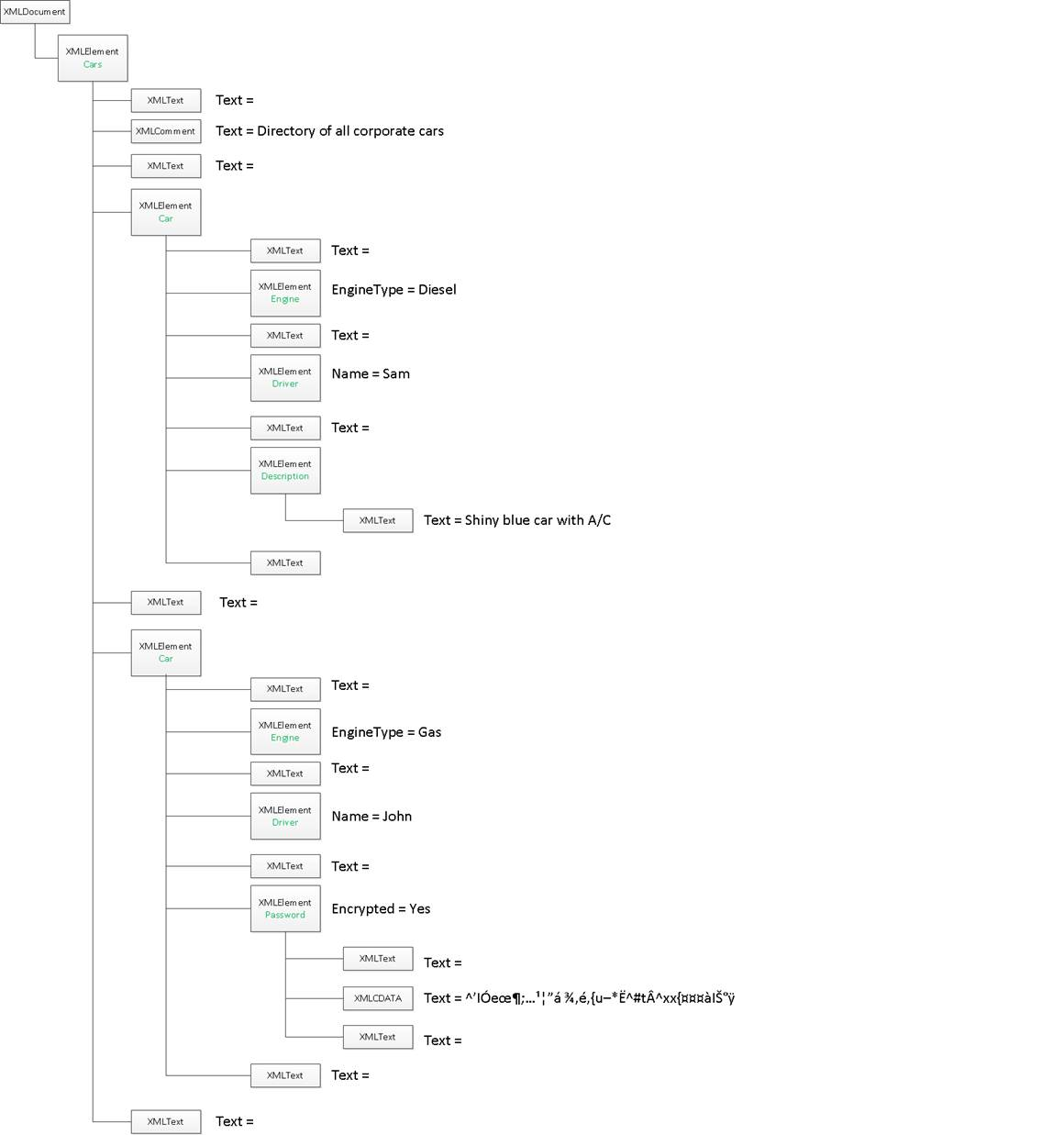
Once loaded in memory, the XML document is represented by a set of EKL objects. For example, the following document:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Cars>
<!-- Directory of all corporate cars -->
<Car>
<Engine EngineType="Diesel"/>
<Driver Name="Sam"/>
<Description> Shiny blue car with A/C </Description>
</Car>
<Car>
<Engine EngineType="Gas"/>
<Driver Name="John"/>
<Password Encrypted="Yes">
<![CDATA[]]>
</Password>
</Car>
</Cars>
Creating, Modifying and Propagating XML Documents
Use CreateXMLDocument() to open an existing XML file from a file path or an existing XML document in database. Use new("XMLDocument", <doc name>,<Owner>) to create an XML Document. You have two possibilities:
- You want to create a XML document on disk, enter the path as second input and enter NULL as third input:
new("XMLDocument", "c:\Temp\MyNewXMLDocument.xml",NULL). - You want to create an XML document in database, enter its name as second input and provide a pre-existing document as third input (preferably empty as it will be overwritten when saving):
new("XMLDocument", "MyNewXMLDocument",anEmptyPreExistingXMLDocument).
A root node is automatically created for your document. You can then create XML Nodes, also using the new function:
- Creating a XML Element:
new("XMLElement","Car",parentElement). - Creating a XML Text:
new("XMLText","blahblahblah",parentElement).
Once you are done with the data structure modification, you can propagate the modifications saved on disk or database by calling the Save() method on the XMLDocument object.
To know more about how to use XML in EKL, see <your install>\win_b64\startup\Knowledgeware\EKL Samples\Sample3.