Sectioning Items | ||
| ||
-
From the section of the action bar,
click Section
 .
.
You can also select the geometry before launching the command. The selected geometry is used to define the section plane. Based on the type of geometry, more geometry selections might be required.
A section plane appears, cutting through the object.A context toolbar also appears.
-
Optional: To customize your section, choose from the following options in
the context toolbar:
Option Description  Flip
Flip
Reverses the cut side.  Position to X
Position to X
Orients the plane normal to the X axis.  Position to Y
Position to Y
Orients the plane normal to the Y axis.  Position to Z
Position to Z
Orients the plane normal to the Z axis.  Position from geometry
Position from geometryPositions the plane based on the selected geometries. The planed is positioned such that its normal (W-axis) is aligned to the normal of the plane defined by selected geometries that is closest to the opposite viewing direction and section plane is resized to fit inside the bounding box of the root product. When this option is selected, the selection filters are not available. If a geometry is selected as the first selection, the Ok option in the message box at the top of the 3D area is enabled. If the first selection is a planer surface, the section plane is automatically repositioned. If required, you can still select another valid second and third geometry for defining the plane.
Tip: When you hover over a geometry, a temporary representation of the expected plane position and orientation is displayed.  Move Viewpoint
Move Viewpoint
Changes the viewpoint to display the section parallel to the screen.  Remove
Remove
Removes the section and exits the Section  command.Note: Depending on their position, some markup objects (such as measurements or annotations) can be hidden to improve the display of cut objects.
command.Note: Depending on their position, some markup objects (such as measurements or annotations) can be hidden to improve the display of cut objects. -
To position your section plane, choose from the options available in the filter bar.
Filters let you position the section by snapping the Robot on the respective geometry type.
Option Description Point 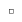
The Robot is snapped on a point and the axes of the Robot are mapped to the reference axes of the root product. Center 
The Robot is snapped on a center of a circle and the axes of the Robot are mapped to the reference axes of the root product. Axis System 
The Robot is snapped on an axis system. Line 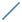
The Robot is snapped on a line. The origin is the point on the line where it is snapped and the w-axis lies on the line. Plane 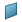
The Robot is snapped on a planar surface. The origin is the point where it is snapped and the w-axis is normal to the planar surface. Cylinder/Cone 
The Robot is snapped on a cylindrical or conical surface. The origin is the intersection point between the axis of the cylinder or cone and the line normal to this axis, passing through the point where the Robot is snapped. Surface 
The Robot is snapped on any surface. The origin is the point where it is snapped and the w-axis is the line normal to the surface. Product 
The Robot is snapped on the plane formed by the two of the main axes, closest to the viewer plane. The Robot is positioned at the center of the product bounding box. Note: For all the filters except the surface and product filter, the high quality representation of the selected geometry is loaded in the session.For line, surface, cylinder, cone, plane, and product, a temporary representation is displayed while snapping the Robot. -
Change the position of the section plane using one of the following methods:
Areas that can be manipulated are highlighted when you hover your mouse over them.
- To rotate the plane, drag its edges.
- To resize the plane, drag its corners.
- To position the plane on a specific surface of the object, use the Robot and the ruler, to position it precisely.Notes:
- You can manually position the origin of the ruler.
- You can enter the required value on the ruler for exact positioning of the section plane.
- In 3DPlay Web App, the ruler is displayed with less opacity.
- To translate the section plane, you can:
- Drag its surface
- Drag the Robot handles and enter the required value on the rule.
After the re-positioning is complete, the section curves are displayed (if the Compute contours preference is enabled.), thus making the contour of the cut geometry more visible and more accessible to create measures.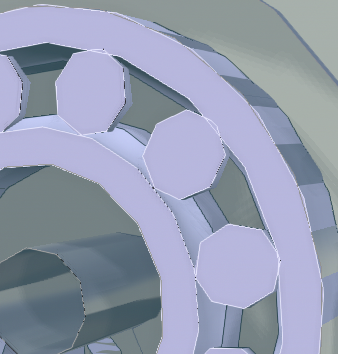
- Optional:
To see the cut elements more clearly and access them more easily while creating the
section, click Hide Section Plane
 .
The section plane is hidden. You can now measure items that were previously not accessible because to the section plane.
.
The section plane is hidden. You can now measure items that were previously not accessible because to the section plane.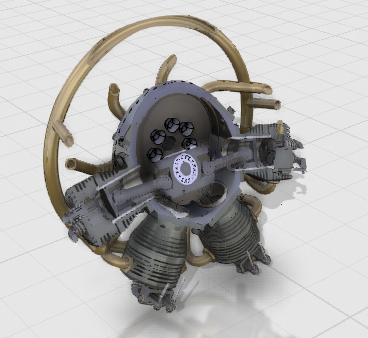
To display the section plane again, click Hide Section Plane
 .Notes:
.Notes:- As long as Hide Section Plane
 remains selected, you can no longer view the section plane,
but you can still manipulate it by selecting the section contour. Of course, you can
also rotate or zoom the object, change your perspective, etc.
remains selected, you can no longer view the section plane,
but you can still manipulate it by selecting the section contour. Of course, you can
also rotate or zoom the object, change your perspective, etc. 
- After you have creating the section, it is automatically hidden and
Hide Section Plane
 is selected. To display the section plane, click to deselect
Hide Section Plane.
is selected. To display the section plane, click to deselect
Hide Section Plane.
- As long as Hide Section Plane