About Contextual Implement Relation Display | ||
| ||
Two types of contextual relation can be displayed:
- Direct contextual relation: the implement relation is directly in context of the functional and logical components in which the allocation view is created.
- Sub contextual relation: the implement relation is indirectly in context through a series of contexts (recursive contexts) starting from the context of sub contextual implement link to the context where the allocation view is created.
Example of Implement Relation Display
The following examples illustrate which implement relation is selected to be represented in an allocation view.
Sub Contextual Relation
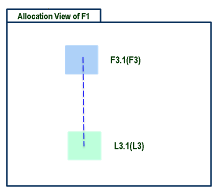
The first example shows a sequence of contextual links between function and logical components: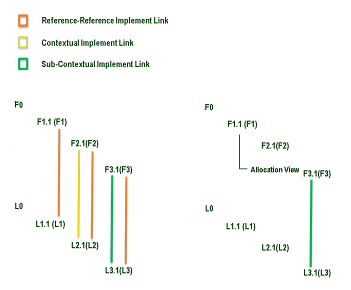
In this case:
- F2.1 and L2.1 have a contextual link in the context of F1 and L1.
- F3.1 and L3.1 have a contextual link in the context of F2 and L2.
As result, the contextual link between F3.1 and L3.1 is selected for the placement in the allocation view.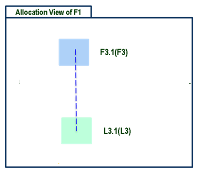
Direct Contextual Relation
In this case, the implement relation is directly in context of the functional and logical components under which the allocation view is placed.
The contextual link between F3.1 and L3.1 is selected for the placement in the allocation view.