About Heat Sink Components | |
| |
Heat Sink Structure
A heat sink is a single part (typically made from a thermally conductive metal) that features numerous equally spaced, parallel fins, as shown below. The fins are designed in a manner to maximize the surface area in contact with the fluid.
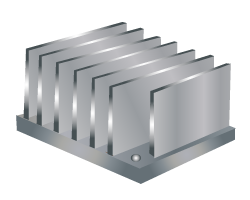
The base of the heat sink attaches to the surface of a heat source, such as a microprocessor or a light-emitting diode (LED).
Energy Transfer
Heat transfers passively from its source, through a heat sink, and to the fluid passing through the fins. First, the base of the heat sink conducts heat away from its source, such as a microprocessor or an LED. Next, the heat travels by conduction from the base of the heat sink to its fins. Finally, by means of conduction and convection, heat dissipates from the fins to the surrounding fluid. It is common to use an active cooling device (for example, a fan) with a heat sink to increase fluid flow around the heat sink. Increasing the convection increases the amount of heat transferred away from the source.