About Intersections | ||||
|
| |||
Support Extension
The Extend linear supports for intersection allows the intersection of non-cutting coplanar linear curves.
You can select this check box to extend the first, second or both elements.
By default, this check box is cleared.
In some cases (for instance shallow angles), this check box may give a more accurate result as it takes into account the geometry rather than the topology.
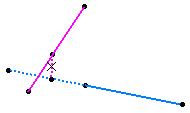
Here is an example with the option selected for both elements.
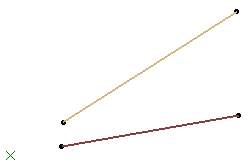
Extrapolation Options
These options are only available for surface-surface intersections.
You can extrapolate the intersection result.
- Clear Extrapolate intersection on to intersect surfaces without
extrapolation.

- Select Extrapolate intersection on and first
element to extrapolate the result on the first element.
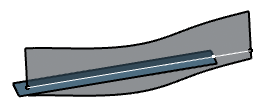
- Select second element to extrapolate the result on the second
element.

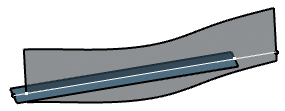
- Select both element to extrapolate the result on both
elements.
Non Coplanar Lines Intersection
You can select the Intersect non coplanar line segments check box to perform an intersection on two non-intersecting lines.
| Important: When you select this check box, both the Extend linear supports for intersection check boxes are selected too. |
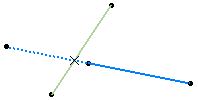
Miscellaneous
- If you select a body or a hybrid body containing both solid and wireframe elements as input, only the solid elements are taken into account to compute the intersection.
- Avoid using input elements which are tangent to each other since this may result in geometric instabilities in the tangency zone.
- If the intersection stops at an edge and providing the edge can be merged with the intersecting element (if the distance is less than 0.1mm), then it is projected onto the intersecting element. The projection is integrated to the intersection result.