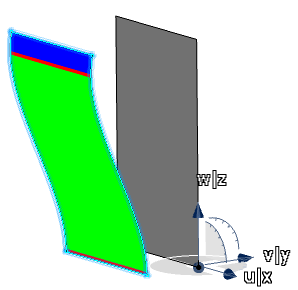
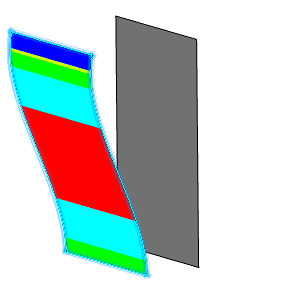
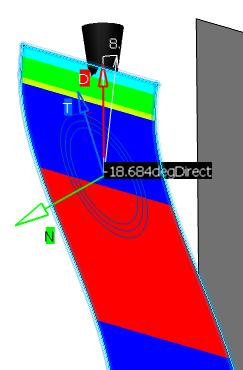
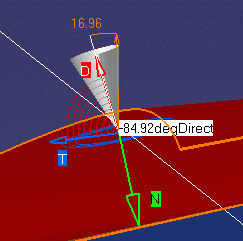
Analyzing the Draft Angle | |||
| |||
Notes:
- Settings are saved when you exit the command, and redisplayed when you
select Feature Draft Analysis
 again.
again. - In case the analysis results are not visible, even though the rendering style is properly set, check that the geometry is up-to-date, or perform an update on the involved elements.
- The analysis results depend of the current object. If you want to change the scope of the analysis, use the Define in Work object contextual command.
- If you have created several draft analyses on the same surface element, you can put any of them on top of the others for the visualization. Select the Set on top contextual command of the required analysis in the tree.
- If a partbody is selected for analysis the following behavior is
observed:
- The result is same as the result displayed if the last modified/created solid in the part body is selected.
- Any changes made in the partbody are taken into account for analysis.
- If the solid above the last updated solid is an in-work object, the analysis is not displayed.