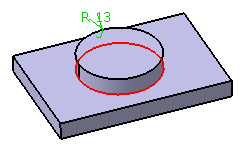
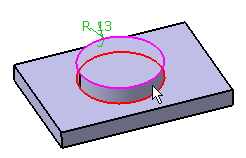
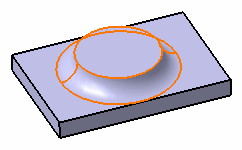
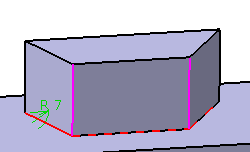
EdgeFillet.x Dialog Box
In EdgeFillet.x dialog box, you can define fillet features using the following options:
Propagation
The propagation modes available are:
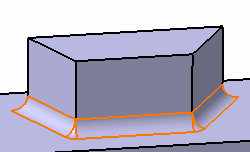
- Minimal: edges tangent to selected edges can be taken into account to some
extent. The app continues filleting beyond the selected
edge whenever it cannot do otherwise. In the following example, the
fillet is computed on the selected edge and on a portion of tangent
edges:
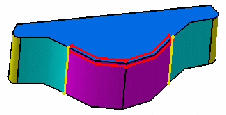
- Tangency: tangencies are taken into account so as to fillet the entire edge and possible tangent edges. The tangent continuous edges of the selected edge are managed to ensure a better fillet stability and robustness (more fillets are automatically rerouted if design changes).
- Intersection: fillets all the edges created by the intersection of the
faces of the selected objects and the rest of the faces of the current body. This mode is based on the selection of the features unlikely to Minimal and
Tangency which are based on the selection of edges or faces.
Intersection fillets edges in a more productive way by reducing the number of selections. This capability takes into account the tangencies of the edges to be filleted.
If you select any Part Design feature, all the sharp edges at the intersection of this feature with the current solid are automatically filleted with the given radius value. You can select one or more features at a time. The selected feature appears in the Object(s) to fillet field and the other feature becomes a current solid.
Important: - The selection of a body used in a Boolean operation is not allowed. To get the intersection edges of an operated body, you need to select the corresponding Boolean operation or one of its features. This selection must be done from tree only.
- If a pattern is selected, only the instances of the pattern are filleted. So it is necessary to add the parent shape of the pattern to the list of objects to be filleted. If you have selected edges in Tangency or Minimal mode, you can change the selection mode to Intersection. In this case, selection is cleared and the Candidate features dialog box opens which gives option to select the features that contains these edges. The selected feature appears in the Object(s) to fillet field.
- Blend corners option is unavailable if the Intersection propagation mode is selected.
- Intersection with selected features: Selecting the geometric features in the Object(s) to
fillet and Selected features boxes automatically
selects the edges at their intersection and fillets them.
Note: If any feature is commonly selected in the above two boxes, the edges of the simplified faces of this feature are not taken into account.
Conic Parameter
You can select the Conic Parameter option to vary the section of the fillet. For a parameter:
- Equal to 0.5, the resulting curve is a parabola
- Between 0 and 0.5, the resulting curve is an arc of an ellipse
- Between 0.5 and 1, the resulting curve is a hyperbola
If the conic mode is activated, the Edge(s) to keep and the Parting element boxes cannot be selected. The Conic Parameter option is unavailable when a Parting Element is already defined or the Edge to keep is either explicit or implicit in nature.
Conical fillets do not handle twist configurations. If a twist is detected, the fillet operation fails.
If the fillet surface curvature is lower than the support curvature, fillet surface re-limitation may fail. In such cases, you need to decrease the conic parameter.
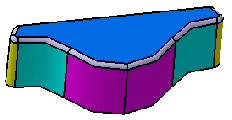
Trim Ribbons
If you set the Tangency mode, the Trim Ribbons option becomes available. You can then trim the fillets to be created.
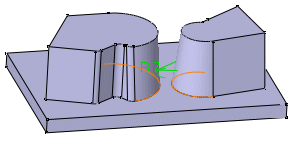
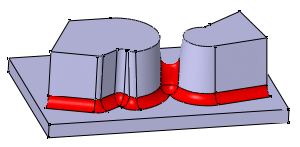
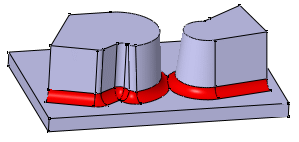
Compare the above results to the fillets created with the
Minimal propagation mode: The fillets are only trimmed.
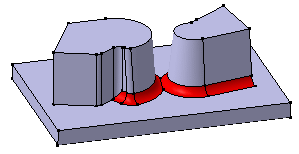
Limiting Elements
- You can define one or more limiting elements.
- You can create the limiting elements using
context menus
available from the
Limiting element(s) box.
If you create any of these elements, the corresponding icon is displayed in front of the Limiting element(s) box. You can click this icon to edit the element.
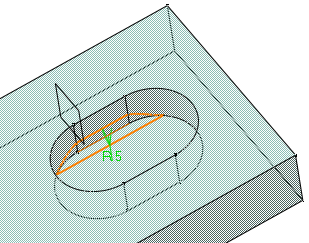
- You can create limiting elements by clicking on the edge to be filleted. This element is displayed as a blue disk.
- You can select points as limiting elements. These points must be located on the edge to be filleted and they must be created using the On curve option available in the Point.x dialog box.
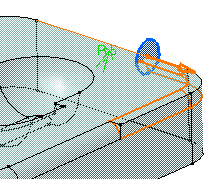
Blend Corners
The Blend Corners option quickly reshapes unsatisfactory corners.