Projecting Curves | |||
| |||
- Select a curve.
-
From the Creation section of the action bar, click Project Curve
 .
.
- Select the projection orientation.
-
Ctrl+ select the surface or set of surfaces onto which
you want to project the curve.
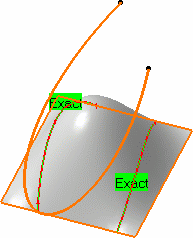
- Projection according to the Robot orientation.
- Projection normal to the surface.
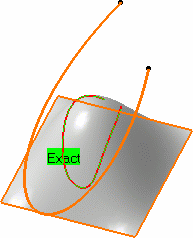
The projected curves are Splines lying on the surface. The converter wizard is automatically used to process the resulting curve. It generates either a 2D NUPBS (Non Uniform Polynomial B-Spline) curve identified by the Exact text, or a 3D NUPBS curve (identified by Cv text).
If you want to further control the projected curve, right-click the displayed text and choose the Edit context menu. The converter wizard is then explicitly launched.
For example, in the case of a 2D curve, you may want to generate a single segment curve. Select both Segmentation and Single in the Converter Wizard, then click OK.
- Projection according to the Robot orientation.
-
Click OK to create the projected curve.
Notes:
- When you project a curve on two surfaces, there may be no tangency continuity.
- Click Furtive Display
 in the App Options panel to see the control points of the projected curve.
in the App Options panel to see the control points of the projected curve. 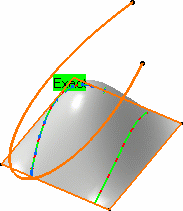
- Select Display Information in the Converter Wizard dialog box to view the order and number of segments of the projected curve.
- The element's topology (for example a relimited curve or surface) is taken into account for the projection.
- Multiselection of curves is allowed.
- Multicell curves can be selected: the resulting projected curve is also a multi-cell curve.