Selecting Using the Multi-Selection | ||
| ||
- From the Wireframe section of the
action bar, click Projection
 .The Projection Definition dialog box appears.
.The Projection Definition dialog box appears. - In the Projected box, select the element to be projected.
Important: - If one element is selected and you select another element, it automatically replaces the element you selected previously, provided the multi-selection dialog box is closed.
- If several elements are selected and you select another element, it is appended to the elements list.
The selected element is highlighted in the tree and in the work area.Tip: When you select or edit an element aggregated under the multi-output node, either in the tree or in the work area, its input is highlighted in the 3D geometry, in the tree, and in the multi-selection panel. - In the Projection Definition dialog box,
click
 .
. The multi-selection is now active: all selected elements are displayed in the dialog box.
- Add elements to the list in the dialog box that opens.
Tips: - You can select an element in the list: it is highlighted in the tree and in the 3D geometry.
- You can select one or more geometrical sets and multi-outputs as inputs of the multi-selection. In that case, all their direct children are selected.
- Use the Remove or Replace buttons to modify the elements list.
Important: Clicking Remove deletes the output feature. Therefore adding a new element in the list creates a new output feature. Click Replace instead to replace an input element by another without deleting the output feature. - Click Close to return to the Projection Definition dialog box.
- In the Support box, select a support element.
- Click OK to create the projection elements.
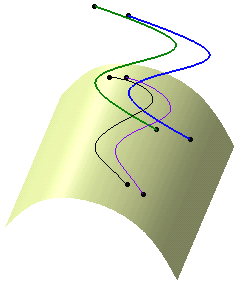
The projection is identified as Multi Output.1 (Project) in the tree.
the created elements are aggregated under Multi Output.1.
Tip: You can create several multi-outputs in the tree, each one grouping one type of elements. - Click Translate
 .The Translate Definition dialog box appears.
.The Translate Definition dialog box appears. - In the Elements box, select the elements to be translated.
- In the Vector Definition list, select Direction, distance.
- In the Direction box, select a direction.
- In the Distance box, enter the distance by which the element is to be translated.
- Click OK to create the translated element.
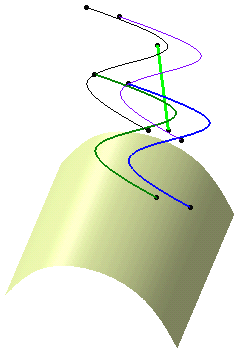
The translation is identified as Multi Output.2 (Translate) in the tree and appears below Multi Output.1.
The created elements are aggregated under Multi Output.2: all common inputs (in our example, Length) are directly aggregated under the Multi Output feature and all generated features reference these inputs by pointing the same attribute.
Important: It is impossible to create multi-output features from the context menu.
| See Also |
| About the Multi-Selection |