Surface Connection Checker | ||||
|
| |||
Analysis Conditions
- Search distance
- Defines the domain in that the command searches edges that might be
merged.
The higher the search distance, the higher the number of candidate edges.
Possible types are:
- Regular, set to 0.1mm.
- Quick, set to 0.001mm.
- User, that lets you enter your own search distance: the value box becomes editable.
The proposed search distance type is Regular.
- Internal edges
-
- If the Internal edges check box is selected, the analysis will be done on the faces. This also enables the Transfer by domain.
- If the Internal edges check box is not selected, the analysis will be done on the surfaces.
Tip: Click Apply after any modification of one of these parameters to restart the analysis. - Surface(s) selected
- Is updated as soon as you select faces or modify the selection (no need to click Apply).
- Transfer by domain
- Available only if Internal edges is selected.
- Enables you to transfer the faces of the surfaces analyzed to geometrical sets corresponding to the connex domains found.
- One geometrical set is created for each domain found.
- Their default name is Domain.x.
- You can edit this name in the text box on the right of Transfer by domain.
Important: - Once you have clicked Transfer by domain, only OK and Cancel are available.
- If you need to transfer the sites of anomalies by domain, select the requested line of anomalies and click Transfer at the bottom of the dialog box.
Analysis Results
Possible connection problems are listed:
- Duplicate: Duplicate faces, with their number.
- Embedded:
Number of locations where one element is completely included in another
one.
- Only faces with the same support may be recognized as embedded.
- For a correct time performance, the search for embedded faces is done on a sampling. Therefore, some faces may be recognized as embedded whereas they are not.
- Multi-Shared edge: Number of locations where elements have multiple connections within themselves.
- Narrow portion: Number of locations where elements have multiple connections with other elements.
- Overlap corner: Number of locations where a corner of one element covers a portion of another one.
- Overlap edge:
Number of locations where an edge of one element covers a portion of another one.
Important: - Sometimes, a visual analysis of the faces may be deceptive: one face seems to overlap another one. However no overlap is detected by the Surface Connection Checker. This is due to the fact that a distance gap exists in the boundary of the first face. Due to this gap, those faces are not overlapping each other and no overlap is detected. Therefore, we recommend to check the model for distance gaps before searching overlapping faces.
- The overlaps detected are those that lead to a bad orientation of the model. Therefore overlaps are detected only if the angle formed by the normals of the faces is greater than 135 degrees.
- Boundary: Number of boundaries found.
- Distance: Number of holes found and their maximum value.
- Tangency: Tangency anomalies and their maximum value.
Locations are graphically highlighted in the work area:
Analysis tune-up
Once a first analysis has been completed, you can examine the anomalies more thoroughly by modifying those parameters.
Transfer
- Transfer
- Starts the Transfer dialog box. The transfer applies to the problems corresponding to the selected line,
e.g. if Tangency is selected, only tangency anomalies are
listed in the Transfer dialog box.
On the left, you find information on the anomalies found:
- Their number (Number of anomalies)
- Their Name (Site.xx, Site being a set of two defective faces)
- The Value of the gap
- The numerical name of their Domain (Domain is a set of several defective faces).
- Anomalies Detected
- The anomalies are ordered in decreasing gap value order. You can order them by name or by domain by clicking on the column title. Ordering the anomalies enables you to isolate and transfer the anomalies found in one site or one domain, or according to the value of the gap, in the same body.
- Arrows
 transfers the selected lines from Anomalies Detected
to Anomalies Selected.
transfers the selected lines from Anomalies Detected
to Anomalies Selected.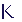 transfers the selected lines from Anomalies Selected
to Anomalies Detected.
transfers the selected lines from Anomalies Selected
to Anomalies Detected. transfers all the lines from Anomalies Detected
to Anomalies Selected.
transfers all the lines from Anomalies Detected
to Anomalies Selected.-
 transfers all the lines from Anomalies Selected
to Anomalies Detected.
transfers all the lines from Anomalies Selected
to Anomalies Detected. -
 transfers all the lines from Anomalies Selected to Anomalies Detected and orders them by domains.
transfers all the lines from Anomalies Selected to Anomalies Detected and orders them by domains. - When you click Transfer, a geometrical set with the name of the anomaly is created for each domain found, and the surfaces or faces are transferred to those geometrical sets.
- When you click Extract, a geometrical set with the name of the anomaly is created for each domain found and sub-sets are created for the sites. The results are generated as extracts performed on each defective face. The extract feature takes the color of the defect. The original tree is kept, completed with the defect geometrical sets. The analysis results are persistent and available when and where needed.
- Transfer to
- Proposes the name of the body to which the defective face will be
transferred, respectively:
- Duplicate faces
- Embedded cases
- Narrow portion cases
- Multi-Shared edge cases
- Overlap_corner cases
- Overlap_Edge cases
- Boundaries
- G0 gaps
- G1 gaps.
Tip: - Those names are editable.
- One geometrical set is created for each transfer.
- If you transfer the anomalies of one type in several shots, several bodies will be created, their names being incremented.
- Anomalies Selected
- Lists the elements to be transferred.
- Transfer
- Starts the transfer and lets the dialog box open for another transfer.
- Close
- Starts the current transfer, closes the dialog box and reverts to the main dialog box. The faces are transferred to the geometrical sets and hidden in the model. This isolates the defective faces that can be healed later on.
A context menu Reframe On is available on each anomaly listed in the Transfer dialog box. The zoom factor is set automatically according to the size of the smallest element. It also works on assembled surfaces. Each face concerned appears in another color.
- Gives you the status of the analysis.
- Enables you to cancel the analysis by clicking Cancel.