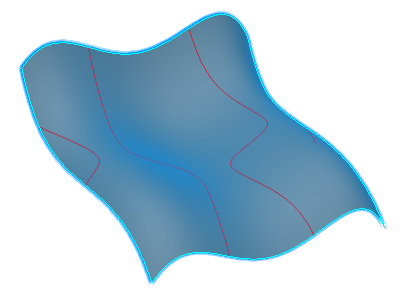
-
Select the surface to analyze.
-
From the Analysis section of the action bar, click Inflection
Lines
 . .
-
In the Local Plane Definition section, select
Parametric.
The inflection lines are displayed on the surface.
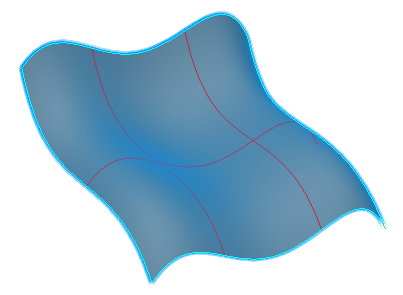
-
Select Robot Plane.
-
Drag the Robot onto the surface.
The Robot base is orientated in the same plane as
the local tangent to the surface and the inflection lines are updated.
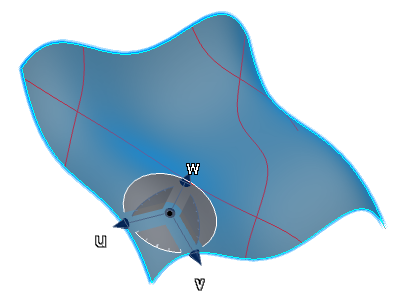
-
Drag the Robot to a new position on the surface.
In the new position, the orientation of the Robot base plane has changed, therefore the
inflection lines are updated on the surface.
-
Click
OK. The analysis
is added to the
tree
and will be updated automatically whenever you modify any of the input
elements.
Notes:
- Creating and retaining inflection lines on a surface is especially useful to
determine at which points the curvature of the intersection between the
cutting planes and the surface is 0.
- When you use this command with the Inflection area
option of the Surfacic Curvature Analysis command,
note that the inflection lines are always created within the green
areas.
- When you select the geometrical set as an input in the tree, all the elements included in this
geometrical set are automatically selected.
|