-
From the Surface section of the action bar, click Adjust
 .
.
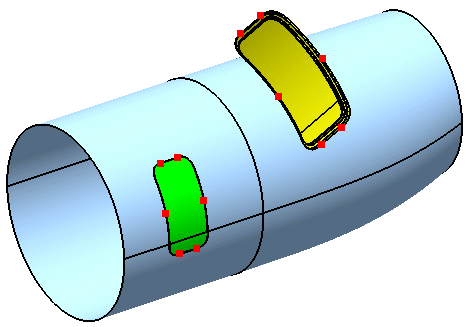
- Select the door geometry to be adjusted.
In the dialog box
Adjust, the
Point box becomes active.
-
In the tree, expand the geometrical sets for Adjust Points and Aperture Points.
These are the points to be used for transformation.
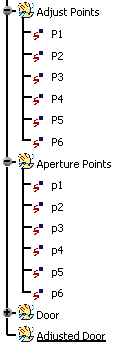
The transformation of the geometry begins by selecting pairs of vector positions.
-
Successively select P1 from the geometrical set Adjust Points and p1 from the geometrical set Aperture Points.
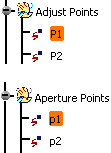
The vector
Translation appears.
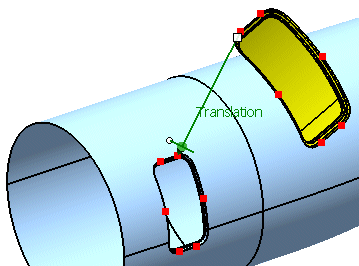
-
Select Translation and click Apply..
The door is translated as a feature result.
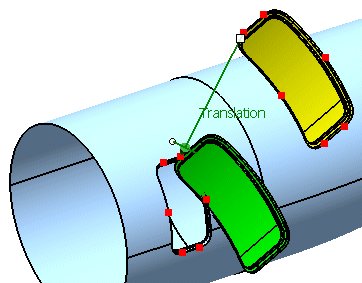
-
Successively select P2 from the geometrical set Adjust Points and p2 from the geometrical set Aperture Points.
The vector
Rotation appears.
-
Select Rotation and click Apply.
The door is rotated.
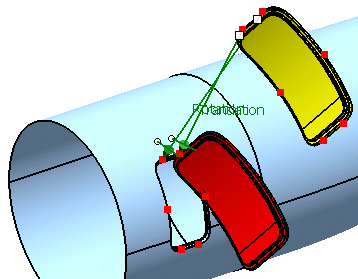
-
Successively select P3 from the geometrical set Adjust Points and p3 from the geometrical set Aperture Points.
The vector Rotation appears, representing the scaling.
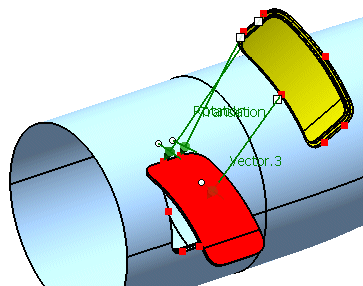
-
Select Scale and click Apply.
The door is now scaled.
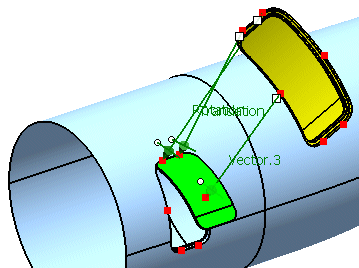
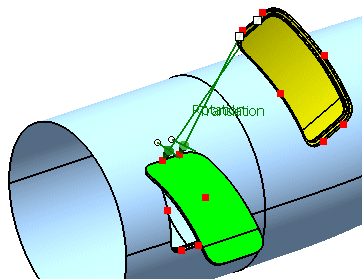
- Select the remaining pairs of points to perform a compensation of the geometry which will fit it exactly into the aperture.
-
Select Compensation and click Apply.
The door is now adjusted to its final position.
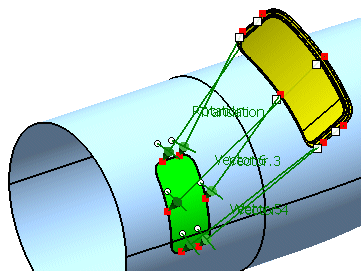
The result of the Adjust operation is a feature result.