The Kinematics solver detects singularities directly (bifurcation singularity) and indirectly
(lock-up singularity). To display the messages related to singularities, click the
Incident Diagnosis
 command to generate the
computation report. Two types of singularity are described here.
command to generate the
computation report. Two types of singularity are described here.
- Bifurcation Singularity
- A bifurcation singularity occurs when multiple
- mechanism
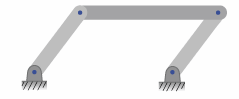
configurations are possible for the same command value. Consider a parallelogram four-bar linkage with two pairs of
equal-length members. The fourth bar does not appear in the figure, it is a construction
line that links the anchor points.
The four
bars are aligned along the same line:
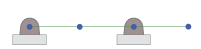
If
body 1 is driven in the positive direction from the flat configuration, two types of
motions are possible and equivalent:

- Based on the configuration, the kinematics solver generates a message as
follows:
A bifurcation singularity area occurred.
The mechanism entered or left a bifurcation singularity area.
At crossing this area, the solver arbitrarily selects a configuration
among several valid configurations.
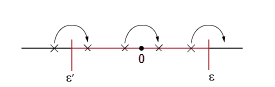
The
figure below describes how the kinematics solver detects the bifurcation singularity area.
The bifurcation singularity occurs at the position marked 0, which lies within a small
range of values known as the singularity area.(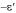
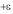 ). The message generated
by the kinematics solver is displayed when the mechanism enters or leaves a singularity
area.
). The message generated
by the kinematics solver is displayed when the mechanism enters or leaves a singularity
area.
- Lock-up Singularity
- In a lock-up singularity, it is impossible to reach certain positions.
Consider a
slider-crank mechanism. In the following configuration, the mechanism is not locked, but
is free to slide back and forth. You can increase or decrease the angle value, marked
Theta 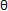 in the figure. The
target value for Theta is 90°.
in the figure. The
target value for Theta is 90°.
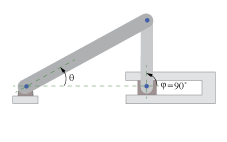
At lock-up
point 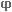 = 90°, the mechanism is
blocked. You can no longer increase the angle value (marked
= 90°, the mechanism is
blocked. You can no longer increase the angle value (marked 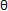 in the figure). Based
on the configuration, the kinematics solver generates a message as
follows:
in the figure). Based
on the configuration, the kinematics solver generates a message as
follows:The target value is not reached.
The kinematics solver failed
to reach the target value.
![]() command to generate the
computation report. Two types of singularity are described here.
command to generate the
computation report. Two types of singularity are described here. 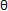 in the figure. The
target value for Theta is 90°.
in the figure. The
target value for Theta is 90°.


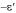
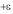 ). The message generated
by the kinematics solver is displayed when the mechanism enters or leaves a singularity
area.
). The message generated
by the kinematics solver is displayed when the mechanism enters or leaves a singularity
area.

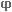 = 90°, the mechanism is
blocked. You can no longer increase the angle value (marked
= 90°, the mechanism is
blocked. You can no longer increase the angle value (marked