Analyze View Geometries Using the Sketch Solving Status
You can analyze view geometries using the sketch solving status.
- Double-click the front view to activate it.
- From the customized section of the action bar, click Sketch Solving Status
 . .
This command gives you a quick diagnosis of the geometry status.
The Sketch Solving Status dialog box appears and provides
a general geometry status, whether it is under-constrained, over-constrained
or iso-constrained.
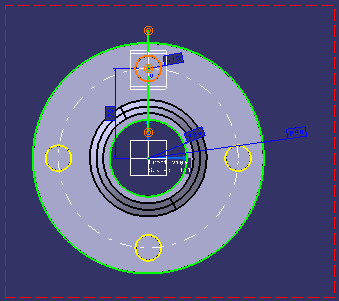
The information given in the Sketch Solving Status
dialog box is highlighted in red in the geometry area and the elements that
are under-constrained are highlighted.
In the example, three points are highlighted indicating that they are under-constrained.
Analyze View Geometries Using the Sketch Analysis
You can analyze view geometries using the sketch analysis.
Before you begin: The Sketch Solving Status dialog
box is still displayed from the previous task.
- Click Sketch Analysis
 in the Sketch Solving Status dialog box or in the Sketch section of the action bar.
in the Sketch Solving Status dialog box or in the Sketch section of the action bar.
The Sketch Analysis dialog box appears. It contains three
tabs: Geometry, Use-edges and
Diagnostic.
Construction elements appear in blue in the geometry. If you click the appropriate section, you can sort
the elements displayed in the dialog box by name, status or type. If you can select elements in the dialog box they
are highlighted in the work area. In the Sketch Analysis dialog box, the Geometry
section: Provides information related to all the connex profiles in the view. General Status: Gives a global status on all the view
geometries. Detailed Information: Provides a
detailed status/comment on each profile of the view. Corrective Actions: Lets you perform any of the following operations: -
 :
Turn the analyzed element into a construction element :
Turn the analyzed element into a construction element
-
 :
Close a profile :
Close a profile
-
 : Erase
an element : Erase
an element
-
 :
Hide all constraints in the view :
Hide all constraints in the view
-
 :
Hide all construction geometries in the view and in the detailed information
area of the Geometry tab. :
Hide all construction geometries in the view and in the detailed information
area of the Geometry tab.
- Click the Diagnostic section. It provides geometry or constraint related information of a view.
The Diagnostic section provides a full
diagnosis of the view geometry that involves a global analysis of the view
as a whole, and specifying whether individual geometrical elements are under-constrained (under-defined), over-constrained (over-defined)
or iso-constrained (well defined): Solving Status: Provides a quick overall analysis of the
view geometry. Detailed Information: Provides a detailed status on each
constraint and geometrical element of the view, and lets you know what
type of element it is (geometry, constraint). - Name: Lists the name of the element under analysis (circle, point, line or parallelism, tangency, etc.)
- Status: Lists the constraint status (Under-Constrained, Iso-Constrained, etc.)
- Type: Lets you know what type of element it is (geometry, constraint)
- Scale check: Defines the status of the element based on size and positioning according to the design range of the 3D area.
Action: Lets you perform any of the following operations:
-
 :
Hide all constraints in the view and in the detailed information area. :
Hide all constraints in the view and in the detailed information area.
-
 :
Hide all construction geometries in the view and in the detailed information
area of the Diagnostic section. :
Hide all construction geometries in the view and in the detailed information
area of the Diagnostic section.
 Erase geometry.
Erase geometry.
- Select Hide Construction Geometries
 in the Sketch Analysisdialog box.
in the Sketch Analysisdialog box.
If you select items in the Detailed Information
table, they are highlighted in the view, which enables you to identify
them easily. To solve constraint-based problems in the view, edit the geometry directly.
- Click the Use-edges section.
It provides
information on each projection or intersection, on constraints and so forth
created in the view.
You can sort the use-edges by type, build
or update status or input geometry. Detailed Information: Provides
a detailed status/comment on each use-edge of the view. Corrective Action: Lets you perform any of the following operations:
-
 :
Isolate the associative use-edge making it non-associative with geometry. :
Isolate the associative use-edge making it non-associative with geometry.
-
 :
Remove the associative use-edge from update process (the use-edge is
still associative to geometry but is not updated). :
Remove the associative use-edge from update process (the use-edge is
still associative to geometry but is not updated).
-
 : Erase
the use-edge. : Erase
the use-edge.
-
 :
Change the input geometrical object projected or intersected (this option
is unavailable in a 2D Layout) :
Change the input geometrical object projected or intersected (this option
is unavailable in a 2D Layout)
-
 :
Hide all constraints in the view. :
Hide all constraints in the view.
-
 :
Hide all construction geometries in the view and in the detailed information
area of the Geometry section. :
Hide all construction geometries in the view and in the detailed information
area of the Geometry section.
Analyze Sketch for Design Range
You can analyze if
an element in the sketch is beyond the design range of the model.
-
From the
Sketch section of the
action bar,
click
Sketch Analysis
 . .
appears.
-
In the
Sketch Analysis dialog box, click the
Diagnostic tab.
-
Under
Detailed Information, the
Scale check of each element is listed.
Scale check can be:
- Valid: inside limits: For the
geometric elements within size limits and with correct positioning.
- Invalid: exceeds limits: For the
geometric elements beyond the size limits of the design range. It is also
applicable for elements which are positioned so far from the origin that they
fall outside the footprint. If you exit
Sketcher,
without scaling down these elements within the size limits of the model, a
warning message appears in 3D prompting the same.
- Ignored: not applicable: For the
elements that do not appear in 3D such as construction elements, or
constraints.
- ???: For the elements whose status
cannot be computed. This is an undesirable status.
-
Resolve errors for invalid elements, if any.
|