Texture-Mapping Types
Various mapping types let you select the most appropriate mapping for the shape of the geometry. They are used for real-time display only.
After selecting Procedural Material in the Type list of the Appearance Domain dialog box, you can choose a mapping type.
The following mapping types are available:
| Mapping Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Planar | For planar geometries, such as a slide projector, or for textures with two privileged directions (chessboard or a wall of bricks). |
| Spherical | For spherical geometries, such as a painted light bulb or a ball, or for textures with no privileged direction (stones or raw metal). |
| Finite Cylindrical | For cylindrical geometries such as a can of food or a bottle, or
for textures having a privileged direction such as shiny metal or
marble. The projection is applied to top and bottom faces as well. |
| Infinite Cylindrical | Same geometries as for Cylindrical Mapping. The projection is infinite and therefore is not applied to top and bottom faces. |
| Cubical | For cubical geometries, such as boxes. Also called “Tri-Planar”. It is very well adapted to any kind of shape if the applied texture represents a small pattern. |
| Geometry UV | Complex-shaped texture with bent area (labels or seats). Note:
This
mapping projector is available only if the geometry is UV.
UV appears after you import a 3D geometry or you use the UV Parameterization command. |
| Important: These mapping types cannot be edited anymore. If mapping issues occur, use the Robot to correctly map the material. |
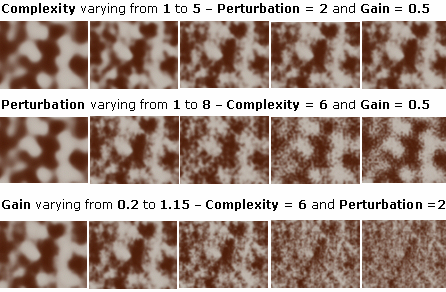
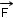 ) for a given point (
) for a given point ( 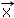 ), the resulting
color is the one of the perturbated point =
), the resulting
color is the one of the perturbated point =