-
Select the geometry to apply.
Note:
No link will be maintained between the Natural Shape geometry and the original geometry.
-
From the Shapes section of the action bar, click Apply Industrial Context
 . .
-
Define the Targeted Feature in the Converted
geometry section of the selection panel.
Note:
Selecting Replace initial geometry replaces all initial
geometry with the Natural Shape features.
-
In the Industrial context of the selection panel, select an
industrial context.
The industrial context identifies the
domain in which you create your model (for example, power train or body in white) and
thereby defines industrial specifications for fillet radii, chamfer distances and angles,
and draft angles.
Note:
Upon selecting an industry, the specifications appear and display the range of
values for the Fillet radius, Chamfer length,
and Chamfer angle.
-
The Options section of the selection panel automatically
recognizes fillets. You can specify which options to automatically recognize.
| Option | Description |
|---|
 |
- Automatically recognize chamfers
- Automatically recognizes chamfers.
- Select Activate color coding to view chamfers in
color.
|
 |
- Automatically recognize linear and circular
patterns
- Pattern instances are identified by a white dot along the pattern's axes.
|
 |
- Automatically recognize threads and
taps
- Recognizes the defined specifications of threads and taps.
- Upon activation, a Create technological results option
appears.
|
Notes:
- Select Apply graphical properties to view colors, textures,
or other applied effects on the converted geometry.
- In the rare event of an imported design discrepancy, the Select Remove
internal cavities option highlights the discrepancy and deletes
it.
-
If two objects clash, you can resolve their behavior in the Clash
options section of the selection panel. Choose between Boolean
union
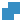 ,
Intersect ,
Intersect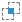 , or
Substract , or
Substract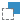 . .
-
Click on the Natural Shape geometry or in the background to apply the industrial
context to your model.
|
 .
.



 ,
Intersect
,
Intersect , or
Substract
, or
Substract .
.