General Principles
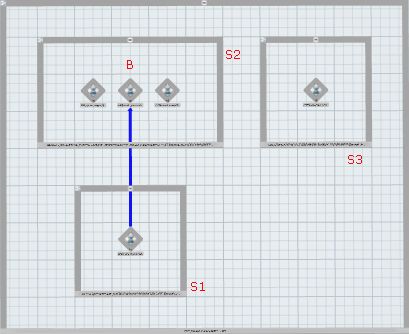
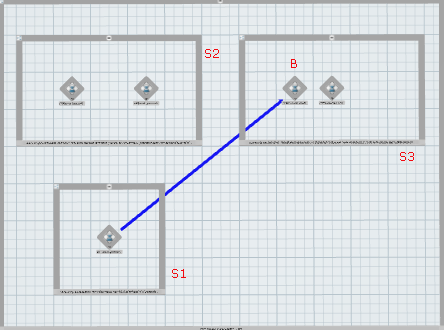
A product flow specifies a precedence constraint from a source to a target.
For example, a product flow from Operation A to Operation B specifies that Operation A must be completed before Operation B. Operation A is the source, while Operation B is the target.
A product flow can link two systems, two operations, or a system and an operation. Operations can belong to the same system or to different systems.
A product flow can only have one source and one target at a time. However, an operation or system can be part of different product flows at the same time.