-
From the Surface Reconstruction section of the action bar, click Segmentation by Color
 . .
- Select the cloud to process.
- Pick a colored point in the cloud.
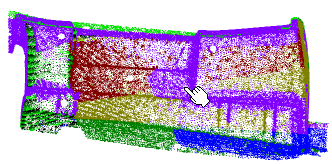
- The color of this point is the reference color, that defines the points to be kept.
- The RGB code of this color, as well as the color itself, are displayed in the dialog box.
- The points to be kept are displayed with bigger symbols.
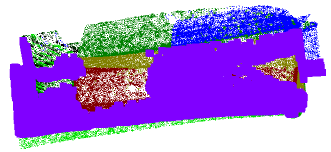
- Nb of points indicates the percentage of points kept from the input cloud, with the current options.
- Pick a point with another color to change the reference color.
-
Set the Tolerance with the slider, between 0 and 1.
This is the distance tolerance in percentage: - 0 (0%) means the color of the point to be kept must be strictly the same as the reference color.
- 1 (100%) means any color matches the distance criterion, and all points are kept.
-
Select a Color space, that is a mathematical model describing the colors.
- RGB-Red/Green/Blue: Additive color model in which red, green, and blue light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The 3 components are homogeneous.
- YUV-Luma/U-Chrom./V-Chrom: Model defining a color space in terms of one luma (Y) and two chrominance (UV) components. You can deal separately with the two parameters (U-Chrom. and V-Chrom) on one hand, and the brightness (Y-Luma) on the other hand. For example, for the same UV plane, in the pictures below Y varies from 0, to 0.5 and then 1.

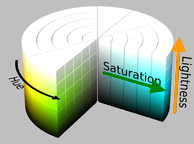
- HSL-Hue/Saturation/Lightness: Common cylindrical-coordinate representation of a color space. The angle around the central axis corresponds to the Hue (black arrow below), the distance from the axis corresponds to the Saturation (green arrow below), and the distance along the axis corresponds to the Lightness (orange arrow below). Those three parameters represent a physical characteristic of the color.
-
Once you have selected a color space, define the Distance formula for it, using the three sliders.
Each of them specifies the importance of the corresponding
parameter from 0 to 2 (0% - 200%): you can increase, decrease, or even nullify the
importance of light over hue or saturation for example.
Two clouds are created: - Kept points contains the points kept.
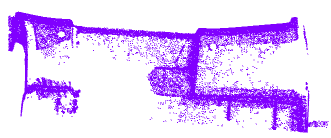
- Rejected points contains the other points.
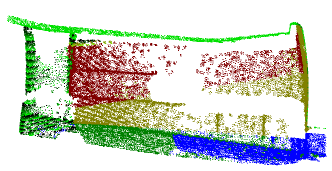
|

