Elements tested
- S3R
- S4
- S4R
- S4R5
- S8R
- S8R5
- S9R5
- STRI3
- STRI65
- SC6R
- SC8R
ProductsAbaqus/Standard Elements tested
Problem description
Model:A quarter model is used because of symmetry. Material:Young's modulus = 1.0 × 107, Poisson's ratio = 0.3. Boundary conditions:Symmetry on plane x = 0 (). Symmetry on plane z = 0 (). Simply supported on plane z = = 0.4 (). Loading:Uniform end shortening. A displacement of −0.0016 is applied incrementally using the RIKS algorithm to all nodes lying on one end of the cylinder with the plane z = 0.4. Reference solutionThis is a test recommended by the National Agency for Finite Element Methods and Standards (U.K.): Test 3DNLG-2 from NAFEMS Publication R0024 “A Review of Benchmark Problems for Geometric Non-linear Behaviour of 3D Beams and Shells (SUMMARY).” The published results of this problem were obtained with Abaqus. Thus, a comparison of Abaqus and NAFEMS results is not an independent verification of Abaqus. The NAFEMS study includes results from other sources for comparison that may provide a basis for verification of this problem. Results and discussionAll elements are tested with meshes using the same nodal spacing. The collapse load is defined as the loading point in the deformation path at which further deformation occurs without an increase in the applied load. The path after this point is termed the postbuckling path. The postbuckling path shows a decrease in the load with further deformation; the postbuckled structure can attain equilibrium only at a load level lower than the buckling load once it has buckled.
Response predicted by Abaqus (element S8R5)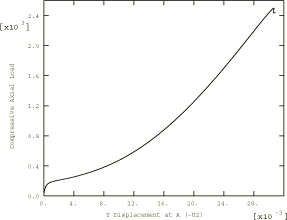 Input files
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||