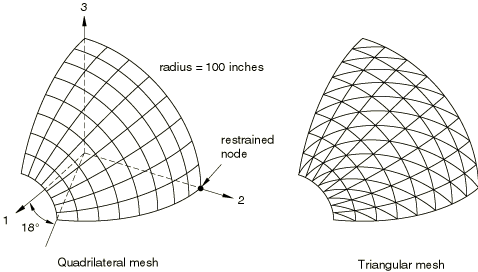
Problem description
A one-eighth symmetrical segment of a spherical surface with a cutout is modeled as a shell section. Symmetry boundary conditions are applied appropriately to the section's edges. The structure has a thickness of 0.4 inch and a radius of 100.0 inches and is subjected to a uniform temperature change. The discretization of this surface yields the following meshes: one consisting of 64 quad elements for use with S4, S4R, S4R5, S8R, and SC8R elements and the other consisting of 128 triangular elements for use with STRI3, STRI65, S3/S3R, and SC6R elements. The shell section is heated uniformly from 0° F to 430° F.
The first step of each input file is a static linear perturbation step. In the second step the loading is repeated as a general step that accounts for geometric nonlinearities. Since the deformations are small, the displacements obtained in the second step are virtually the same as the displacements obtained in the linear perturbation step. In some of the input files, solution controls are used to relax the equilibrium tolerances somewhat. This is necessary because the nodal forces in the final solution are zero; hence, the maximum force and moment residuals are (almost) of the same order of magnitude as the force and moment norms.