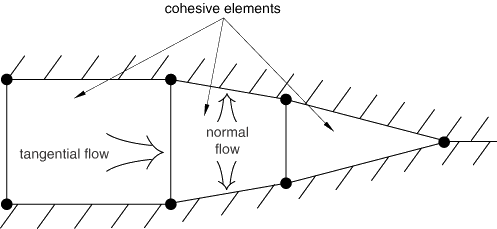
By default, there is no tangential flow of pore fluid within the cohesive
element. To allow tangential flow, define a gap flow property in conjunction
with the pore fluid material definition.
Newtonian Fluid
In the case of a Newtonian fluid the volume flow rate density vector is
given by the expression
where
is the tangential permeability (the resistance to the fluid flow),
is the pressure gradient along the cohesive element, and
is the gap opening.
In
Abaqus
the gap opening, ,
is defined as
where
and
are the current and original cohesive element geometrical thicknesses,
respectively; and
is the initial gap opening, which has a default value of 0.002.
Abaqus
defines the tangential permeability, or the resistance to flow, according to
Reynold's equation:
where
is the fluid viscosity and
is the gap opening. You can also specify an upper limit on the value of
.
Power Law Fluid
In the case of a power law fluid the constitutive relation is defined as
where
is the shear stress,
is the shear strain rate,
is the fluid consistency, and
is the power law coefficient.
Abaqus
defines the tangential volume flow rate density as
where
is the gap opening.
Bingham Plastic Fluid
In the case of a Bingham plastic fluid the volume flow rate density vector is given by the
expression
where
is the fluid consistency,
is the yield stress, and
is the gap opening. The unyielded fluid is modeled as a Newtonian
fluid with viscosity equal to
, where
has a default value of 107.
Herschel-Bulkley Fluid
In the case of a Herschel-Bulkley fluid the volume flow rate density vector is given by the
expression
where
is the fluid consistency,
is the power law coefficient,
is the yield stress, and
is the gap opening. The unyielded fluid is modeled as a Newtonian
fluid with viscosity equal to
, where
has a default value of 107.