PROJECTION CARTESIAN | |
| |
Description
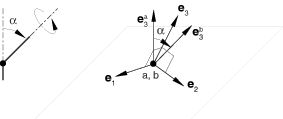
The PROJECTION CARTESIAN connection does not impose kinematic constraints. It defines three local directions as a function of the directions at both nodes a and b. These directions are the projection directions defined by the PROJECTION FLEXION-TORSION connection. The PROJECTION CARTESIAN connection measures the change in position of node b relative to node a along the (projection) coordinate directions .
The position of node b relative to node a is
The available components of relative motion are
where , , and are the initial coordinates of node b relative to node a along the initial directions. The connector constitutive displacements are
The local directions in a PROJECTION CARTESIAN connection are “centered” between the systems at the two connector nodes. PROJECTION CARTESIAN connections are appropriate where isotropic or anisotropic material response is modeled and the local material directions evolve as a function of the rotations at both ends of the connection. The kinetic force is
In two-dimensional analysis , , , and .
Summary
| PROJECTION CARTESIAN | |
|---|---|
| Basic, assembled, or complex: | Basic |
| Kinematic constraints: | None |
| Constraint force output: | None |
| Available components: | |
| Kinetic force output: | |
| Orientation at a: | Optional |
| Orientation at b: | Optional |
| Connector stops: | |
| Constitutive reference lengths: | |
| Predefined friction parameters: | None |
| Contact force for predefined friction: | None |