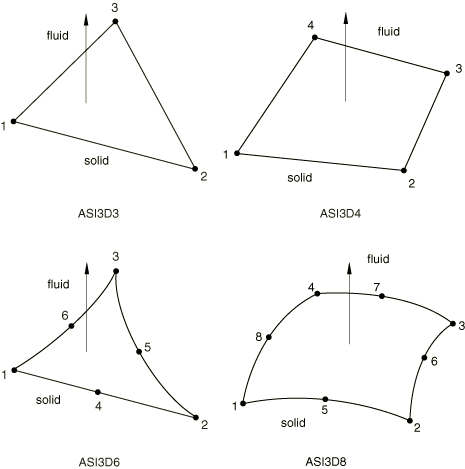
Typical Applications
The acoustic interface elements are used in simulations where the motion of a solid structure influences the pressure in the acoustic fluid, such as when the vibrations of a car frame produce noise in the passenger compartment; or where the pressure in the fluid affects a neighboring structure, such as when the small-amplitude sloshing of a fluid inside a container affects its response.
User-specified acoustic interface elements are also useful in problems involving only an acoustic medium because they allow you to specify displacement, velocity, or acceleration boundary conditions directly on the nodes of the acoustic interface elements. In this application, however, you must be aware that the tangential displacements are not coupled to the fluid. Therefore, zero-energy modes may arise involving the displacement degrees of freedom if these nodes are not constrained in the tangential direction. When acoustic interface elements are used to couple fluid and solid elements, this problem does not arise because of the stiffness and inertia of the solid.