|
Element Types
Plane Strain Solid Continuum Infinite Elements
-
CINPE4
-
4-node linear, one-way infinite
-
CINPE5R(S)
-
5-node quadratic, one-way infinite
Active Degrees of Freedom
1, 2
Additional Solution Variables
None.
Plane Stress Solid Continuum Infinite Elements
-
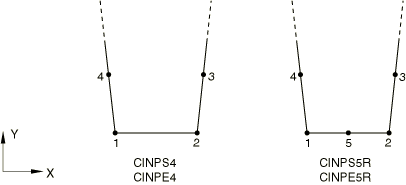
CINPS4
-
4-node linear, one-way infinite
-
CINPS5R(S)
-
5-node quadratic, one-way infinite
Active Degrees of Freedom
1, 2
Additional Solution Variables
None.
3D Solid Continuum Infinite Elements
-
CIN3D8
-
8-node linear, one-way infinite
-
CIN3D12R(S)
-
12-node quadratic, one-way infinite
-
CIN3D18R(S)
-
18-node quadratic, one-way infinite
Active Degrees of Freedom
1, 2, 3
Additional Solution Variables
None.
Axisymmetric Solid Continuum Infinite Elements
-
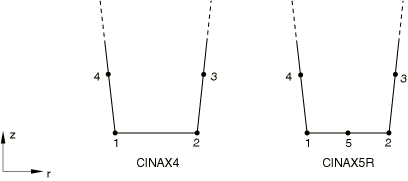
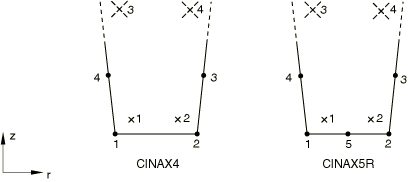
CINAX4
-
4-node linear, one-way infinite
-
CINAX5R(S)
-
5-node quadratic, one-way infinite
Active Degrees of Freedom
1, 2
Additional Solution Variables
None.
2D Acoustic Infinite Elements
-
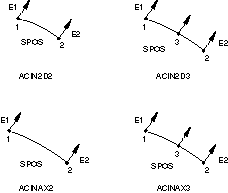
ACIN2D2
-
2-node linear, acoustic infinite
-
ACIN2D3(S)
-
3-node quadratic, acoustic infinite
Active Degrees of Freedom
8
3D Acoustic Infinite Elements
-
ACIN3D3
-
3-node linear, acoustic infinite triangular element
-
ACIN3D4
-
4-node linear, acoustic infinite quadrilateral element
-
ACIN3D6(S)
-
6-node quadratic, acoustic infinite triangular element
-
ACIN3D8(S)
-
8-node quadratic, acoustic infinite quadrilateral element
Active Degrees of Freedom
8
Axisymmetric Acoustic Infinite Elements
-
ACINAX2
-
2-node linear, acoustic infinite
-
ACINAX3(S)
-
3-node quadratic, acoustic infinite
Active Degrees of Freedom
8
Nodal Coordinates Required
Plane stress and plane strain solid continuum elements:
X, Y
2D acoustic
elements: X, Y
3D solid
continuum and acoustic elements: X,
Y, Z
Axisymmetric solid
continuum and acoustic elements: r,
z
Normal directions are not specified at nodes
used in acoustic infinite elements; they will be computed automatically. See
Infinite Elements
for details.
Element Property Definition
For
two-dimensional, plane strain, and plane stress elements, you must provide the
thickness of the elements; by default, unit thickness is assumed.
For three-dimensional and axisymmetric solid elements, you do not need to
specify a thickness.
For acoustic elements, you must specify the
reference point in addition to the thickness.
Element-Based Loading
Element Output
Stress, Strain, and Other Tensor Components
No
output is available from
Abaqus/Explicit
for infinite elements. Stress and other tensors (including strain tensors) are
available from
Abaqus/Standard
for infinite elements with displacement degrees of freedom. All tensors have
the same components. For example, the stress components are as follows:
-
S11
-
direct stress or radial stress for axisymmetric elements.
-
S22
-
direct stress or axial stress for axisymmetric elements.
-
S33
-
direct stress (not available for plane stress elements) or hoop stress for
axisymmetric elements.
-
S12
-
shear stress or shear stress for axisymmetric elements.
-
S13
-
shear stress (not available for plane stress, plane strain, and axisymmetric
elements).
-
S23
-
shear stress (not available for plane stress, plane strain, and axisymmetric
elements).
Node Ordering and Face Numbering on Elements
Plane Stress and Plane Strain Solid Continuum Elements
Axisymmetric Solid Continuum Elements
Three-Dimensional Solid Continuum Elements
Two-Dimensional and Axisymmetric Acoustic Infinite Elements
Three-Dimensional Acoustic Infinite Elements
Numbering of Integration Points for Output
Plane Stress and Plane Strain Solid Continuum Elements
Axisymmetric Solid Continuum Elements
Three-Dimensional Solid Continuum Elements
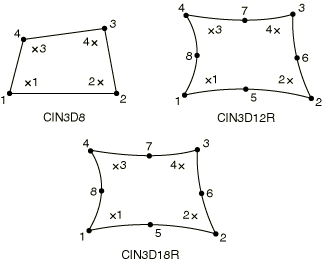
This shows the scheme in the layer closest to the 1–2–3–4 face. The
integration points in the second layer are numbered consecutively.
|