|
Element Types
2D Rigid Elements
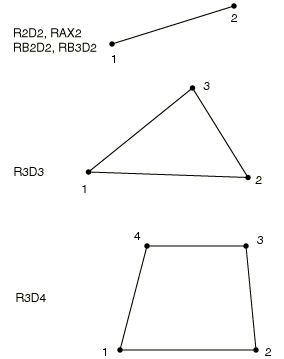
- R2D2
2-node, linear link (for use in plane strain or plane stress) - RAX2
2-node, linear link (for use in axisymmetric planar geometries) - RB2D2(S)
2-node, rigid beam Secondary Degrees of Freedom
R2D2 and
RAX2: 1, 2
RB2D2: 1, 2, 6
Main Degrees of Freedom
R2D2, RAX2, and RB2D2: 1, 2, 6 at the rigid body reference node
Additional Solution Variables
None.
3D Rigid Elements
- R3D3
3-node, triangular facet - R3D4
4-node, bilinear quadrilateral - RB3D2(S)
2-node, rigid beam Secondary Degrees of Freedom
R3D3 and R3D4: 1, 2, 3
RB3D2: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Main Degrees of Freedom
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 at the rigid body reference node
Additional Solution Variables
None.
Nodal Coordinates Required
R2D2 and RB2D2: X, Y
RAX2: r, z
R3D3, R3D4, and RB3D2: X, Y, Z
Element Property Definition
For R2D2, RB2D2, and RB3D2 elements you can specify the cross-sectional area of the element. In Abaqus/Standard if no area is given, unit area is assumed; the area is required in Abaqus/Explicit.
For RAX2, R3D3, and R3D4 elements you can specify the thickness of the element. In Abaqus/Standard if no thickness is given, unit thickness is assumed; the thickness is required in Abaqus/Explicit.
The cross-sectional area or element thickness is used for the purpose of defining body forces, which are given in units of force per unit volume, and, in Abaqus/Explicit, determining the total mass.
Element-Based Loading
Distributed Loads
Distributed loads are available for elements with displacement degrees of freedom. They are specified as described in Distributed Loads.
*dload
Available for R2D2 elements only:
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BX(S)
- FL−3
Body force in global X-direction.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BY(S)
- FL−3
Body force in global Y-direction.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BXNU(S)
- FL−3
Nonuniform body force in global X-direction with magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BYNU(S)
- FL−3
Nonuniform body force in global Y-direction with magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): CENT(S)
- FL−4 (ML−3T−2)
Centrifugal load (magnitude is input as , where is the mass density per unit volume and is the angular velocity).
- Load ID (*DLOAD): CORIO(S)
- FL−4T (ML−3T−1)
Coriolis force (magnitude is input as , where is the mass density per unit volume and is the angular velocity). The load stiffness due to Coriolis loading is not accounted for in direct steady-state dynamics analysis.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): P(E)
- FL−2
Pressure on the element surface. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): PNU(E)
- FL−2
Nonuniform pressure on the element surface with magnitude supplied via user subroutine VDLOAD. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
*dload
Available for RAX2 elements only:
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BR(S)
- FL−3
Body force per unit volume in the radial direction.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BZ(S)
- FL−3
Body force per unit volume in the axial direction.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BRNU(S)
- FL−3
Nonuniform body force per unit volume in the radial direction, with the magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BZNU(S)
- FL−3
Nonuniform body force per unit volume in the z-direction, with the magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): CENT(S)
- FL−4 (ML− 3T−2)
Centrifugal load (magnitude given as , where is the mass density and is the angular speed). Since only axisymmetric deformation is allowed, the spin axis must be the z-axis.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): HP(S)
- FL−2
Hydrostatic pressure on the element surface and linear in global Z. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): P
- FL−2
Pressure on the element surface. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): PNU
- FL−2
Nonuniform pressure on the element surface with the magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD in Abaqus/Standard and VDLOAD in Abaqus/Explicit. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRSHR
- FL−2
Shear traction on the element surface.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRSHRNU(S)
- FL−2
Nonuniform shear traction on the element surface with magnitude and direction supplied via user subroutine UTRACLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRVEC
- FL−2
General traction on the element surface.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRVECNU(S)
- FL−2
Nonuniform general traction on the element surface with magnitude and direction supplied via user subroutine UTRACLOAD.
*dload
Available for R3D3 and R3D4 elements only:
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BX(S)
- FL−3
Body force in the global X-direction.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BY(S)
- FL−3
Body force in the global Y-direction.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BZ(S)
- FL−3
Body force in the global Z-direction.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BXNU(S)
- FL−3
Nonuniform body force in the global X-direction with magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BYNU(S)
- FL−3
Nonuniform body force in the global Y-direction with magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): BZNU(S)
- FL−3
Nonuniform body force in the global Z-direction with magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): CENT(S)
- FL−4 (ML−3T−2)
Centrifugal load (magnitude is input as , where is the mass density per unit volume and is the angular velocity).
- Load ID (*DLOAD): CORIO(S)
- FL−4T (ML−3T−1)
Coriolis force (magnitude is input as , where is the mass density per unit volume and is the angular velocity). The load stiffness due to Coriolis loading is not accounted for in direct steady-state dynamics analysis.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): HP(S)
- FL−2
Hydrostatic pressure on the element surface and linear in global Z. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): P
- FL−2
Pressure on the element surface. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): PNU
- FL−2
Nonuniform pressure on the element surface with magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD in Abaqus/Standard and VDLOAD in Abaqus/Explicit. The pressure is positive in the direction of the positive element normal.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRSHR
- FL−2
Shear traction on the element surface.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRSHRNU(S)
- FL−2
Nonuniform shear traction on the element surface with magnitude and direction supplied via user subroutine UTRACLOAD.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRVEC
- FL−2
General traction on the element surface.
- Load ID (*DLOAD): TRVECNU(S)
- FL−2
Nonuniform general traction on the element surface with magnitude and direction supplied via user subroutine UTRACLOAD.
Abaqus/Aqua Loads
Abaqus/Aqua loads are specified as described in Abaqus/Aqua Analysis.
*cload/ *dload
Available for R3D3 and R3D4 elements only:
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): PB
- FL−2
Buoyancy force.
*cload/ *dload
Available for RB2D2 and RB3D2 elements only:
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): FDD
- FL−1
Transverse fluid drag force.
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): FD1
- F
Fluid drag force on the first end of the rigid link (node 1).
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): FD2
- F
Fluid drag force on the second end of the rigid link (node 2).
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): FDT
- FL−1
Tangential fluid drag load.
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): FI
- FL−1
Transverse fluid inertia load.
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): FI1
- F
Fluid inertia load on the first end of the rigid link (node 1).
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): FI2
- F
Fluid inertia load on the second end of the rigid link (node 2).
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): PB
- FL−1
Buoyancy force (with closed-end condition).
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): WDD
- FL−1
Transverse wind drag force.
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): WD1
- F
Wind drag force on the first end of the rigid link (node 1).
- Load ID (*CLOAD/ *DLOAD): WD2
- F
Wind drag force on the second end of the rigid link (node 2).
Surface-Based Loading
Distributed Loads
Surface-based distributed loads are available for elements with displacement degrees of freedom. They are specified as described in Distributed Loads.
*dsload
Available for RAX2, R3D3, and R3D4 elements only:
- Load ID (*DSLOAD): HP(S)
- FL−2
Hydrostatic pressure on the element surface and linear in global Z. The pressure is positive in the direction opposite to the surface normal.
- Load ID (*DSLOAD): P
- FL−2
Pressure on the element surface. The pressure is positive in the direction opposite to the surface normal.
- Load ID (*DSLOAD): PNU
- FL−2
Nonuniform pressure on the element surface with the magnitude supplied via user subroutine DLOAD in Abaqus/Standard and VDLOAD in Abaqus/Explicit. The pressure is positive in the direction opposite to the surface normal.
- Load ID (*DSLOAD): TRSHR
- FL−2
Shear traction on the element surface.
- Load ID (*DSLOAD): TRSHRNU(S)
- FL−2
Nonuniform shear traction on the element surface with magnitude and direction supplied via user subroutine UTRACLOAD.
- Load ID (*DSLOAD): TRVEC
- FL−2
General traction on the element surface.
- Load ID (*DSLOAD): TRVECNU(S)
- FL−2
Nonuniform general traction on the element surface with magnitude and direction supplied via user subroutine UTRACLOAD.
Element Output
Node Ordering on Elements
|