Sequence Diagram View Structure
A sequence diagram view is always created in a sheet. This sheet can be attached to a function or a logical component.
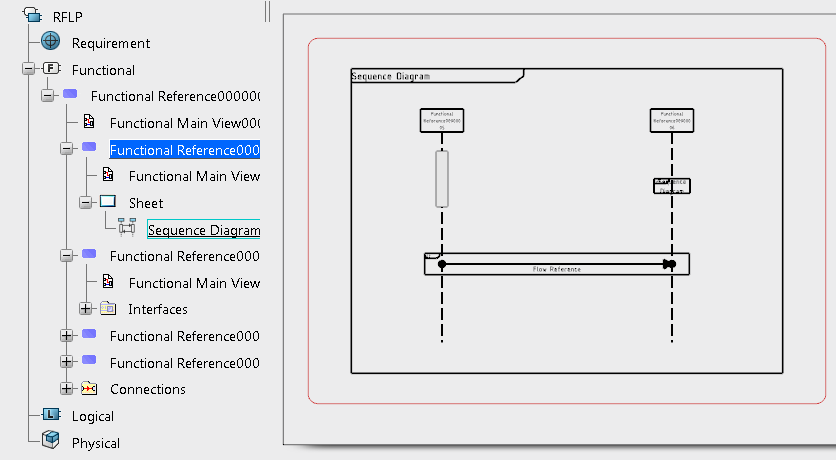
Sequence Diagram View StructureA sequence diagram view is always created in a sheet. This sheet can be attached to a function or a logical component.
Elements of a Sequence Diagram ViewIn a sequence diagram view, you can insert different elements. Actor and LifelineAn actor is a basic component of a system. It is associated to a lifeline. In a sequence diagram view, it represents a function or a logical component. An actor can interact with other actors. ActivationAn activation is an execution specification. It indicates that the actor answers to messages. MessageA message is a communication link or a signal transmitted from an actor to another. A message or multiple messages can be inserted between two actors displayed in a sequence diagram view. When you create a message, a message point is created to connect the following objects:
There are three types of messages you can define when you create a message:
A message can be defined with several variables:
Note:
For more information about message variables, see About Message Variables
Interaction UseAn interaction use can be inserted in a sequence diagram view. It represents another sequence diagram in the current sequence diagram view. An interaction use can be associated to message points and linked to one or several lifelines. Block and GuardA block can be inserted in a sequence diagram view to group messages and interaction use elements. Multiple blocks can be grouped in a guard. A guard can be inserted in a sequence diagram view to group multiple blocks and apply them a condition. There are five conditions:
| |||||||