Normal Distribution | ||||
|
| |||
The normal or Gaussian distribution is a two-parameter distribution defined in terms of the mean and standard deviation of the random variable .
The normal distribution probability density function is
The distribution function corresponding to the density function of the previous equation is given by
where 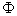 is the standard normal distribution function ( and ) defined by
is the standard normal distribution function ( and ) defined by
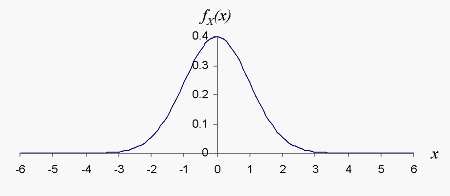
The corresponding standard normal density function, illustrated in the following figure, is given by
The normal distribution, which is shown in the figure below, is the common “bell curve” distribution,
often used for physical measurements, product dimensions, and average
temperatures.