About Swept Volumes | |
| |
A sweep collectively plots the position of the selected part at each step in the simulation, then connects the discrete position plots with continuous geometry based on the specified interpolation options. The result is a smooth three-dimensional body.
A swept volume is defined by one or several bodies associated with existing products, and according to a reference marker. By default, the reference marker is a stationary, universal reference marker used to represent the true motion of the selected elements in a three-dimensional space.
You can specify another marker from a different moving product of the active mechanism as the reference point. In this case, the generated swept volume represents the motion of the elements according to the relative motion of the reference part or product.
The following figure illustrates the swept volume of a pendulum: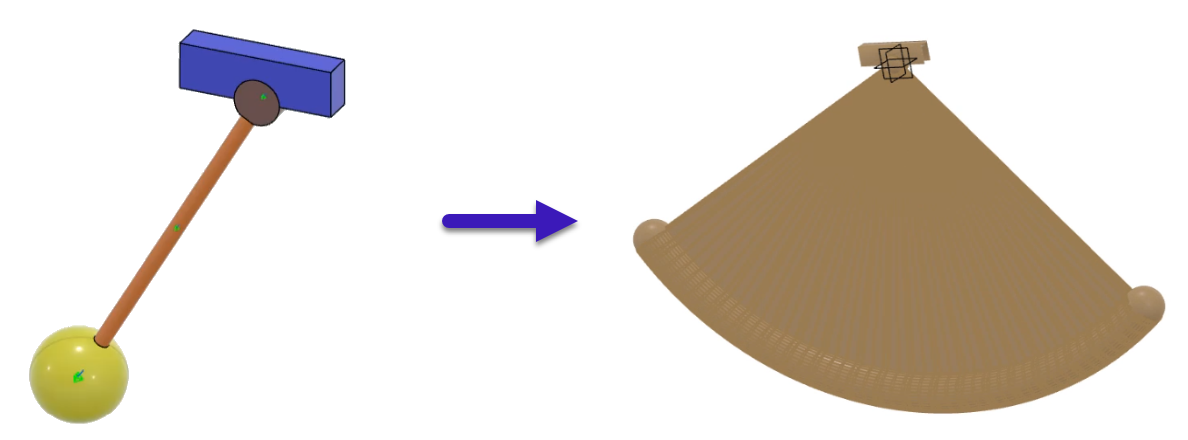
You can generate the swept volume of a product or part according to the following parameters:
- Filtering Positions
- Wrapping
- Simplification