About Approximation | ||||
|
| |||
The approximation is computed in two steps:
-
Creation of an initial B-Spline
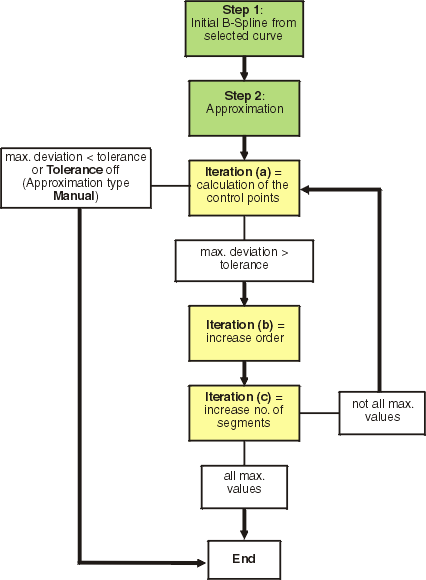
With the first step, for each selected curve is created an initial B-Spline, defining the parametrization and the number of control points, but not their values. The B-Spline results from the B-Spline of the curve to be approximated as well as from the minimum and maximum values of the order and the number of segments specified by the user:
Order and number of segments of the B-Spline are taken from the curve to be approximated, if they are within the specified minimum and maximum ranges. Otherwise, they are increased or reduced to the corresponding minimum or maximum value.
Note: If in the selected geometry G2 discontinuities are found, they are transferred as sharp bends to the initial B-Spline. In this case, the initial B-Spline may contain more segments than the maximum value specified for the segmentation. -
Iterations
After the creation of the initial B-Spline, the actual approximation is computed in the second step. This is realized by a three-step iteration:
-
Iteration (a)
In the first iteration, the (optimal) values of the control points of the B-Spline are computed using a Newton method. The control points allow the computation of the maximum deviation between the computed approximation curve and the original curve. If this value is smaller than the tolerance value specified by the user, the iteration is terminated successfully.
-
Iteration (b) + (c)
If the computed deviation is larger than the tolerance specified, the B-Spline will be modified by increasing order and number of segments, and the iteration (a) is restarted.
Independent from the approximation type set, first the order and then the number of segments is increased. This way, the number of segments of the created curves can be minimized.
-