Perform a Deviation Analysis
You can specify several parameters to perform the deviation analysis.
- From the View section of the action bar, click Customize View
 .
. - From the Tools section of the action bar, click Deviation Analysis
 .
. - Select the Reference
data and the data To measure:
- Reference data can be a volume, a surface, a plane, a point, a curve, or a cloud of points.
- To measure data can be clouds of points, points, curves, surfaces, or volumes.
- When the data To measure are curves, surfaces, or volumes, they are discretized.
- Multiselection is available:
 is available to hide or show the Reference and the To measure data.
is available to hide or show the Reference and the To measure data.
- Set the computation parameters:
- Determine the discretization Accuracy, available only when at least one curve, volume, or surface is selected as Reference.
- Select Only Orthogonal to eliminate points that are not projected orthogonally on the Reference:
- Select Absolute to perform the analysis with absolute values only.
- When the Reference is a curve, a surface or a body, and for more precise results, select Exact to project the To measure geometry on the Reference exact curve (instead of on its discretization) , or on exact surface (instead of on its tessellation). The projection is either orthogonal or along the chosen direction.
- Select Direction to define a projection direction by picking a plane or
a line.
Notes:
- Right-click Direction and select the required menu item.
- Or right-click the Robot and select Lock Privileged Plane Orientation Parallel to Screen and Robot Direction.
- If you change the direction, do not forget to update the deviation analysis feature.
- Specify the Visualization parameters:
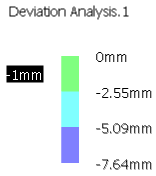
- Select Spikes to activate the visualization of the spikes.
- Select Points to change the display to points.
- Click Options to customize the display of
Spikes
and Points.
Use
- Spike scale to change the length of the spikes.
- Point to change the display symbol of points.
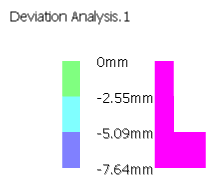
- Select Texture to display the deviations
as textures.
Notes:
- Texture is applied to the data To measure.
- The data To measure must be a mesh, a surface or a volume.
- The Render Style must be Shading with Material. If this is not the case, a message asks you to switch to this Render Style.
- Texture mode is available on meshes only, their display mode being either Flat or Smooth.
- Texture mode is always available but only triangles with values on their
three vertices are displayed. In the example below, the triangles on the top and
on the left are not displayed in Texture mode.

- There must be a color for each value. The No color and the Hide dimmed points options apply to spikes and points visualizations only. They have no effect on texture mode.
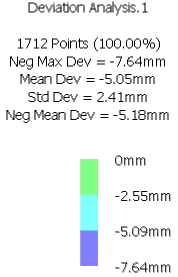
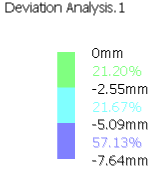
- Select Max values to display the maximum deviation values (positive and negative) and their locations on the data To measure.
- Click More>>.
- Define Advanced Parameters and the
Display
Format.
- Select Homogeneous filtering to reduce the number of points of the data To measure to take into account. A sphere filtering is applied. The parameter represents the radius of this sphere.
- Select Threshold to remove points with a deviation higher than this threshold.
- Select Step when the data to measure are curves, surfaces, oror volumes. It controls the length of the discretization triangles f surfaces or volumes, or of the segments for curves. If you do not select this check box and enter a value, Deviation Analysis computes the step, but in some cases it is better that you define your own step value.
- Set the Display Format:
- Style: three styles are available:
- Scientific
- Decimal
- Automatic
- Define the Number of significant digits between 1 and 15.
- Style: three styles are available:
- Click Apply to take any modification into
account.If Points or Spikes are selected, when you move the pointer over the element To measure, the deviation value between the point below the pointer and the Reference data is displayed.
An editable Deviation Analysis.x feature is created.