About Lattices | |||||
|
| ||||
Lattice Commands
The following two commands are available in Lattice Design for lattice creation:
- Lattice Struts
 : creates the visualization of the lattices with the selected visualization mode, in a
separate body.Note: In the tree, under the Lattice.x feature, the volume parameter displayed is approximate.
: creates the visualization of the lattices with the selected visualization mode, in a
separate body.Note: In the tree, under the Lattice.x feature, the volume parameter displayed is approximate. - Lattice Geometry
 :
creates the actual lattice geometry from the visualization created using the
Lattice Struts command.
:
creates the actual lattice geometry from the visualization created using the
Lattice Struts command.
Lattice Types
The following two types of lattice are available for selection:
- Rectangular
 : A rectangular
lattice is a regular 3D pattern, connected along three noncollinear directions with a
constant step size in each direction. In most cases, the directions are always
perpendicular to each other.
: A rectangular
lattice is a regular 3D pattern, connected along three noncollinear directions with a
constant step size in each direction. In most cases, the directions are always
perpendicular to each other.
- Cylindrical
 : A cylindrical
lattice is a 3D pattern, connected along two noncollinear directions:
: A cylindrical
lattice is a 3D pattern, connected along two noncollinear directions:
For the cylindrical lattices, a reference axis needs to be defined. Apart from the axis, you can specify the following axis options:
- Neutral radius: It is the distance from the axis where the actual length or the instantiated cells are close to the specified cell.
- Minimum bar length: This is the minimum permissible size of a cell. The cells with length shorter than this value are not created.
Lattice Visualization Modes
The following three visualization modes are available for selection:
- Cavity: displays the lattice area cavity with the selected lattice cell texture.
- Wireframe: generates the lattices in the form of wireframes
inside the lattice area.
 By default, this mode is selected.
By default, this mode is selected. - Bars: generates the lattices in the form of bars inside the lattice area.
Advanced Options
The following advanced options are available for modifying the lattice design:
- Decimation Sag: simplifies the tessellation of a polyhedral
object to reduce the number of bars and triangles.
Table 1. Decimation Sag Result Decimation Sag=0.5mm Decimation sag=2mm 

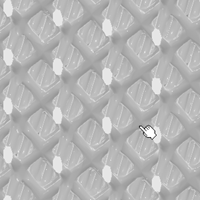
- Smoothing Value: improves the smoothness of the intersection of the bars at the nodes. The smoothness increases with the value.
| Smoothing Value=0 | Smoothing Value=10 |
|---|---|
 |
 |