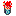The Multi-Motion Editor appears when you click
Edit Robot Motion  from a drilling and riveting or milling operation dialog box. It displays one robot motion for each toolpath move.
from a drilling and riveting or milling operation dialog box. It displays one robot motion for each toolpath move.
- Linking Motion identifies points such as approach, retract, and linking points.
- Cutting Motion identifies a point that corresponds to a machining position.
Motions
For each motion, the Multi-Motion Editor provides information such as:
- Status: displays if the robot reaches the target point.

| Unchecked reachability |

| Reachable |
| Unreachable |
- Target: displays the values of the motion target.
- Configuration: displays the name of the current robot configuration.
- Joint value of the auxiliary device.
- Turn value of the joint. The value can be positive or negative depending on the robot structure. You can modify the value if you want the robot joint to be superior to 360 degrees.
- Motion type: displays whether the motion is joint or linear. By default, the first motion is joint, and following motions are linear.
Commands
- Check Reachability

- Checks that the robot reaches a specified tool path motion. If not, it automatically computes a value at which the robot can reach the position. This command is available for auxiliary devices (rails) with one DOF only.
Simulation Player
The simulation player lets you navigate from one motion to another during simulation of the robot.
 | Play | Plays the entire robot task, from the first motion to the last motion. |
 | Pause | Pauses the simulation at the current motion. |
Recommendations
- To correctly position the robot at each point of the tool path, you must define a direction for the lateral axis (x-axis) when creating a machining operation.
- To define a repeatable move on robots controlled by a motion controller, you must set the configuration and turn values of the robot.
![]() from a drilling and riveting or milling operation dialog box. It displays one robot motion for each toolpath move.
from a drilling and riveting or milling operation dialog box. It displays one robot motion for each toolpath move.