Multi-Axis Swarf Milling | ||||
|
| |||
Resource Parameters
The Resource tab allows you to select a tool.
- Resource Tab
-
Parameter Description Select a Tool from Session 
Selects a tool in Resource Configuration View. Select from Catalog 
Selects a tool from a reference tool file or PLM catalog. Select from Database 
Selects a tool from the database. Display Tool Properties 
Accesses tool parameters. Define Tool Axis 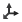
Defines the tool axis. Tool Number Defines the number of tools. Display Tool Displays the tool position. Default Displays the tool at default position. User Defined Displays the tool at a position defined by the user. Note: You can define the tool position using Select a Tool from Session .
. - Tools
- Recommended tools for Multi-Axis Swarf Milling operation are
End Mills
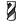 and T-Slotters
and T-Slotters 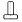 .
.
Geometry
the Geometry allows you to define the geometric parameters that are machined.
- Mandatory Parameters
-
Parameter Description Drive Defines the drive surfaces to be followed by the flank of the tool. Start Element Defines the first drive on which the tool path starts. Stop Element Defines the last drive on which the tool path ends. Tool Axis Defines the tool axis. - Optional Parameters
-
Parameter Description Part Selects the parts to machine. Check Specifies surfaces to exlude from the machining activity (geometry saves on the deburring feature). - Other Parameters
-
Parameter Description Start Positions the tool with respect to the start elements by selecting one of the proposed options: - In
- On
- Out
Stop Positions the tool with respect to the stop elements by selecting one of the proposed options: - In
- On
- Out
Offset Along Tool Axis Specifies the offset along the tool axis.
Strategy Parameters
The Strategy tab allows you to specify the strategy and user parameters.
- Machining

- Finishing Parameters

-
Parameter Description Side Finish Pass Mode Specifies the side finish pass mode. You can select one of the following modes: - No Finish Pass
- Side Finish at Last Level
- Side Finish at Each Level
- Finish Bottom Only
- Side Finish at Each Level and Bottom
- Side Finish at Last Level and Bottom
- Tool Axis Strategy Parameters

-
Parameter Description Fixed Axis for Semi-Finishing Paths Defines useful cutting length on current tool when Control Fanning Using Tool Parameter is activated. Guidance Specifies the tool axis strategy. Tanto Fan The tool is tangent to the drive surface at a given contact height, and the tool axis is interpolated between the start and end positions. Fixed Axis The orientation of the tool axis is fixed. Contact Height Determines a point on the drive surface where the tool must respect tangency conditions. The Contact Height is measured from the tool tip along the tool axis. The point on the drive is computed such that its projection normal to the drive onto the tool axis respects the Contact Height value. Tilt Angle Specifies a positive angle to lean the tool right. Note: Tilt angle parameter is disabled in Fixed Axis mode.Lead Angle Specifies a positive angle to lean the tool forwards. Note: Lead Angle parameter is disabled in Fixed Axis mode. Sometimes with Tanto Fan mode, constraints on the tool path cannot be applied. - High Speed Milling (HSM) Strategy Parameters
-
Parameter Description Cornering Specifies whether or not cornering is to be done on the trajectory for HSM. Radius Specifies the radius used for rounding the corners along the trajectory of a HSM operation. Value must be smaller than the tool radius. Finishing Cornering Specifies whether or not tool path cornering is to be done on side finish paths. Radius Specifies the corner radius used for rounding the corners along the side finish path of a HSM operation. Value must be smaller than the tool radius. - Output Parameters

-
Parameter Description Output Type Defines the output type: - No
- 3d Radial (PQR)
- 2D Radial - TIP (G41/G42)
Tool Axis Parameters
- Collisions Checking
-
Parameter Description Offset on Tool Defines the tolerance distance specific to the tool radius and tool length. Offset on Tool Assembly Defines the tolerance distance specific to the tool assembly radius and tool length.
- Machine Kinematics
- This tab lets you correct problems encountered with respect of the machine kinematics.
Macros Parameters
The Macros tab allows you to define transition paths in your machining operations by means of NC macros.
- Approach
- Retract
- Clearance
- Linking Retract
- Linking Approach
- Return in a Level Retract
- Return in a Level Approach
- Return Finish Pass Retract
- Return Finish Pass Approach
- Return Between Levels Retract
- Return Between Levels Approach
For more information, see NC Machining Apps Common Services: Using the Working Area: Creating Machining Operations: Defining Macros: NC Macros.
Feeds and Speeds Parameters
The Feeds and Speeds tab allows you to define the following feeds and speeds parameters.
- Feedrate
-
Parameter Description Feedrate Unit Two available feedrate units: - Linear
- Angular
Approach Feedrate Defines the speed of linear/angular advancement of the tool during its approach, before cutting. Machining Feedrate Defines the speed of linear/angular advancement of the tool during machining. Retract Feedrate Defines the speed of linear/angular advancement of the tool during its retract, after cutting. Finishing Feedrate Defines the speed of linear/angular advancement of the tool during finishing. Transition Activates the transition. Feedrate Transition Transition options: - Machining
- Approach
- Retract
- RAPID
- Local
Local Value Specifies the local feedrate value. RTCP ON When selected, activates RTCP mode on transition paths between the previous and current operations. - Feedrate Reduction in Corners Combined with Local Slowdown Rate
- If the Feedrate reduction in corners option is selected and
local Slowdown rates are applied to drives, the general rule is that the corner feedrate
reduction rate is applied after the local Slowdown rate on the
current feedrate. For a machining feedrate, the feedrate will be equal to:
machining feedrate * local Slowdown rate * corner Reduction rate.
. - Spindle Speed
-
Parameter Description Spindle Unit Angular or linear. Machining Spindle Defines the speed of the spindle linear/angular advancement.