Certain operations can safely be performed on each VM using
the Hyper-V Manager, but others are not supported because they
change the ComputerID, which in turn invalidates the license
keys. Like for physical machines, backup/restore are
not supported.
-
You can perform the following operation (which do not change the
ComputerID):
- Turn Off (then Start) VM
- Shutdown (then Start) VM
- Save (then Start) VM
- Pause (then Resume) VM
- Reset VM
- Move VM, including Live Migration
- Rename VM.
Note:
Export VM is supported, but is not useful
since Import VM is not supported.
-
Do not perform the following operations (which do change the
ComputerID):
- Import
- Replication
- Checkpoint (ensure checkpoints have been disabled).
Offline Licensing Restrictions
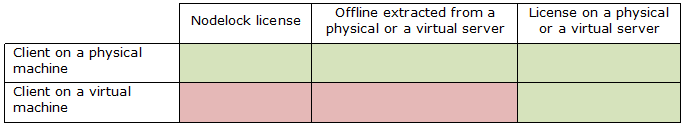
Generally, any V5/V6/3DEXPERIENCE DSLS licensing client works the same way when connected to a DS License Server running in a VM, but there are restrictions concerning offline licensing.
In particular, when running a licensing client
in a virtual machine, it is still not possible to extract an offline
license. There is no difference if the license server itself is running in a
virtual machine or a physical machine.
And it is still not possible to get nodelock
licenses to work in a VM.
The following table summarizes the different cases (green = supported; red = not supported):
Limitations
The following list summarizes limitations:
- When the DS License Server runs as a service in
a physical machine, the account used is
Network Service. However,
when running in a VM, the account used by the Windows
service is Local System. - Standalone license server is not
supported
- Nodelock licenses are not supported
- Windows versions lower than Windows Server 2016 are not supported
- Linux is not supported
- VMWare and other hypervisors are not supported
- Microsoft Azure is not supported. This is because the Hyper-V implementation in Azure
is different from its implementation on physical computers.
- Nested VMs are not supported: the VM in which the license server runs must be hosted by a physical machine, and not by another VM.
