About Proximity and Orientation Requirements | ||||
|
| |||
When you use the contact detection tool or directly create surface-based contact pairs (either sliding or bonded):
- The two surfaces must be roughly facing each other.
- Display options may affect the distance between surfaces.
Separation Tolerance
For contact detection, the search tolerance for detecting potential contact surfaces is very small (0.001 mm). For surface-based contact, the effective separation distance is not considered.
Typically heat transfer between surfaces occurs only when the surfaces are touching each other. Therefore, two surfaces must be very close to each other to create a meaningful thermal (surface-based) contact feature.
Orientation
Two surfaces must be facing each other to allow bonded or sliding contact to be defined. For
example, contact could not be created in the following geometry. The parallel faces
in each component are offset from each other, and the angle between the
perpendicular faces is too large. 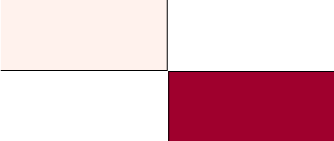
Display Options
The separation calculations for contact surface pairs are based on the display geometry of a
model. The display geometry may differ from the true geometry based on your display
accuracy settings (see
3D Accuracy). A low accuracy setting
can introduce tessellation to your display geometry, which in turn can impact the
tolerance calculations. For example, tessellation on a convex surface may cause
increased separation from a mating surface: 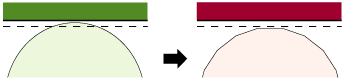
If contact detection does not work or you are unable to define surface-based contact between two surfaces, increasing the display accuracy may decrease the separation distance between the surfaces. However, more commonly you must adjust the geometry of the model to bring the surfaces into conformance with the proximity requirements.