Top level configuration class(es) | ||||||
|
| |||||
The framework will usually:
-
manage the serialized configuration (as an XML object),
-
unserialize it,
-
create an instance of the given class, and allow you to edit its properties,
-
handle the configuration of components from the Administration Console.,
-
etc.
The exact workflow is specific to each component type. For example, some component types may not have any configuration at all.
A configuration class must implement the empty
CVComponentConfig
(com.exalead.mercury.component.config.CVComponentConfig) interface to
be accepted as a valid configuration class.
Example:
/**
* The configuration class for the filesystem connector.
**/
@CVComponentDescription("Filesystem simple demo (java)")
public class DemoFileSystemConnectorConfig extends ConnectorConfig
{
private File startingFolder = null;
@IsMandatory(false)
public void setStartingFolder(final File startingFolder)
{
this.startingFolder = startingFolder;
}
public File getStartingFolder()
{
return startingFolder;
}
/**
* Optional method listing all option names as they will be displayed in the UI
**/
public static String[] getMethods()
{
return new String[] { "StartingFolder" };
}
}
getMethods may be defined in a configuration class, to
return properties in a specific order. This method should be public, taking no
argument, and returning an array of String corresponding to the ordered
property names.
Example :
public static String[] getMethods()
{
return new String[]{"Proxy", "ProxyPort"};
}
|
Interface |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Allows you to define a
This method is used to perform specific post-actions related to filled properties. This interface is not required to get a working configuration. |
|
|
Allows you to define a
This method is used to fill properties with a real-world
example. For example, a
|
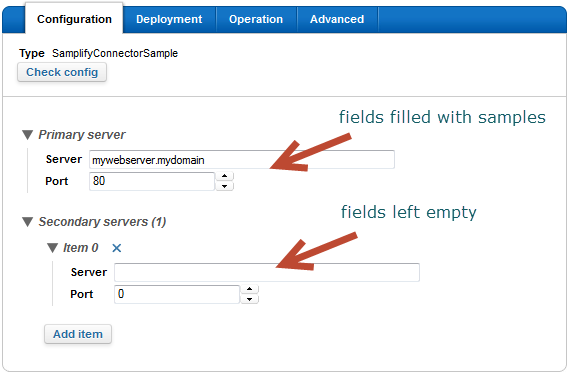
The following example shows the
CVComponentConfig class using the
samplify method.
package com.exalead.connectors;
import com.exalead.papi.framework.connectors.ConnectorConfig;
import com.exalead.config.bean.ConfigurationException;
import com.exalead.config.bean.IsMandatory;
import com.exalead.mercury.component.config.CVComponentConfig;
import com.exalead.mercury.component.config.CVComponentConfigSamplify;
public class SamplifyConnectorSampleConfig
extends ConnectorConfig
implements CVComponentConfigSamplify {
@IsMandatory(true)
public void setPrimaryServer(final WebServer primaryServer) {
this.primaryServer = primaryServer;
}
public WebServer getPrimaryServer() {
return this.primaryServer;
}
@IsMandatory(false)
public void setSecondaryServers(final WebServer[] secondaryServers) {
this.secondaryServers = secondaryServers;
}
public WebServer[] getSecondaryServers() {
return this.secondaryServers;
}
@Override
public void samplify() {
// samplify is called after the config instantiation.
this.primaryServer.setServer("mywebserver.mydomain");
this.primaryServer.setPort(80);
// Thus there will be a default value for the primary server name
// but it won't appear when adding a new secondary server
}
// a webserver is made of a server name and a network port
public static class WebServer {
@IsMandatory(true)
public void setServer(final String server) {
this.server = server;
}
public String getServer() {
return this.server;
}
@IsMandatory(true)
public void setPort(final int port) {
if (port < 0 || port > 65535) {
final ConfigurationException e =
new ConfigurationException("Invalid network port: " + port);
e.setConfigKey("Port");
throw e;
}
this.port = port;
}
public int getPort() {
return this.port;
}
public static String[] getMethods() {
return new String[] {
"Server",
"Port"
};
}
private String server;
private int port;
}
private WebServer primaryServer = new WebServer();
private WebServer[] secondaryServers;
public static String[] getMethods() {
return new String[] {
"PrimaryServer",
"SecondaryServers"
};
}
}
The UI should be similar to the following screenshot: